How many organelles are there in a human cell?
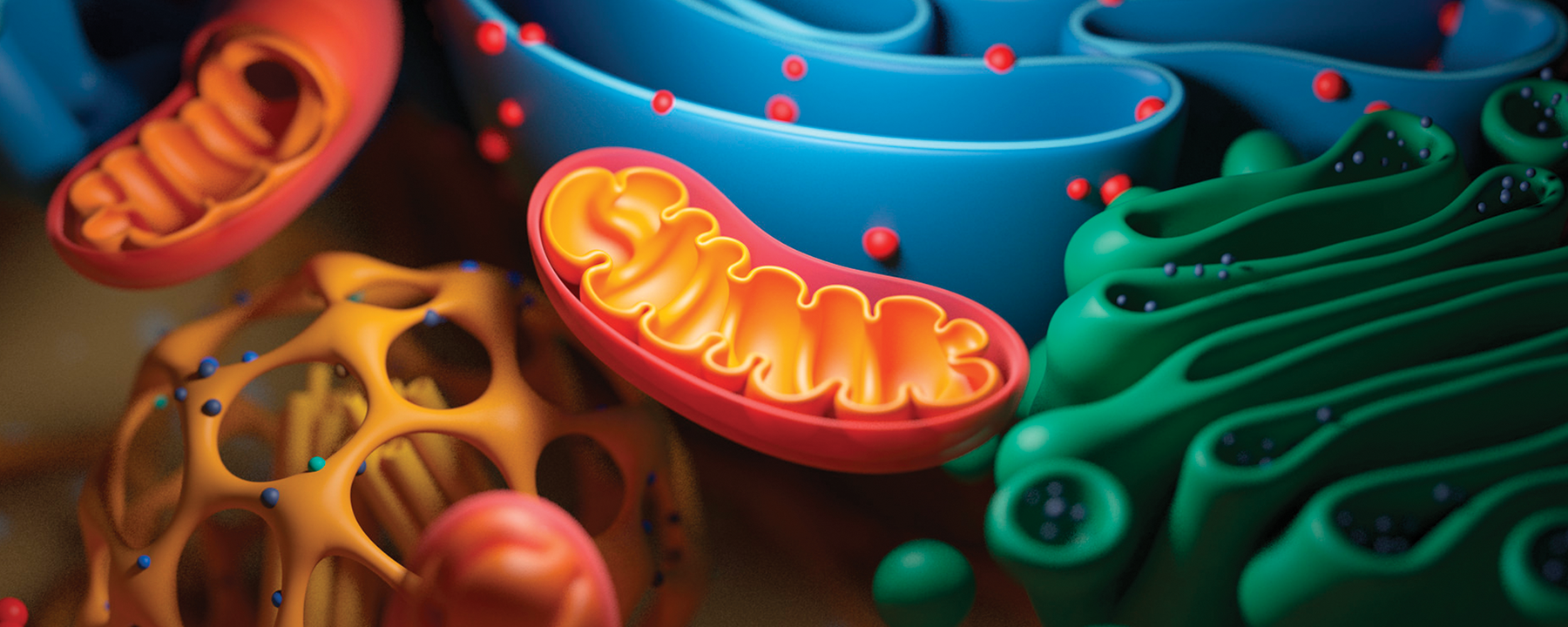
6 Cell OrganellesNucleus. Known as the cell's “command center,” the nucleus is a large organelle that stores the cell's DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). ... Ribosomes. Ribosomes are the protein factories of the cell. ... Endoplasmic reticulum. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. ... Golgi apparatus. ... Chloroplasts. ... Mitochondria.
What are the 17 cell organelles?
Within the cytoplasm, the major organelles and cellular structures include: (1) nucleolus (2) nucleus (3) ribosome (4) vesicle (5) rough endoplasmic reticulum (6) Golgi apparatus (7) cytoskeleton (8) smooth endoplasmic reticulum (9) mitochondria (10) vacuole (11) cytosol (12) lysosome (13) centriole.
