
All nucleic acids are made up of the same building blocks (monomers). Chemists call the monomers "nucleotides." The five pieces are uracil, cytosine, thymine, adenine Adenine is a nucleobase. It is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The three others are guanine, cytosine and thymine. Its derivatives have a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both t…Adenine
Which monomer is used to build RNA and DNA?
What are the four building blocks of protein?
- Amino Group.
- Carboxyl Group.
- R Group (Or Side Chain)
What is monomer used to build RNA and DNA?
Monomers of DNA and RNA | Their Chemistry & Shape
- Ribose
- Deoxyribose
- Adenine
- Guanine
- Thymine
- Cytosine
- Uracil
What organic molecules are in a nucleic acid?
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, or large biomolecules, essential to all known forms of life.They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base.The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is the ...
What are the three subunits of nucleic acid?
what are the subunits of dna and their function
- Structure of DNA polymerase III enzyme I Subunits of DNA polymerase III and their functions. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. ...
- (OLD VIDEO) DNA Structure and Function. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. ...
- The Structure of DNA. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. ...
What are nucleic acids?
Regina Bailey. Updated January 25, 2020. Nucleic acids are molecules that allow organisms to transfer genetic information from one generation to the next. These macromolecules store the genetic information that determines traits and makes protein synthesis possible.
Where are nucleic acids found?
These molecules are composed of long strands of nucleotides held together by covalent bonds. Nucleic acids can be found within the nucleus and cytoplasm of our cells .
What is RNA made of?
RNA is composed of a phosphate-ribose sugar backbone and the nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil ( U). Sponk/Wikimedia Commons. RNA is essential for the synthesis of proteins. Information contained within the genetic code is typically passed from DNA to RNA to the resulting proteins.
What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA?
DNA is composed of a phosphate-deoxyribose sugar backbone and the four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). OpenStax/Wikimedia Commons/CC BY-SA 3.0. DNA is the cellular molecule that contains instructions for the performance of all cell functions.
What are the bases of nucleotides?
Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. DNA is composed of a phosphate-deoxyribose sugar backbone and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). RNA has ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases A, G, C, and uracil (U). Two examples of nucleic acids include ...
What are the macromolecules that store genetic information and enable protein production?
Key Takeaways: Nucleic Acids. Nucleic acids are macromolecules that store genetic information and enable protein production. Nucleic acid s include DNA and RNA. These molecules are composed of long strands of nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group.
What is messenger RNA?
There are several types of RNA. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is the RNA transcript or RNA copy of the DNA message produced during DNA transcription. Messenger RNA is translated to form proteins. Transfer RNA (tRNA) has a three-dimensional shape and is necessary for the translation of mRNA in protein synthesis.
What are the three monomers of nucleic acids?
What are 3 monomers of nucleic acids? The term nucleic acid is the overall name for DNA and RNA . They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Click to see full answer.
How many nucleotide monomers are there in DNA?
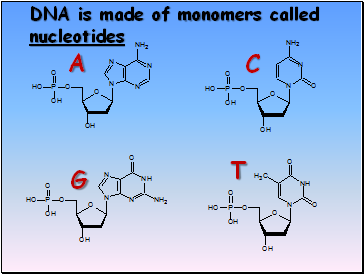
There are four nucleotide monomers In contrast, the DNA “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers. They have short and easy to remember names: A, C, T, G. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nucleobase.
What are the functions of nucleic acids?
Similarly one may ask, what are the 3 main functions of nucleic acids? Key Takeaways: Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are macromolecules that store genetic information and enable protein production. Nucleic acids include DNA and RNA. These molecules are composed of long strands of nucleotides.
How many elements are in a nucleic acid polymer?
Nucleic Acid Elements. Each nucleotide monomer, and therefore each nucleic acid polymer, is composed of a group of five elements. These elements bind to form monosaccharides, phosphate groups, and nucleobases, otherwise known as nitrogenous bases. In both RNA and DNA the phosphate group is the same form, but there are differences in ...
What are the elements that make up a nucleic acid chain?
The five elements necessary to construct a nucleic acid chain are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. The addition of phosphorus makes nucleic acid different to other categories of biocompounds, namely carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins.
What is the backbone of sugar phosphate?
The combination of ribose or deoxyribose and phosphate group forms the sugar-phosphate backbone. The nitrogenous base is attached to the sugar molecule. The addition of a phosphate group to the nucleoside created by sugar and nitrogenous base forms a nucleotide.
What pairs with uracil and guanine?
In RNA, adenine pairs with uracil and guanine with cytosine. The following images show the chemical structure of each type of monomer, where the pentagonal shape of the monosaccharide and its attached phosphate group and specific nucleobase are clearly defined.
What are the two forms of pentose sugar?
In nucleic acids, pentose sugars come in two different forms, ribose and deoxyribose. The former possesses an additional oxygen molecule, which, in combination with hydrogen, forms a hydroxyl group. This feature is absent in deoxyribose. Nitrogenous bases are categorised according to size.
What are the elements of a nucleic acid?
Nucleic Acid Elements and Monomer. Nucleic acids are biocompounds, which are essential for living organisms. Found in two forms— deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA)—these polymer chains are composed of the same basic elements and similar monomer nucleotides, yet with specific differences relating to form and function.
How many nitrogen atoms are in a single ringed form of DNA?
