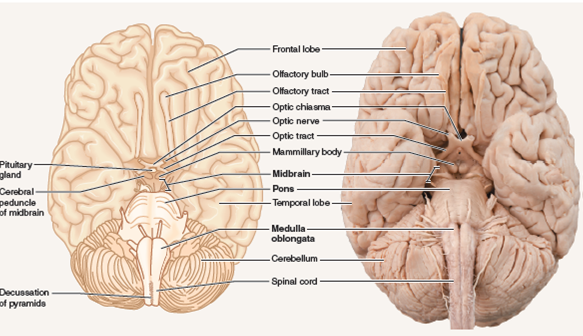
Brain Subdivisions
| Major division | Ventricle | Subdivision | Main structures |
| Prosencephalon ( Forebrain) | Lateral Ventricle | Telencephalon | Cerebral Cortex |
| Prosencephalon ( Forebrain) | Lateral Ventricle | Telencephalon | Basal Ganglia |
| Prosencephalon ( Forebrain) | Lateral Ventricle | Telencephalon | Limbic System |
| Prosencephalon ( Forebrain) | Third Ventricle | Diencephalon | Thalamus |
What are the three main subdivisions of the human brain?
Parts of the Human Brain and their Subdivisions
- Telencephalon/Cerebrum—Anterior Part Of Forebrain. Further composed of cerebral cortex, limbic and basal ganglia, it is the superior-most part of the vertebrate CNS (Central Nervous System) and is divided into two ...
- Mesecephalon/Midbrain. ...
- Metencephalon—Anterior Part Of Hindbrain. ...
- Myelencephalon/Medulla Oblongata—Posterior Part Of Hindbrain. ...
What are the 4 divisions of the brain?
What are the 4 parts of the brain and their functions?
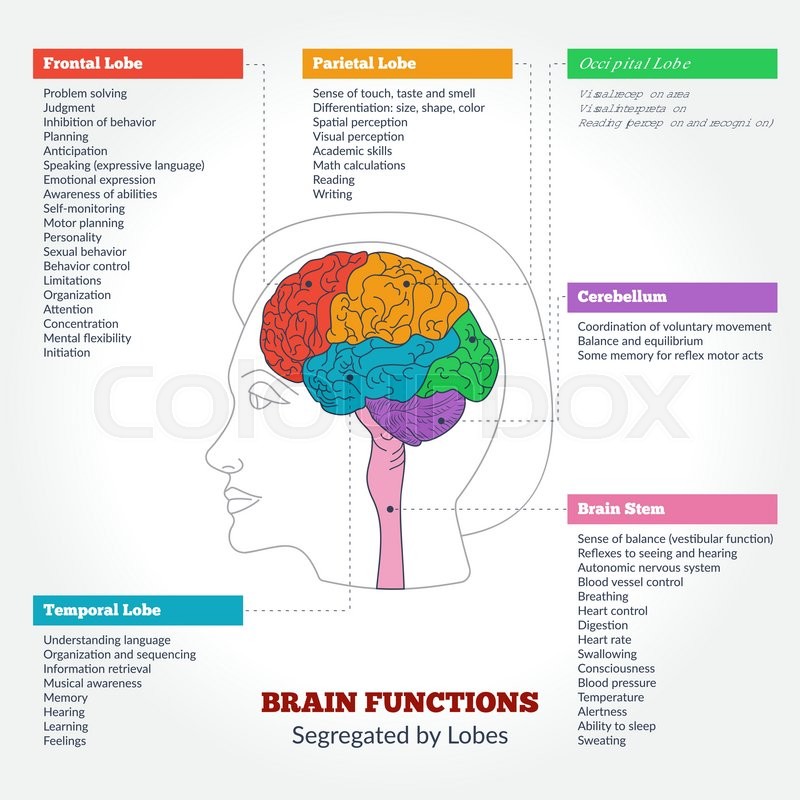
- Frontal Lobe. This section controls attributes, such as reasoning, planning, parts of speech, general movement, emotions, problem-solving, smell and personality.
- Parietal Lobe. ...
- Occipital Lobe. ...
- Temporal Lobe.
What are the structures of the brain?
Structure and Function of the Brain
- Development of the Human Brain. The mental processes and behaviors studied by psychology are directly controlled by the brain, one of the most complex systems in nature.
- Lower-Level Structures. ...
- Cerebral Cortex. ...
- Cerebral Hemispheres and Lobes of the Brain. ...
- The Limbic System. ...
- Neuroplasticity. ...
Is the cerebellum the division of the brain?