What are the 12 organelles found in cells?
General cell organelles: General cell organelles are found in both animal and plant cells – cell membrane, reticulum, Golgi apparatus, cytosol, nucleus, mitochondrion, cytoplasm, lysosome, rough and smooth endoplasmic peroxisome, and the cytoskeleton.
What are 5 organelles found in cells?
Organelles in animal cells include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, and vacuoles. Ribosomes are not enclosed within a membrane but are still commonly referred to as organelles in eukaryotic cells.
What are the 15 organelles in a plant cell?
Each plant cell will have a cell wall, cell membrane, a nucleus, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, plastids, mitochondria, vacuoles, and various vesicles like peroxisomes. All of these organelles will be held in the cytoplasm and surrounded by the cytoskeleton.
What are the 14 organelles in a plant cell?
Plant Cell Organelles Plant cells contain all of the same organelles as animal cells, including mitochondria, a nucleus, ribosomes, smooth and rough ER, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes, cytoplasm, and a cell membrane.
What are the 8 major cell organelles?
Table of ContentsWhat are Cell Organelles?List of Cell Organelles and their Functions.Plasma Membrane.Cytoplasm.Nucleus.Endoplasmic Reticulum.Mitochondria.Plastids.More items...
What are the 8 organelles in a cell?
Organelles in animal cells include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, and vacuoles. Ribosomes are not enclosed within a membrane, but they are still commonly referred to as organelles in eukaryotic cells.
What are the 13 organelles in an animal cell?
The thirteen parts of an animal cell are vacuoles, cytoplasm, vesicles, centrioles, ribosomes, nuclear membrane, cell membrane, cytoskeleton, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, Golgi apparatus and nucleus.
Which is the largest organelle in human body?
The largest cellular organelle in a cell (plant or animal cell) is a nucleus.In a plant cell, chloroplast (plastids) are the largest in size.The plastids are the cellular organelles which manufacture and stores different chemical compounds required by the autotrophic cells.So, the correct answer is ' Plastids'.
What are cell organelles and its functions?
Organelles are small structures within the cytoplasm that carry out functions necessary to maintain homeostasis in the cell. They are involved in many processes, for example energy production, building proteins and secretions, destroying toxins, and responding to external signals.
What are the 8 organelles in eukaryotes?
Overview of the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vacuoles, mitochondria, chloroplasts and lysosomes.
What are class7 organelles?
Organelles are special and organized structures seen in living cells. Some of the membrane-bound organelles are vacuoles, nucleus, chloroplasts, lysosomes etc. The nucleus is the largest organelle in the cell.
What are cell organelles name them?
The cell organelles are - Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosomes, Golgi apparatus,Lysosomes, Mitochondria, Plastids, Vacuoles, Peroxisomes and Centrosome.
What are organelles Class 9?
An organelle is a specialised part of the cell that serves a specific purpose within the cell. There are many organelles present within a cell and they also vary depending on what kind of cell we are talking about, whether it be a plant or animal cell.
What are the cell organelles and their function?
Organelles are small structures within the cytoplasm that carry out functions necessary to maintain homeostasis in the cell. They are involved in many processes, for example energy production, building proteins and secretions, destroying toxins, and responding to external signals.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus, whereas eukaryotic cells do. A nucleus is a large organelle that stores DNA and serves as the cell’s command center. Single-cell organisms are usually prokaryotic, while multi-cell organisms are usually made of eukaryotic cells.
What is the organelle of an eukaryotic cell?
Another large organelle found in eukaryotic cells is the mitochondrion, an organelle responsible for making ATP, a chemical that organisms use for energy. Cells often contain hundreds of mitochondria. These mitochondria have an outer membrane, which encases the organelle, and an inner membrane, which folds over several times to create a multi-layered structure known as cristae. The fluid inside the mitochondria is called the matrix, which is filled with proteins and mitochondri al DNA.
