
Objectives of Non-Aligned Movement
- Safeguard sovereignty of member states
- Fight for decolonization
- Fight against racial discrimination
- Get better terms of trade
- Improve agriculture and raise food production by availing funds
- Discourage neo-colonialism
- Work towards the disarmament of superpowers
- Participate in UNO programs
- Have one voice in international affairs
What is the Non-Aligned Movement?
Non-Aligned Movement – Modern History Notes for UPSC! The Non-aligned movement is an organisation of States formalised with the objective of remaining independent and not aligned with the US or USSR. India played a significant role and its formalisation. After the United Nations, the non-aligned movement is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
What is the importance of Non-Aligned Movement in UPSC?
After the United Nations, the non-aligned movement is the largest grouping of states worldwide. The non-aligned movement is important from the perspective of UPSC IAS Examinations and falls under General Studies Paper 2 and particularly under the international relations section.
What did the Nonaligned Movement do in Angola?
The 1976 world conference of the Nonaligned Movement applauded Cuban internationalism, "which assisted the people of Angola in frustrating the expansionist and colonialist strategy of South Africa's racist regime and its allies.".
What is non-alignment in international politics?
However, the idea of nonalignment does not signify that a state ought to remain passive or even neutral in international politics. On the contrary, from the founding of the Non-Aligned Movement, its stated aim has been to give a voice to developing countries and to encourage their concerted action in world affairs.

What are the main objectives of NAM?
To advocate sovereign equality of all states. To encourage friendly relations among countries. To advocate peaceful settlement of international disputes. To oppose the use of force and the use of nuclear weapons.
What is the concept of Non-Aligned Movement?
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
What is Non-Aligned Movement Class 12?
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a term used for an international organization who do not want to officially align themselves with, or against, any major power bloc (group of countries).
What is the Non-Aligned Movement what is its significance Class 8?
Hint: The Non Aligned Movement included a group of nations who were not associated with any of the major power blocs i.e the USA or the USSR. It was established during the fall of the colonial powers all over the world and the struggle for independence for Asia, Africa, Latin America and others during the cold war.
Who was the founder of NAM?
Jawaharlal NehruJosip Broz TitoGamal Abdel NasserSukarnoKwame NkrumahNon-Aligned Movement/Founders
Who introduced Non-Aligned Movement?
According to Rejaul Karim Laskar, the Non-Aligned Movement was devised by Nehru and other leaders of newly independent countries of the Third World to "guard" their independence "in face of complex international situation demanding allegiance to either of the two warring superpowers".
Who was the leader of NAM?
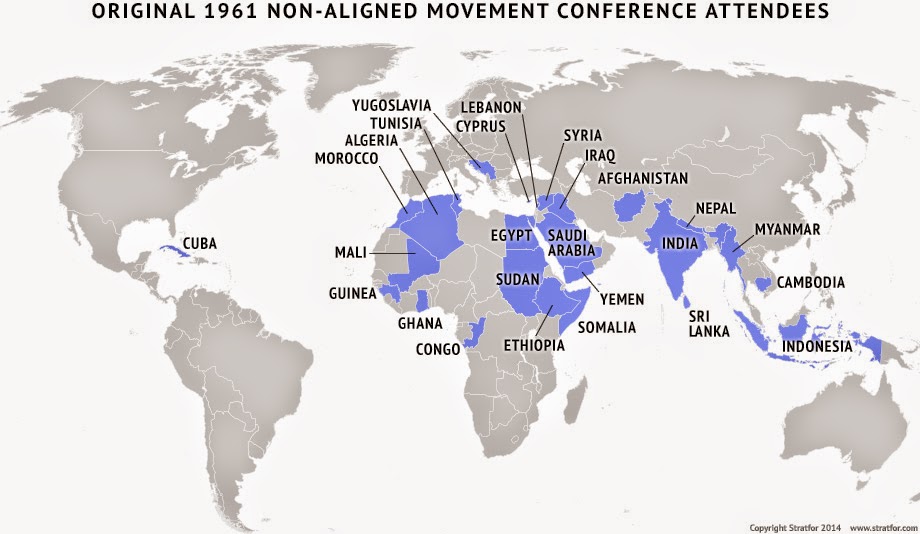
The Non-Aligned Movement was founded and held its first conference (the Belgrade Conference) in 1961 under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito of Yugoslavia, Gamal Abdel Nasser of Egypt, Jawaharlal Nehru of India, Kwame Nkrumah of Ghana, and Sukarno of Indonesia.
