Where are the paravertebral ganglia located?
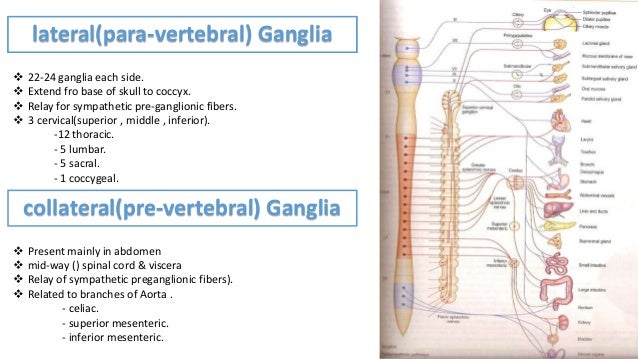
Paravertebral Ganglia. Paravertebral ganglia lie bilaterally along the dorsal body wall ventrolateral to the vertebral column. With their connecting trunks they form bilaterally symmetrical chains, which extend from C1 to S2, with one pair of ganglia per thoracic and lumbar spinal cord segment.
What are the characteristics of the sympathetic paravertebral ganglia?
Sympathetic paravertebral ganglia. Within sympathetic paravertebral ganglia (in the sympathetic chains), ganglionic neurons have uniform properties. Each convergent cholinergic preganglionic axon produces an excitatory postsynaptic potential by activating nicotinic receptor channels.
What is the usual complement of the paravertebral ganglia?
The usual complement of paravertebral ganglia includes 2-3 cervical, 11-12 thoracic, 3-4 lumbar, and 4-5 sacral ganglia. Want to thank TFD for its existence?
What are the two types of ganglia in the vertebral column?
…divided into two major groups, paravertebral and prevertebral (or preaortic), on the basis of their location within the body. Paravertebral ganglia generally are located on each side of the vertebrae and are connected to form the sympathetic chain, or trunk.
What are the 3 major prevertebral ganglia?
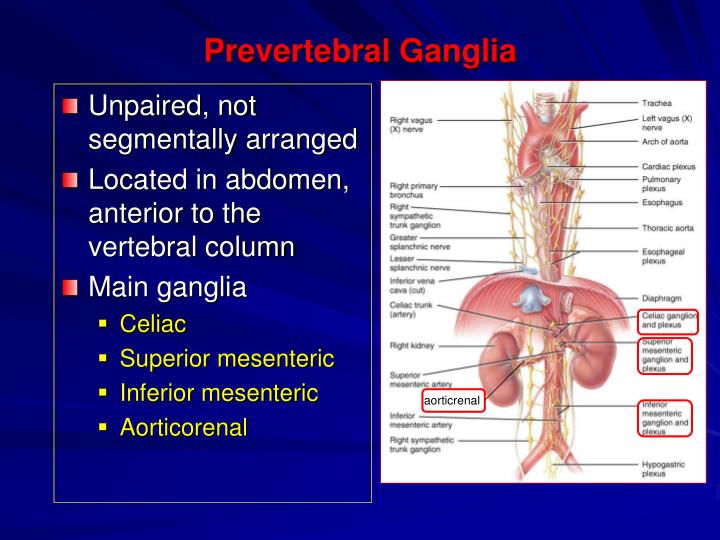
The celiac, superior, and inferior mesenteric ganglia are the major components of the prevertebral ganglia (PVG).
How many paravertebral ganglia are there?
They contain the cell bodies of neurons that innervate the structures and surface of the body wall and extremities. In humans there are usually 24 paravertebral ganglia in each chain.
Where is the paravertebral ganglion?
Paravertebral ganglia generally are located on each side of the vertebrae and are connected to form the sympathetic chain, or trunk. There are usually 21 or 22 pairs of these ganglia—3…
What are Paravertebral or sympathetic chain ganglia?
The sympathetic ganglia, or paravertebral ganglia are autonomic ganglia, of the sympathetic nervous system. Ganglia are 20,000 to 30,000 afferent and efferent nerve cell bodies that run along on either side of the spinal cord.
What are the different types of ganglia?
There are two types of ganglia in our bodies—sensory and motor. Sensory ganglia are ovoid in shape and contain oval cell bodies with nuclei that form in a circular pattern. In the spine, motor ganglia form a long chain from the base of the skull down to the tail end of the spine.
How many sympathetic ganglia are there?
There are usually 21 or 22 pairs of these ganglia—3 in the cervical region, 10 or 11 in the thoracic region, 4 in the lumbar region, and 4 in the sacral region—and a single unpaired ganglion lying in front of the…
What is the difference between sympathetic trunk ganglia and prevertebral ganglia?
Distinguish between the sympathetic trunk ganglia and the prevertebral ganglia. Sympathetic trunk ganglia are part of the sympathetic trunks, which are located lateral to the vertebral column. Prevertebral ganglia are located anterior to the vertebral column and cluster around the origins of major abdominal organs.