What are lysosomes made of?
They are embedded with proteins called enzymes, which break down macromolecules, including amino acids, carbohydrates, and phospholipids . Lysosomes are produced by a larger organelle called the Golgi complex, which manufactures other cellular machinery as well.
Which organelle retains its own DNA?
Chloroplasts are another organelle that contain a double membrane and retain their own DNA. Unlike mitochondria, however, the inner membrane of chloroplasts is not folded. They do, however have a third, internal membrane called the thylakoid membrane, which is folded. In addition, unlike mitochondria, chloroplasts are only present in plant cells. They are responsible for converting sunlight into energy through a process called photosynthesis.
Which organelle is responsible for converting sunlight into energy?
In addition, unlike mitochondria, chloroplasts are only present in plant cells. They are responsible for converting sunlight into energy through a process called photosynthesis. Other organelles like lysosomes are responsible for digesting and recycling toxic substances and waste.
What happens when a cell dies?
Whenever a cell dies, it self-destructs using its own lysosomes. Just as organs are separate body parts that perform certain functions in the human body, organelles are microscopic sub-units that perform specific functions within individual cells. Photograph by Science Source. cell. Noun.
What are the organelles?
Organelles. Organelles are specialized structures that perform various jobs inside cells. The term literally means “little organs.”. In the same way organs, such as the heart, liver, stomach, and kidneys, serve specific functions to keep an organism alive, organelles serve specific functions to keep a cell alive.
What is the process of autophagy?
Autophagy (aka “self-eating”) is a process that cells recycle some of their existed proteins and organelles due to the shortage of nutrient supply. Damaged proteins or organelles will be put on a “garbage tags”.
What organelle produces energy for plants?
Chloroplasts are organelles that conduct photosynthesis and produce energy for the plant cells. Chloroplasts convert the light energy of the Sun into sugars (a process called “ photosynthesis ”) that can be used by cells. At the same time, the reaction produces oxygen (O 2) and consumes carbon dioxide (CO 2 ).
What is an organelle?
What is organelle? An organelle is a tiny cellular structure that performs specific functions within a cell. You can think of organelles as a cell’s internal organs. For example, the nucleus is the cell’s brain, and the mitochondria are the cell’s hearts.
What is the nucleus?
Nucleus. The nucleus (plural: nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle that stores most of our genetic information (genome). The key feature that separates eukaryotic cells (animals, plants, and fungi) from prokaryotic cells (bacteria and archaea) is the presence of a nucleus.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondrion (plural: mitochondria) is a rod-shaped organelle that is considered the power generators of the cell. Mitochondrion performs cellular respiration, which converts glucose and oxygen to adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the biochemical energy “currency” of the cell for all activities.
Which organelle generates ATP?
Mitochondrion generates ATP like a hydraulic dam. It happens via the electron transport chain across the IMM. Mitochondria (in plant cells, chloroplasts, too) are the only organelles that have their own DNA other than the nucleus. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is circular and encoded only 13 genes.
Which organelle contains fluid?
Vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle that contains a mass of fluid.
What are the organelles of animal cells?
Organelles are involved in many vital cell functions. Organelles in animal cells include the , mitochondria. , endoplasmic reticulum. , Golgi apparatus. , , and . are not enclosed within a membrane, but they are still commonly referred to as organelles in. eukaryotic.
Where are the organelles of eukaryotic cells?
The jellylike material that makes up much of a cell inside the cell membrane, and, in eukaryotic cells, surrounds the nucleus. The organelles of eukaryotic cells, such as mitochondria, the endoplasmic reticulum, and (in green plants) chloroplasts, are contained in the cytoplasm.
What is the meaning of the ribosomal subunits in Figure 4.6.1?