What are the achievements of Non-Aligned Movement?
The most important achievement of NAM movement was that it initiated an active international struggle for global peace at height of cold war and militarism. It played significant role in prevention of some of the regional conflicts and also made efforts towards end of cold war.
What is mean by non-alignment very short answer?
Non-alignment is a policy adopted by India and other countries of not joining either of the two power blocs (USA and USSR) and having their own foreign policy without the interference of superpowers.
Why is the Non-Aligned Movement important?
Because the Non-Aligned Movement was formed as an attempt to thaw out the Cold War, it has struggled to find relevance since the Cold War ended. After the breakup of Yugoslavia, a founding member, its membership was suspended in 1992 at the regular Ministerial Meeting of the Movement, held in New York during the regular yearly session of the General Assembly of the United Nations. The successor states of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia have expressed little interest in membership, though Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina have observer status. In 2004, Malta and Cyprus ceased to be members and joined the European Union. Belarus is the only member of the Movement in Europe. Azerbaijan and Fiji are the most recent entrants, joining in 2011. The applications of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Costa Rica were rejected in 1995 and 1998, respectively.
When was the 50th anniversary of the Non-Aligned Movement?
The Non-Aligned Movement celebrated its 50th anniversary in Belgrade on 5–6 September 2011.
What is the NAM?
The Non-Aligned Movement ( NAM) is a forum of 120 developing world states that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide. The movement originated in the 1950s as an effort by some countries to avoid the polarized world of the Cold War between Communist ...
What was the main goal of the Lusaka Conference?
At the Lusaka Conference in September 1970, the member nations added as aims of the movement the peaceful resolution of disputes and the abstention from the big power military alliances and pacts. Another added aim was opposition to stationing of military bases in foreign countries.
What was the significance of the 1955 Bandung Conference?
Equality and mutual benefit. Peaceful co-existence. A significant milestone in the development of the Non-Aligned Movement was the 1955 Bandung Conference, a conference of Asian and African states hosted by Indonesian president Sukarno, who gave a significant contribution to promote this movement.
What were the five principles of peaceful coexistence?
Nehru used the phrase in a 1954 speech in Colombo, Sri Lanka. In this speech, Zhou Enlai and Nehru described the Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence to be used as a guide for Sino-Indian relations called Panchsheel (five restraints); these principles would later serve as the basis of the Non-Aligned Movement.
Why did Colombia and Peru suspend their participation in the Movement under the presidency of Venezuela?
In 2019, Colombia and Peru suspended their participation in the Movement under the presidency of Venezuela because their governments did not recognize the legitimacy of Nicolás Maduro 's government.
What are the objectives of the NAM?
The other important objectives of the NAM are the following: To eliminate all those causes which could lead to war. To protect the nascent freedom of the new-born independent countries of Asia and Africa from colonial domination. To oppose colonialism imperialism and radial discrimination.
What was the main objective of the NAM at the beginning?
The main objective of the NAM at the beginning was to keep away the newly independent countries of Asia and Africa from the superpower rivalry and to protect and preserve their newly acquired independence.
What was the non-aligned movement?
The Non-Aligned Movement emerged in the contextof the wave of decolonizationthat followed World War II. At the 1955 Bandung Conference(the Asian-African Conference), the attendees, many of whose countries had recently gained their independence, called for “abstention from the use of arrangements of collectivedefense to serve the particular interests of any of the big powers.” In the context of the Cold War, they argued, countries of the developing world should abstain from allying with either of the two superpowers (the United Statesand the U.S.S.R.) and should instead join together in support of national self-determination against all forms of colonialismand imperialism. The Non-Aligned Movement was founded and held its first conference (the Belgrade Conference) in 1961 under the leadership of Josip Broz Titoof Yugoslavia, Gamal Abdel Nasserof Egypt, Jawaharlal Nehruof India, Kwame Nkrumahof Ghana, and Sukarnoof Indonesia.
How many states were there in the Non-Aligned Movement?
In the early 21st century the Non-Aligned Movement counted 120 member states. The Non-Aligned Movement emerged in the context of the wave of decolonization that followed World War II.
What is the NAM?
