The four types of nucleotides, also calledbases, are Adenine Adenine is a nucleobase. It is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The three others are guanine, cytosine and thymine. Its derivatives have a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both t… Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine. It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached. The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine. In Watson-Crick base pairing, it forms three hydrog… Guanine is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine. In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is called guanosine. Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase. In RNA, thymine is replaced by the nucleobase uracil. Thy…Adenine
Cytosine
Guanine
Thymine
What is the only difference between the four nucleotides?
While both are essentially the foundation of nucleic acid, the molecular composition is highly varying, with nucleotides containing sugar, base and a phosphate group, and nucleosides containing only sugar and a base. Additionally, a nucleotide occurs before the formation of DNA and RNA, but a nucleoside occurs before the formation of a nucleotide.
What are the 5 steps of DNA replication in order?
What are the steps of DNA replication in order quizlet?
- Starts at? DNA Replication begins at the Origin of Replication.
- Unwinds. …
- Holds strands. …
- Two types of strands added 3′ to 5′ …
- RNA Primer. …
- Add bases. …
- Fix mistakes, remove RNA Primer. …
What three basic molecules are nucleotides composed of?
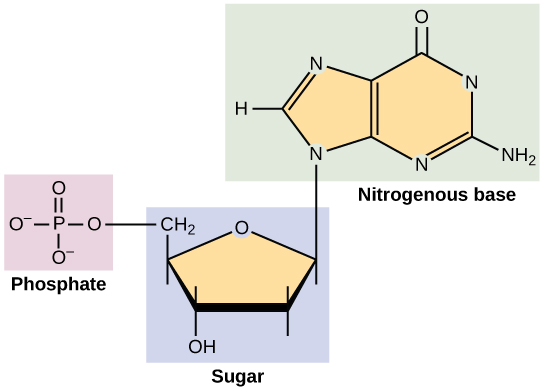
Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine.
What are the three components of a nucleotide?
They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. RNA contains uracil, instead of thymine.

What are the four types of nucleotides?
DNA is made up of four building blocks called nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The nucleotides attach to each other (A with T, and G with C) to form chemical bonds called base pairs, which connect the two DNA strands.
What are the names of each nucleotide?
Names of Nucleotides The five bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which have the symbols A, G, C, T, and U, respectively. The name of the base is generally used as the name of the nucleotide, although this is technically incorrect.
What are the names of the four nucleotides of RNA?
RNA consists of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine.
What are the four nucleotides found in DNA and RNA?
Because there are four naturally occurring nitrogenous bases, there are four different types of DNA nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
What are the 4 functions of nucleotides?
Nucleotide FunctionNucleotides are the building block of DNA and RNA. ... Nucleotides act as coenzymes, which are required to catalyse many biochemical reactions by enzymes.Energy is stored in our body as ATP. ... NAD, NADP has an essential role to play in many redox reactions, they act as an electron carrier.More items...
What do the 4 nucleotides have in common?
The four types of nucleotides contain four types of nitrogenous bases. Adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine are nitrogenous bases present in DNA and uracil instead of thymine in RNA.
What is the nucleotide name of adenine?
adenosinesAdenine nucleotides, which are also sometimes referred to as adenosines or adenylates, are a group of organic molecules including AMP, ADP and ATP. These molecules present the major players of energy storage and transfer.
What are the example of nucleotides?
A nucleotide is a monomer that serves as the building blocks for deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA). Examples of nucleotides are ribonucleotides or deoxyribonucleotides.
What are Mrna nucleotides?
mRNAs, like DNA, are nucleic acids that contain a specific sequence of nucleotides. These nucleotides are 'read' (translated) by ribosomes to assemble a polymer of amino acids, a protein.
What are the 4 DNA proteins?
The four types of nitrogen bases found in nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C).
What are the 5 nucleotide base pairs?
The four bases in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). These bases form specific pairs (A with T, and G with C). Base pair may also refer to the actual number of base pairs, such as 8 base pairs, in a sequence of nucleotides.