The slender silver strand is the messenger (mRNA) bringing the code for a out into the cytoplasm. The purple and green structures are ribosomal subunits (which together form a single ), which can “read” the code on the mRNA and direct the bonding of the correct sequence of amino acids to create a protein. All living — whether they are#N#prokaryotic#N#or#N#eukaryotic#N#— contain , but only eukaryotic cells also contain a and several other types of#N#organelles#N#.
Which organelle converts oxygen and nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP)?
A double-membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. Mitochondria convert oxygen and nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the chemical energy "currency" of the cell that powers the cell's metabolic activities.
Which organelle controls the cell's energy?
It controls gene expression, including controlling which proteins the cell makes. The mitochondrion (plural, mitochondria. ) is an organelle that makes energy available to the cells.
Which type of cell has a single nucleus?
nucleoplasm. , which is similar in composition to the found in the cytoplasm outside the nucleus. Most eukaryotic cells contain just a single nucleus, but some types of cells (such as red blood cells) contain no nucleus and a few other types of cells (such as muscle cells) contain multiple nuclei.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The function of the nucleus is to regulate gene expression, including controlling which proteins the cell makes. In addition to DNA, the nucleus contains a thick liquid called. nucleoplasm.
How do ribosomes synthesize proteins?
Ribosomes, either free in the cytosol or associated with rER, synthesize proteins as polypeptide chains. This occurs through the translation of RNA. Specifically, ribosomes bind to messenger RNA, abbreviated mRNA. The ribosome reads a series of nucleotide bases in groups of three called codons. The first codon read is the start codon. Each codon following the start codon represents a specific amino acid that is then brought to the ribosome by transfer RNA, abbreviated tRNA. The tRNA carrying the amino acid is bound into the A site of the ribosome. Here the amino acid is linked to the amino acid that precedes it, in the P site. The bond between two amino acids in a polypeptide chain is referred to as a peptide bond. After the peptide bond is created the ribosome translocates to the next three nucleotide bases on the mRNA strand and repeats the process until a stop codon is reached.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large network of membranes responsible for the production of proteins, metabolism and transportation of lipids, and detoxification of poisons. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum with separate functions: smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum. The presence or absence of ribosomes in the ER’s plasma membrane determines whether it is classified as smooth or rough ER.
What are non-membrane organelles?
Most non-membranous organelles are part of the cytoskeleton, the major support structure of the cell. These include: filaments, microtubules , and centrioles.
What are the functions of organelles?
Organelles are small structures within the cytoplasm that carry out functions necessary to maintain homeostasis in the cell. They are involved in many processes, for example energy production, building proteins and secretions, destroying toxins, and responding to external signals. Organelles are considered either membranous or non-membranous.
What is the function of transport vesicles?
Transport vesicles are used to move proteins around the cell and to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic space.
What is the function of peroxisomes?
Peroxisomes are single membrane compartments that contain enzym es used to remove hydrogen atoms from substrates. The free hydrogen atoms then bind to oxygen and create hydrogen peroxide.
What is the function of a ser?
Its functions vary among cell types. For example, sER in cells of the liver have detoxifying functions while sER in cells of the endocrine system mainly produce steroid hormones. Detoxification occurs through enzymes associated with the sER membrane and usually involves adding hydroxyl groups to molecules.
What is the structure of the nucleus that extends in the cytoplasm?
Endoplasmic reticulum: This is also a sac-like structure attached to the nucleus and extends thereof like being suspended in the cytoplasm. It is of two types: rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). Lysosome: Lysosomes are cell organelles found mostly bound to the cell membrane.
What are the pouches in the cell that store water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates?
Vacuole: Vacuoles are pouches in the cell that store materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Where are lysosomes found?
Lysosome: Lysosomes are cell organelles found mostly bound to the cell membrane. This organelle is found in all the cells and contains hydrolytic enzymes.
Why do mitochondria multiply?
Hence mitochondria multiply within the cell even before a cell divides. This is because they are worn out during the process of respiration. So, they form new ones to carry out the function non-stop. Check for its structure Mitochondria structure.