Non-Aligned Movement (NAM), international organization dedicated to representing the interests and aspirations of developing countries. The NAM was founded and held its first conference in 1961 under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito, Gamal Abdel Nasser, Jawaharlal Nehru, Kwame Nkrumah, and Sukarno.
When was the first non-aligned conference held?
The Non-Aligned Movement was founded and held its first conference (the Belgrade Conference) in 1961 under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito of Yugoslavia, Gamal Abdel Nasser of Egypt, Jawaharlal Nehru of India, Kwame Nkrumah of Ghana, and Sukarno of Indonesia.
How is the position of the movement reached?
The movement’s positions are reached by consensus in the Summit Conference of Heads of State or Government , which usually convenes every three years. The administration of the organization is the responsibility of the country holding the chair, a position that rotates at every summit.
Does the Non-Aligned Movement have a secretariat?
Unlike the United Nations (UN) or the Organization of American States, the Non-Aligned Movement has no formal constitution or permanent secretariat. All members of the Non-Aligned Movement have equal weight within its organization.
Can non-aligned states be part of NATO?
As a condition for membership, the states of the Non-Aligned Movement cannot be part of a multilateral military alliance (such as the North Atlantic Treaty Organization[NATO]) or have signed a bilateral military agreement with one of the “big powers” if it was “deliberately concluded in the context of Great Power conflicts.” However, the idea of nonalignment does not signify that a state ought to remain passive or even neutral in international politics. On the contrary, from the founding of the Non-Aligned Movement, its stated aim has been to give a voice to developing countries and to encourage their concerted action in world affairs.
Non-Aligned Movement Founders
- The movement developed in the 1950s following the independence of Asian nations (India, Pakistan e.t.c.) and African states 1. 1955 — Asian and African states convened a conference in Bandung, Indonesia. Conveners of the conference 1. Jawaharlal Nehru India 2. Surkano — Indonesia 3. Marshal Tito — Yugoslavia 4. Gamal Nasser — Egypt 5. Chou En-Lai –China Note…
Reasons For The Rise of Non-Aligned Movement
- The newly independent states did not want to be entangled in the superpower rivalry between the USA and USSR.
- They wanted to establish a forum to enable them to exert their influence in world politics
- They wanted to avoid the arms race between the superpowers
- To enhance friendly relations! peace in the world
Objectives of Non-Aligned Movement
- Safeguard sovereignty of member states
- Fight for decolonization
- Fight against racial discrimination
- Get better terms of trade
- Safeguard sovereignty of member states
- Fight for decolonization
- Fight against racial discrimination
- Get better terms of trade
Performance and Achievements of Non-Aligned Movement
- Non-aligned countries have gained influence in world affairs. They have increased their voting power in the UNO
- NAM members have attempted to gain neutrality in world affairs. They can seek aid from either the West or East power blocs.
- Facilitating the attainment of independence in previously colonized countries
- Non-aligned countries have gained influence in world affairs. They have increased their voting power in the UNO
- NAM members have attempted to gain neutrality in world affairs. They can seek aid from either the West or East power blocs.
- Facilitating the attainment of independence in previously colonized countries
- Has enabled members to safeguard their independence and territorial integrity
Challenges Facing The Non-Aligned Movement
- Shortage of funds — Due to economic problems in some member countries, they have not been able to remit contributions.
- Personality differences among some leaders
- Lack of commitment since NAM members owes allegiance to other organs e.g. OAU, UNO, Commonwealth e.t.c.
- Shortage of funds — Due to economic problems in some member countries, they have not been able to remit contributions.
- Personality differences among some leaders
- Lack of commitment since NAM members owes allegiance to other organs e.g. OAU, UNO, Commonwealth e.t.c.