What are Paravertebral or sympathetic chain ganglia quizlet?
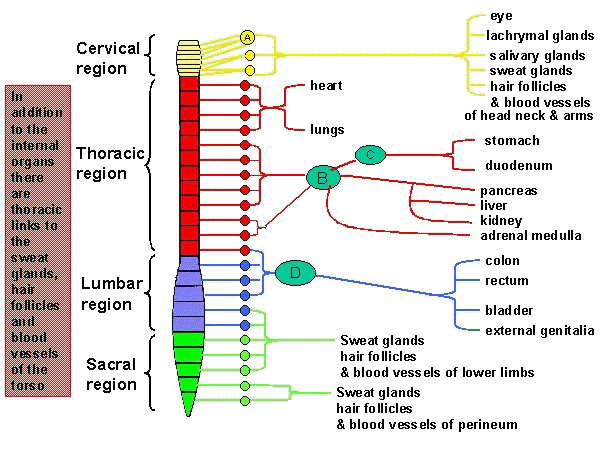
Sympathetic Ganglia: Sympathetic Trunk Ganglia. Paired, vertical chain on either side of the spine. Also called vertebral chain or paravertebral ganglia. Innervate organs ABOVE the diaphragm. Head, neck, shoulders, and heart.
What is Paravertebral?
Medical Definition of paravertebral : situated, occurring, or performed beside or adjacent to the spinal column paravertebral ganglia.
What are the 4 parasympathetic ganglia?
Parasympathetic ganglia which innervate targets in the head are located in four main ganglia: the ciliary, pterygopalatine, submandibular and otic ganglia. Scattered microganglia may also be distributed along cranial nerves.
What are sympathetic ganglia?
Sympathetic ganglia are the ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system. They deliver information to the body about stress and impending danger, and are responsible for the familiar fight-or-flight response.
Are prevertebral ganglia parasympathetic?
Prevertebral ganglia (or collateral ganglia, or preaortic ganglia) lie between the sympathetic ganglia and the target organ.
Where are the motor ganglia located?
…are referred to as paravertebral ganglia. Prevertebral motor ganglia are located near internal organs innervated by their projecting fibres, while terminal ganglia are found on the surfaces or within the walls of the target organs themselves. Motor ganglia have multipolar cell bodies, which ...
What are the two main groups of the nervous system?
In human nervous system: Sympathetic ganglia. …divided into two major groups, paravertebral and prevertebral (or preaortic), on the basis of their location within the body. Paravertebral ganglia generally are located on each side of the vertebrae and are connected to form the sympathetic chain, or trunk.
How many pairs of ganglia are there?
There are usually 22-23 pairs of these ganglia: 3 in the cervical region ( cervical ganglia ), 11 in the thoracic region (note the presence of the stellate cervicothoracic ganglia), 4 in the lumbar region and 4-5 in the sacral region. Throughout human evolution, the first thoracic and inferior cervical ganglia merged - and this resulting ganglion ...
Where are the sympathetic chain ganglia located?
The bilaterally symmetric sympathetic chain ganglia, also called the paravertebral ganglia, are located just ventral and lateral to the spinal cord. The chain extends from the upper neck down to the coccyx, forming the unpaired coccygeal ganglion. Each ganglion within this chain is either cervical, thoracic, lumbar, or sacral. Preganglionic nerves from the spinal cord synapse at one of the chain ganglia, and the postganglionic fiber extends to an effector, a visceral organ in the thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, or pelvic cavity .
Where are the preganglionic nerves located?
Preganglionic nerves from the spinal cord synapse at one of the chain ganglia, and the postganglionic fiber extends to an effector, a visceral organ in the thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, or pelvic cavity . There are usually 22-23 pairs of these ganglia: 3 in the cervical region ( cervical ganglia ), 11 in the thoracic region ...
Which ganglia receives input from the splanchnic nerves and innervate organs of
Collateral ganglia. Neurons of the collateral ganglia, also called the prevertebral ganglia, receive input from the splanchnic nerves and innervate organs of the abdominal and pelvic region. These include the celiac ganglia, superior mesenteric ganglia, and inferior mesenteric ganglia .
Which nerve cells bring information from the brain to the spinal cord?
Afferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the body to the brain and spinal cord, while efferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. The cell bodies create long sympathetic chains that are on either side of the spinal cord.
Where do the nerve fibers in the sympathetic nervous system come from?
Here they arise from the thoracolumbar (T1-L2) regions' lateral horn of grey and emerge via the ventral root. They enter their respective spinal nerve (e.g. T5), and thus enter the white ramus communicans.
Which neuron exits the sympathetic chain?
The postganglionic neurons extend across most of the body. Upon exiting the sympathetic chain, the fibres enter a less-myelinated gray ramus communicans. There is still a myelin sheath present – just in far lower amounts compared to the white ramus communicans.
What are the two groups of the ganglia?