The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain, behind the brainstem, below the temporal and occipital lobes, and beneath the back of the cerebrum. The cerebellum is also divided into two hemispheres, like the cerebral cortex. Unlike the cerebral hemispheres, each hemispheres of the cerebellum is associated with each side of the body.

What are the 6 major divisions of the brain?
Terms in this set (6)Medulla Oblongata. -Spinal cord connects to the brain at the medulla oblongata. ... The Pons. - Extends from the medulla oblongata to the mesencephalon. ... Mesencephalon (Midbrain) -Part of the brain stem. ... The Diencephalon. -Is the most superior part of the brain stem. ... Cerebellum. ... Cerebrum.
What are the three main subdivisions of the brain?
All the parts of the brain work together, but each part has its own special properties. The brain can be divided into three basic units: the forebrain, the midbrain, and the hindbrain. The hindbrain includes the upper part of the spinal cord, the brain stem, and a wrinkled ball of tissue called the cerebellum (1).
How many subdivisions of the brain are there?
The brain presents three main divisions: forebrain (prosencephalon), midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon).
What is the division in the brain called?
There are three major divisions of the brain, with each division performing specific functions. The major divisions of the brain are the forebrain (or prosencephalon), midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon).
What are the 4 subdivisions of the brain?
Each brain hemisphere (parts of the cerebrum) has four sections, called lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital.
What are the 5 major subdivisions in the vertebrate brain?
These three vesicles further differentiate into five subdivisions: telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon, and the myelencephalon (Figure 1.1B).
Why is the brain divided into multiple compartments?
In other words, if one part of the brain is taking care of one specific function such as language and speech, then another part remains free to take care of something else, such as facial recognition. This may in turn allow the brain to juggle these different functions more efficiently.
What are the two major divisions of the hindbrain?
Dissect these questions and learn more about human organs. The hindbrain is composed of the medulla oblongata and the pons. The medulla transmits signals between the spinal cord and the higher parts of the brain; it also controls such autonomic functions as heartbeat and respiration.
What are the subdivisions of the 3 large compartments of the vertebrate brain?
Adult vertebrate brains can be subdivided into three major territories: forebrain (prosencephalon), midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) (Figure 1).
What are the two divisions of the midbrain?
There are three main parts of the midbrain - the colliculi, the tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles.
What's limbic system?
The limbic system is the part of the brain involved in our behavioural and emotional responses, especially when it comes to behaviours we need for survival: feeding, reproduction and caring for our young, and fight or flight responses.
What are the divisions of the brain and what structures are found in each division?
Embryonic Brain DivisionDerived Brain StructuresAssociated Cranial NervesFOREBRAIN Telencephalon DiencephalonCerebrum Thalamus, Hypothalamus,...Olfactory (I) Optic (II)MIDBRAIN MesencephalonMidbrainIII & IVHINDBRAIN Metencephalon MyelencephalonPons & Cerebellum Medulla oblongataTrigeminal (V) VI - XII
What is the most important part of the brain?
The Brainstem: Middle of the Brain Think of the brainstem like a computer hard-drive. It is the body's main control panel and is responsible for conveying messages between the brain and other parts of the body. The cerebrum, the cerebellum and the spinal cord are all connected to the brainstem.
What is fore brain mid brain and hind brain?
Forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain are the three areas of the brain, constituting different parts of the brain. Forebrain comprises cerebrum, thalamus and hypothalamus. Midbrain is located between the thalamus of the forebrain and pons of the hindbrain. Hindbrain comprises pons, cerebellum and medulla.
What is the innermost surface of the dura?
Innermost surface of dura is arachnoid mater. Strands extend across subarachnoid space to pia mater, which directly covers the brain.
What is the hollow cavity in the CNS?
Walls of neural tube become neurons and glial cells, hollow cavity forms central canal in spinal cord and ventricles in the brain.
How many lobes are there in the cerebrum?
Identify the five lobes of the cerebrum and their functions. Also identify important gyri and their functions.
What is the fourth ventricle?
Fourth ventricle: diamond shaped, bordered anteriorly by pons and posteriorly by cerebellum. Narrows to become central canal of medulla and spinal cord
What are the major subdivisions of the brain?
Describe the major subdivisions and anatomical landmarks of the brain. Major subdivisions: cerebrum, diencephalon, midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata, cerebellum. Describe the locations of the gray and white matter. The brain exterior is gray matter whereas the interior is white matter.
Which nerve carries information from the retina to the optic chiasm?
Optic nerv e: close to pituitary gland, carries info from retina to optic chiasm where optic tracts carry info to the brain.
Where does sensory information filter?
Filters sensory info on its way to the cortex.