- Member countries still retain ties with former colonial masters and hence find it difficult to pursue independent policies
Overview
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath of the Korean War, as an effort by some countries to counterbalance the rapid bi-polarization of the world during t…
History
The term 'Non-Alignment' was used for the first time in 1950 at the United Nations by India and Yugoslavia, both of which refused to align themselves with either side in the multi-alliances involving Korean War. Drawing on the principles agreed at the Bandung Conference in 1955, the Non-Aligned Movement as an organization was founded on the Brijuni islands in Yugoslavia in 1956 and was f…
Organizational structure and membership
The movement stems from a desire not to be aligned within a geopolitical/military structure and therefore itself does not have a very strict organizational structure. Some organizational basics were defined at the 1996 Cartagena Document on Methodology The Summit Conference of Heads of State or Government of Non-Aligned States is "the highest decision making authority". The chairmanship rotates between countries and changes at every summit of heads of state or …
Policies and ideology
Chairpersons of the NAM have included such diverse figures as Suharto, a militaristic anti-communist, and Nelson Mandela, a democratic socialist and famous anti-apartheid activist. Consisting of many governments with vastly different ideologies, the Non-Aligned Movement is unified by its declared commitment to world peace and security. At the seventh summit held in New D…
Current activities and positions
The movement has been outspoken in its criticism of current UN structures and power dynamics, and advocating for the reforming of the United Nations Security Council, stating that the organisation has been used by powerful states in ways that violate the movement's principles. It has made a number of recommendations that it says would strengthen the representation and power of "non-aligned" states. The proposed UN reforms are also aimed at improving the transpa…
Summits
The conference of Heads of State or Government of the Non-Aligned Countries, often referred to as Non-Aligned Movement Summit is the main meeting within the movement and are held every few years:
A variety of ministerial meetings are held between the summit meetings. Some are specialist, such as the meeting on "Inter-Faith Dialogue and Co-operation f…
Members, observers and guests
The following countries are members of the NAM, arranged by continent, showing their year of admission:
Currently every African country (except South Sudan and Western Sahara) is a member of the Non-Aligned Movement.
1. Algeria (1961)
See also
• Asian–African Conference
• Dual loyalty
• Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence
• G-77
• Neutral country
Non-Aligned Movement
Member Countries of Nam
- They founding members of a NAM were: 1. Yugoslavia, 2. India, 3. Egypt, 4. Ghana and 5. Indonesia. At present, 120 nations are its members. Some of them are Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka Nepal Bhutan, Myanmar and Afghanistan. China has an observer status in Naam. All the African countries except for western Sahara and South Sudan are the member nations of NAM. …
Principles of Nam
- The Non-Aligned Movement was guided by the Panchsheel principles. the principles were as follows: 1. Respect for the principals enshrined in the charter of the United Nations and international law. 2. Respect for the sovereignty sovereign equality and territorial integrity of all states. 3. Peaceful settlement of all international conflicts in accordance with the charter of the U…
Objectives of Nam
- The major objectives of NAM are as follows: 1. “To forge an autonomous route in international politics that would not result in member States becoming pawns in the struggles between the big powers” 2. To create an independent path in world politics that would not result in member states becoming pawns in the struggle between the major powers. 3. To...
Functioning of Nam
- There is no permanent Secretariat in Naam. The Summit conference of heads of state takes place every 3 years. The management rotates between the member Nations and is non hierarchical. The decisions are taken through consensus and have to be substantial and not universal. Every member country has the same weightage and the chair is elected for a tenure of 3 years. It has …
Phases of Non Aligned Movement
- Phase 1:
The first face lasted from India’s independence in 1947 to the end of Indo Pak war in 1965. The key political figure during this period was India’s first Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru. - Phase 2:
This face started after Nehru’s death in 1964. During this phase, the key political figure was Indira Gandhi and India leaned towards the Soviet Union as the key International partner.
Nam in The Cold War Era
- The group played an important role during the cold war years in furthering many of the issues. Against apartheid it was prevalent in African countries like South Africa. This was on the agenda right from the first conference. During the second conference the Government of South Africa was wond against the discriminatory practices of apartheid. Disarmament: NAM called for cession of …
India and The Non Aligned Movement
- India played an important role in the multilateral movement of colonies and newly independent countries that wanted to become part of NAM. India was a prominent participant in the meetings until the 1970’s. The non-aligned movement was an effective means of promoting India’s diplomatic presence and securing economic assistance internationally. India’s ties to the former …
Failure of Nam
- The relevance of NAM began to be questioned in the current geopolitical scenario. 1. One of the principles of NAM was to respect the sovereignty of the member states. This has created many alignments among the countries due to the lack of uniform structure. 2. It could not prevent regional confrontations. 3. There is a tendency among NAM to ignore the Human Rights violatio…
Relevance of Nam
- NAM continues to hold relevance due to its principles. 1. Third world nation: The third world Nations fighting against social economic problems since they have been exploited for a long time. Now after does a protector for these third world Nations against the West hegemony. 2. Territorial integrity and sovereignty:NAM stands with his principle and has proved its relevance with the ide…