Why is the cell wall important in plants?
Cell wall: Since plants are mostly non-motile, cell wall presence imparts rigidity, capacity to tolerate harsh conditions like wind, heat, wear and tear, etc. It imparts a definite shape to the cell.
Which layer of the cell is a lipid bilayer?
It is a lipid bilayer that encloses the entire cell and its organelles. It is a selectively permeable, flexible layer of the cell. It is one of the largest organelles in a cell structure. Mitochondria: These are sac-like organelles inside the cells. They have their own single-stranded DNA.
What is the basic element of all living organisms?
A group of cells forms a tissue, groups of tissues form an organ, groups of organs form an organism. So the cell is a basic element of all living organisms. In microbes like the amoeba, paramecium, bacteria, etc., a single cell even carries out complex functions like eating, digestion, moving, sex, reproduction, excretion, etc., ...
Why is the rough endoplasmic reticulum so called?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is so-called because its surface is studded with ribosomes, the molecules in charge of protein production. When a ribosome finds a specific RNA segment, that segment may tell the ribosome to travel to the rough endoplasmic reticulum and embed itself.
How are mitochondria unique?
Mitochondria are also somewhat unique in that they are self-replicating and have their own DNA, almost as if they were a completely separate cell. The prevailing theory, known as the endosymbiotic theory, is that eukaryotes were first formed by large prokaryotic cells engulfing smaller cells that looked a lot like mitochondria (and chloroplasts, more on them later). Instead of being digested, the engulfed cells remained intact and the arrangement turned out to be advantageous to both cells, which created a symbiotic relationship.
How does DNA turn into proteins?
The processes to transform DNA into proteins are known as transcription and translation , and happen in different compartments within the cell. The first step, transcription, happens in the nucleus, which holds our DNA. A membrane called the nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus, and its job is to create a room within the cell to both protect the genetic information and to house all the molecules that are involved in processing and protecting that info. This membrane is actually a set of two lipid bilayers, so there are four sheets of lipids separating the inside of the nucleus from the cytoplasm. The space between the two bilayers is known as the perinuclear space.
Which organelle is the final destination for proteins coming through the Golgi?
Lysosome: The final destination for proteins coming through the Golgi is the lysosome. Vesicles sent to this acidic organelle contain enzymes that will hydrolyze the lysosome ’s content.
Where are organelles found?
You can think of organelles as smaller rooms within the factory, with specialized conditions to help these rooms carry out their specific task (like a break room stocked with goodies or a research room with cool gadgets and a special air filter). These organelles are found in the cytoplasm, a viscous liquid found within the cell membrane that houses the organelles and is the location of most of the action happening in a cell. Below is a table of the organelles found in the basic human cell, which we’ll be using as our template for this discussion.
What is the basic requirement for a factory?
At its most basic, a factory needs a building, a product, and a way to make that product. All cells have membranes (the building), DNA (the various blueprints), and ribosomes (the production line), and so are able to make proteins (the product - let’s say we’re making toys).
What are the two types of cells?
There are two main types of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotes are cells that do not have membrane bound nuclei, whereas eukaryotes do. The rest of our discussion will strictly be on eukaryotes. Think about what a factory needs in order to function effectively.
What organelle contains hydrogen peroxide?
Perioxisomes. These organelles are very similar to the lysosomes and contain enzymes that act together in the form of hydrogen peroxide to neutralize substances that may be toxic to the cell. Perioxisomes are formed directly from the endoplasmic reticulum rather than from the Golgi apparatus like lysosomes.
What are the microtubules and microfilaments?
Microfilaments and microtubules are rigid protein substances that form the internal skeleton of the cell known as the cytoskeleton . Some of these microtubules also make up the centrioles and mitotic spindles within the cell which are responsible for the division of the cytoplasm when the cell divides.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a membranous structure that contains a network of tubules and vesicles. Its structure is such that substances can move through it and be kept in isolation from the rest of the cell until the manufacturing processes conducted within are completed.