The ganglia can be broadly categorized into two groups, that is, sensory ganglia (relating to the somatic nervous system (SNS)), and autonomic ganglia (relating to the autonomic nervous system (ANS) ). Collection of neuron cell bodies located in the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Which nerve contains two ganglia?
As with the vagus nerve, the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) contains two ganglia. The superior ganglion contains cell bodies of neurons which innervate the middle ear and internal surface of the tympanic membrane.
What nerve sends nerve fibers to the brain?
Facial nerve (CN VII) The neurons from the lacrimal and superior salivatory nuclei of the brainstem send fibers in the pterygopalatine ganglion and submandibular ganglion. The postganglionic fibers go on to innervate the lacrimal gland and glands in the nasal mucosa.
What is the sympathetic chain ganglia?
Sympathetic chain ganglia, also known as paravertebral ganglia, are the autonomic ganglia of the SNS. They consist of a paired chain of ganglia found ventral and lateral to the spinal cord. The ganglia extend from the upper neck to the coccyx, where the two chains fuse to form the unpaired ganglion impar.
What is a ganglion in 2021?
Reading time: 13 minutes. A ganglion is a collection of neuronal bodies found in the somatic and autonomic branches of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) . Ganglia can be thought of as synaptic relay stations between neurons.
What are preganglionic and postganglionic neurons?
Preganglionic vs postganglionic neurons 1 Have short preganglionic fibers, and long postganglionic fibers 2 Contain lightly myelinated preganglionic fibers, and unmyelinated postganglionic fibers 3 Originate within the lateral horn of the spinal cord, in the thoracic and upper lumbar regions (T1 to L2,3)
How many parasympathetic ganglia are there in the head?
In the head and neck there are four parasympathetic ganglia : ciliary, pterygopalatine, otic and submandibular. A good mnemonic to remember the parasympathetic ganglia is: " C ats P refer S exy O wners". Those ganglia are related to the following nerves:
Where are the basal ganglia located?
The basal ganglia are located in the brain stem, thalamus, and cerebral cortex areas of the brain. Being in the brain, they are part of the central nervous system, not the peripheral nervous system, as other ganglia are. This group of structures is important in regulating voluntary movements. In addition to playing a role in motor control, this ...
What is the function of ganglia?
Ganglia play an essential role in connecting the parts of the peripheral and central nervous systems.
What is the plural of ganglion?
Ganglia is the plural of the word ganglion. Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies found throughout the body. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and carry nerve signals to and from the central nervous system. They are divided into two broad categories, the sensory ganglia and the motor ganglia ...
What are the dorsal roots of spinal nerves?
Dorsal roots of spinal nerves. Roots of some cranial nerves like the trigeminal nerve. One portion of these sensory ganglia connects to the peripheral nervous system. The other is connected to the central nervous system via the brain or spinal cord. Motor ganglia are part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
Which ganglia are ovoid?
Sensory ganglia are ovoid in shape and contain oval cell bodies with nuclei that form in a circular pattern. In the spine, motor ganglia form a long chain from the base of the skull down to the tail end of the spine. Motor ganglia contain irregularly shaped cell bodies.
Can basal ganglia damage be reversible?
Some causes of basal ganglia damage, for instance, are reversible and respond well to rehabilitation. Treatments are also available for heavy metal poisoning. Depending on the individual, there may not be any lingering symptoms after treatment.
What is the prevertebral ganglia?
Anatomical terminology. Prevertebral ganglia (or collateral ganglia, or preaortic ganglia lie between the sympathetic ganglia and the target organ.
Which neuron innervates the prevertebral ganglia?
Once inside the prevertebral ganglia, the individual neurons comprising the nerve synapse with their postganglionic neuron. The postganglionic nerve then proceed to innervate their targets (pelvic visceral organs).
What nerves exit the lateral horn of the spinal cord?
Nerves arising from the lateral horn of the spinal cord are those of the autonomic nervous system. They exit through the ventral root of the spinal cord, and continue through the ventral rami. At that point, they sharply branch to go through the white ramus communicans of the paravertebral body. Unlike the thoracic and cutaneous nerves, the ANS nerves destined for the pelvic viscera continue through the paravertebral ganglia without synapsing. Instead of synapsing, they continue through splanchnic nerves until they reach a prevertebral ganglia (located proximally to their target organ). Once inside the prevertebral ganglia, the individual neurons comprising the nerve synapse with their postganglionic neuron. The postganglionic nerve then proceed to innervate their targets (pelvic visceral organs).
Which ganglia innervates the pelvic viscera?
The nerves that synapse in the prevertebral ganglia innervate the pelvic viscera.
What is the abdominal portion of the sympathetic trunk?
Abdominal portion of the sympathetic trunk, with the celiac plexus and hypogastric plexus. The celiac ganglia with the sympathetic plexuses of the abdominal viscera radiating from the ganglia. Prevertebral ganglia (or collateral ganglia, or preaortic ganglia lie between the sympathetic ganglia and the target organ.