What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide?
Three Parts of NucleotideSugar.Nitrogenous Base.Phosphate Group.
What are the five different nucleotides?
The five bases that are found in nucleotides are often represented by their initial letter: adenine, A; guanine, G; cytosine, C; thymine, T; and uracil, U. Note that A, G, C and T occur in DNA; A, G, C and U occur in RNA.
What are the six major nucleotides?
Nucleic acids are broadly divided into two major types; Ribonucleic acid (RNA) which is single stranded containing Adenine (A), Uracil (U), Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G) ribonucleotides and deoxyribonucleic acid which is double stranded containing Adenine, Thymine (T), Cytosine and Guanine deoxyribonucleotides.
What are the different types of nucleotides?
Although most people learn only the five main types of nucleotides, there are others, including, for example, cyclic nucleotides (e.g., 3'-5'-cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP.) The bases can also be methylated to form different molecules .
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
Each nucleotide is a polymer made up of three parts: A five-carbon sugar (2'-deoxyribose in DNA or ribose in RNA) A phosphate molecule. A nitrogenous (nitrogen-containing) base.
What is the helix of a nucleotide?
The helix of the molecules forms when two complementary bases form hydrogen bonds with each other. Adenine binds with thymine (A-T) in DNA and with uracil in RNA (A-U). Guanine and cytosine complement each other (G-C). To form a nucleotide, a base connects to the first or primary carbon of ribose or deoxyribose.
How are nucleotides named?
Nucleotides are named based on the number of phosphate residues they contain. For example, a nucleotide that has an adenine base and three phosphate residues would be named adenosine triphosphate (ATP). If the nucleotide has two phosphates, it would be adenosine diphosphate (ADP). If there is a single phosphate, ...
What is the chemical formula for adenine?
The chemical formula of adenine is C 5 H 5 N 5. Adenine (A) binds to thymine (T) or uracil (U). It's an important base because it's used not only in DNA and RNA, but also for the energy carrier molecule ATP, the cofactor flavin adenine dinucleotide, and the cofactor nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD).
How do bases form nucleotides?
To form a nucleotide, a base connects to the first or primary carbon of ribose or deoxyribose. The number 5 carbon of the sugar connects to the oxygen of the phosphate group. In DNA or RNA molecules, a phosphate from one nucleotide forms a phosphodiester bond with the number 3 carbon in the next nucleotide sugar.
How many bases does DNA have?
Both DNA and RNA use four bases, but they don't use all the same ones. DNA uses adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine, while RNA uses adenine, guanine, and cytosine but has uracil instead of thymine. The helix of the molecules forms when two complementary bases form hydrogen bonds with each other.
What is a nucleotide made of?
A nucleotide consists of only a base and a sugar.
How many types of RNA are there?
There are three major types of RNA. Which of the following is a major type of RNA?
Where does messenger RNA carry information?
Messenger RNA carries protein synthesis information from the nucleus to the ribosomes.
Is thymine a pyrimidine?
thymine and uracil are both pyrimidines, but thymine has a met hyl group on carbon 5.
How many nucleotides are upstream of the start codon?
3-9 nucleotides upstream of the start codon.
Where does DNA and RNA 5 start?
DNA and RNA - 5 starts at the top left hand side and you move down 4,3,2,1...each corner you go past.
What is the activity of DNA polymerase I?
DNA polymerase I - has 5' to 3' exonuclease activity to remove primer and fills gap with DNA.
How many copies of a strand are produced in semiconservative replication?
Semiconservative replication = produce two copies that each contained one of the parental (original) strands and one new strand.
When an amino acid binds to the 3'-end of a tRNA, we say the?
When an amino acid binds to the 3'-end of a tRNA, we say the tRNA is charged with that amino acid. The amino acid group and the hydroxyl group (OH) are linked together by an ester bond.
How many ATPs does a tat system need?
The TAT system needs 100,000 H+ molecules and 4+/ATP costs about 25,000 ATPs to get one molecule out!!