How do organelles work in the human body?
The functions of the human cell varies based on the type of cell and its location in the human body. All the organelles work together to keep the cell alive and allow it to carry out its specific function. Sometimes these organelles are highly specialized and can vary in size, shape and number.
What is the function of lysosomes?
Lysosomes contain enzymes that help with the digestion of nutrients in the cell and break down any cellular debris or invading microorganisms like bacteria.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane allows substances to enter and leave the cell. While certain substance like oxygen can easily diffuse through the cell membrane, others have to actively transported through the process of endocytosis. Small particles are transported by the process of pinocytosis while larger particles are moved by the process of phagocytosis. These functions can become highly specialized to allow cells to perform specific activities, like the macrophages that phagocytose invading bacteria to neutralize it.
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is the outer coating of the cell and contains the cytoplasm, substances within it and the organelle. It is a double-layered membrane composed of proteins and lipids. The lipid molecules on the outer and inner part (lipid bilayer) allow it to selectively transport substances in and out of the cell.
How do cells grow and replicate?
In order for cells to grow and replicate, they must produce the necessary building blocks to achieve this feat. Additionally, some cells – like the β-cells of the pancreas – produce protein based hormones to help maintain homeostasis . This process is achieved by ribosomes. Ribosomes are complex ribonucleic acid based molecules (i.e. ribosomal-ribonucleic acid; r-RNA) that are responsible for translating coded sequences of the messenger-RNA (m-RNA) to proteins. They are made up of a small and a large subunit which coordinate with each other to translate the m-RNA strand. Some ribosomes are membrane bound, while others float freely in the cytoplasm. While free ribosomes synthesize proteins that are used within the cell, the proteins synthesized by bound ribosomes are meant to be exported.
What is the smallest cell in an organism?
The cell is the smallest functional unit within a living organism, which can function independently. It is made up of several types of organelles that allow the cell to function and reproduce. There are two general classes of cells that exist: the self-sustaining simple cells known as prokaryotic (bacteria and archaea) and the more complex dependent cells known as eukaryotic. The eukaryotic cells types are generally found in animals, plants, algae, and fungi. For the purpose of this article, the primary focus will be the structure and histology of the animal cell. The major differences between animal and plant cells will be explored as well.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
The plasma membrane is the outermost layer of the cell. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its environment. It is often referred to as a fluid mosaic phospholipid bilayer that is hydrophilic externally and internally, but hydrophobic at its core. The hydrophilic property arises from the charged phosphate molecule that forms the head of the phospholipid, and the hydrophobic nature is from the two lipid tails which forms the core. This feature allows the selective permeability of the membrane. For instance, particles that are hydrophilic (e.g. ions) are not able to pass through the hydrophobic core, and those that are hydrophobic (e.g. fats) are repelled from the outer surface. As a result, the cell is able to isolate its internal environment from the external environment.
How does the cell move substances?
The controlled movement of substance is done by protein channels and carrier proteins anchored in the plasma membrane that selectively or generally allow particular particles to enter and leave the cell.
Which type of cell has ribosomes bound to its surface, stores proteins, and is the extension of the?
Rough - has ribosomes bound to its surface, stores proteins, and is the extension of the nuclear membrane
What are the components of a cell?
As previously stated, the fundamental components of a cell are its organelles. These organelles are made up of varying combinations of atoms and molecules. The organelles drive different functions of the cell from metabolism, to energy production and subsequently to replication.
What is the process of engulfing foreign material in the plasma membrane?
In the case of substances that can neither pass through the membrane or use membrane channels, the plasma membrane has the ability to engulf foreign material in a process known as endocytosis. This process involves recognition of either foreign microorganisms or native substances by receptors on the cell membrane and subsequent folding of that region of the membrane around the intended structure being transported into the cytoplasm. Endocytosis can be further subdivided into three types.