Single ringed forms, known as pyrimidines, contain between two and three nitrogen atoms and are smaller and shorter. This is important in the double-strand feature of DNA and the process of translation, as only certain pairings of nitrogenous bases are possible (Watson-Crick pairings).
What is the name of the molecule that contains nitrogenous bases?
Adding more phosphate groups makes a nucleoside di- and tri-phosphate, and so on. Nucleotides have nitrogenous bases of two kinds, purine or pyrimidine. In RNA, the 5-carbon sugar group is called ribose, and in DNA the 5-carbon sugar is deoxyribose.
What is the name of the chemical that takes the DNA code and uses it to make proteins?
RNA. RNA (ribonucleic acid) are the nucleic acids that take the code form DNA and use it to construct proteins. In other words, they are the biological machinery that extracts the genetic code from the DNA and executes the instructions. Like DNA, strands of RNA are made of polynucleotide chains.
What is the basic genetic code of an organism?
DNA . DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the molecule that contains the basic genetic code of an organism. Molecules of DNA contain purine and pyrimidine nucleotide bases. The purine bases are adenine and guanine (A and G) while the pyrimidine bases are cytosine and thymine (C and T).
What are the strands of polynucleotide called?
Assemblies of polynucleotide strands are called nucleic acids, DNA and RNA. Nucleotides are extremely important because they serve as the fundamental bits of information in DNA, analogous to the binary 1 and 0 of a digital computer.
How do nucleotides bond?
Nucleotides bond to form polynucleotide chains. These polynucleotide chains form by a dehydration reaction, in which the sugar in one nucleotide is bonded to the phosphate group of another and a water molecule is removed. These phosphodiester linkages are what form the sugar-phosphate backbone of strands of DNA and RNA.
What are the strands of RNA made of?
Like DNA, strands of RNA are made of polynucleotide chains. Unlike DNA, RNA molecules exist as single strands that loop back on themselves. RNA also uses a different set of nitrogenous bases than DNA. RNA contains 3 bases found in DNA, adenine, guanine, and cytosine.
What are the building blocks of DNA and RNA?
Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA, two molecules essential for life as we know it. Molecules of both DNA and RNA serve as the genetic code that uniquely identifies every living organism. One can think of DNA and RNA as sets of instructions that guide the construction of proteins and the cellular organization of the body.
What are the monomers of nucleic acid polymers RNA and DNA called?
The monomers of the nucleic acid polymers RNA and DNA are called nucleotides. These are made up of three components: a 5-carbon sugar (Ribose and Deoxyribose, respectively), a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. 6.6K views. ·.
What are the two types of nucleic acids?
There are two types of nucleic acids:-Ribonucleic acid (RNA) and Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) Ribonucleotides are monomers of RNA and Deoxyribonucleotides are monomers of DNA. A ribonucleotide monomer is composed a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine), a ribose sugar and a phosphate group.
What is the difference between deoxyribose and nucleic acid?
The difference is that deoxyribose lacks one oxygen atom, hence the name deoxyribose. First, it is important to know what the nucleic acids are and how they become a functional unit (protein). Now, the nucleic acid is comprised of a Phosphate group, Pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
What is the central dogma of Molecular Biology?
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology goes like this: DNA -> RNA -> Proteins. (DNA to RNA is transcription, RNA to Proteins is translation) Now, the nucleic acid is comprised of a Phosphate group, Pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
How many amino acids are there in the human body?
There are many type of amino acids but the body uses 20 amino acids. Continue Reading. Amino acids do not have monomers of themselves. They are simple compounds with an amino group and a carboxylic acid group attached to the same molecule.
What are carbohydrates made of?
Carbohydrates generally come in the form of amylose (starch) and glycogen (both polysaccharides). Amylases are enzymes that convert those polysaccharides into smaller disaccharides and polysaccharides. Then, the enzymes in the small intestine further break them down into monosaccharides.
What are the structural features of proteins?
Most proteins consist of linearpolymers built from series of up to 20 different L-α-amino acids. Allproteinogenic amino acids possess common structural features, including an α-carbon to which an amino group, acarboxyl group, and a variable side chain are bonded .
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DNA_nitrogenous_bases-5b63374b46e0fb00250bcaa1.jpg)
Nucleic Acid Monomers
DNA Structure
- DNA is the cellular molecule that contains instructions for the performance of all cell functions. When a cell divides, its DNA is copied and passed from one cellgeneration to the next. DNA is organized into chromosomes and found within the nucleusof our cells. It contains the "programmatic instructions" for cellular activities. When organisms produce offspring, these inst…
RNA Structure
- RNA is essential for the synthesis of proteins. Information contained within the genetic code is typically passed from DNA to RNA to the resulting proteins. There are several types of RNA. 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is the RNA transcript or RNA copy of the DNA message produced during DNA transcription. Messenger RNA istranslated to form proteins. 2. Transfer RNA (tRNA)has a t…
DNA and RNA Composition
- The nucleic acids DNA and RNA differ in composition and structure. The differences are listed as follows: DNA 1. Nitrogenous Bases:Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thymine 2. Five-Carbon Sugar:Deoxyribose 3. Structure: Double-stranded DNA is commonly found in its three-dimensional, double-helix shape. This twisted structure makes it possible for DNA to unwind for DNA replicati…
More Macromolecules
- Biological Polymers: macromolecules formed from the joining together of small organic molecules.
- Carbohydrates: include saccharides or sugars and their derivatives.
- Proteins: macromolecules formed from amino acid monomers.
- Lipids: organic compounds that include fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes.