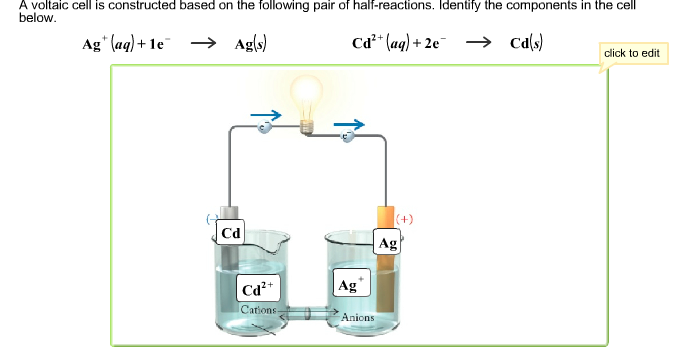
The important parts of a voltaic cell:
- The anode is an electrode where oxidation occurs.
- The cathode is an electrode where reduction occurs.
- A salt bridge is a chamber of electrolytes necessary to complete the circuit in a voltaic cell.
- electrode: a strip of metal where the reaction takes place.
- anode: an electrode where oxidation occurs.
- cathode: an electrode where reduction occurs.
- salt bridge: chamber of electrolytes needed to complete the circuit in a voltaic cell.
What are the main components of a voltaic cell?
The cathode is an electrode where reduction occurs. A salt bridge is a chamber of electrolytes necessary to complete the circuit in a voltaic cell. Click to see full answer. In this way, what are the main components of an electrochemical cell? The anode: the compartment where oxidation occurs. The cathode: the compartment where reduction occurs.
What is another name for a voltaic cell?
A voltaic cell is also called a galvanic cell. The mechanism of a magnesium-copper simple cell with sodium chloride solution as the electrolyte is shown in Figure. Why is an electrolyte able to conduct electricity while a Nonelectrolyte Cannot? What does electrochemical series mean? How is electrolysis used in the industry?
How do you make a voltaic cell?
A simple voltaic cell is made by placing two different metals in contact with an electrolyte. The metals act as the electrodes for the voltaic cell. The electrodes are connected to a voltmeter, a galvanometer or an electric bulb using connecting wires.
What is the anode and cathode in a voltaic cell?
The anode is an electrode where oxidation occurs. The cathode is an electrode where reduction occurs. A salt bridge is a chamber of electrolytes necessary to complete the circuit in a voltaic cell. The oxidation and reduction reactions are separated into compartments called half-cells.
What 3 components are needed to build a voltaic cell?
What Are Three Important Parts Needed to Make a Battery?Voltaic Cells. Some metals lose electrons more readily than other metals. ... The Cathode. A cathode is one of the two electrodes in a polarized device such as a voltaic cell. ... The Anode. ... The Electrolyte. ... Making a Battery.
How is a voltaic cell constructed?
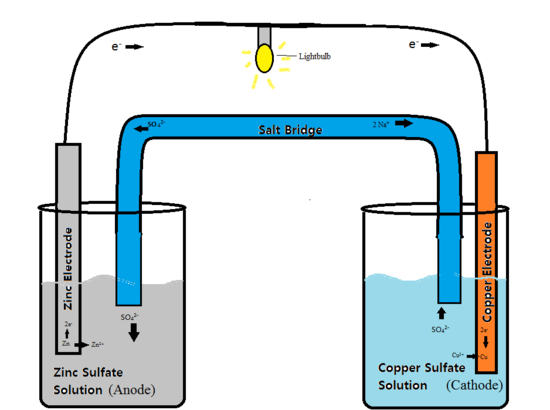
A simple voltaic cell is made by immersing one zinc plate and one copper plate inside a water diluted sulfuric acid solution. As shown in the figure, if the copper plate and zinc plate are connected externally with an electrical load, an electric current starts flowing from copper plate to zinc plate through the load.
What is the structure of a galvanic cells?
Electrochemical cells typically consist of two half-cells. The half-cells separate the oxidation half-reaction from the reduction half-reaction and make it possible for current to flow through an external wire. One half-cell, normally depicted on the left side in a figure, contains the anode.
Which electrodes are used in voltaic cell?
The voltaic cell uses two different metal electrodes, each in an electrolyte solution. The anode will undergo oxidation and the cathode will undergo reduction. The metal of the anode will oxidize, going from an oxidation state of 0 (in the solid form) to a positive oxidation state, and it will become an ion.
What is the cathode made in a voltaic cell?
The cathode is an electrode where reduction occurs. A salt bridge is a chamber of electrolytes necessary to complete the circuit in a voltaic cell. The oxidation and reduction reactions are separated into compartments called half-cells.
How do you label a voltaic cell?
0:176:11Labeling a Voltaic Cell - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo let's start by labeling of the zinc electrode first which is going to be the negative electrode.MoreSo let's start by labeling of the zinc electrode first which is going to be the negative electrode. Right. So we have this piece of metal right here is zinc solid.
How do you find the anode and cathode in a voltaic cell?
The anode is always placed on the left side, and the cathode is placed on the right side.
What is the anode and cathode in a galvanic cell?
In both kinds of electrochemical cells, the anode is the electrode at which the oxidation half-reaction occurs, and the cathode is the electrode at which the reduction half-reaction occurs. Table 1: Properties of Galvanic and Electrochemical Cells. Electrochemical cell (Galvanic Cell)
What is a voltaic cell quizlet?
Voltaic cell. An electrochemical cell in which a spontaneous chemical reaction produces the flow of electrons.
What are the metals in the voltaic cell?
Notes: A voltaic cell is an electrochemical cell that uses a chemical reaction to produce electrical energy. Zinc is used as anode and copper is used as cathode.
What is cathode and anode?
The Anode is the negative or reducing electrode that releases electrons to the external circuit and oxidizes during and electrochemical reaction. The Cathode is the positive or oxidizing electrode that acquires electrons from the external circuit and is reduced during the electrochemical reaction.
Which electrode serves as the anode and which as the cathode?
Difference Between Anode And CathodeAnodeCathodeThe anode is the electrode where electricity moves into.The cathode is the electrode where electricity is given out or flows out.The anode is usually the positive side.A cathode is a negative side.It acts as an electron donor.It acts as an electron acceptor.2 more rows
Principle of Voltaic Cell
The working principle of Voltaic cell is based on the fact that, the electric work is done by a voltaic cell due to the Gibbs free energy of spontaneous redox reactions in the voltaic cell.
Parts of Voltaic Cell
Cathode – The cathode of voltaic cell is made up of copper. This is the positive terminal of the cell and Reduction occurs at this electrode.
Working of Voltaic Cell
In a voltaic cell, when an electrode is dipped into the electrolyte at the contact surface of electrode and electrolyte, the atoms of the electrode have a tendency to generate positive ions in the electrolytic solution and leaving the electrons at the electrode. Hence, the electrode becomes negatively charged.
How does a voltaic cell produce electricity?
A voltaic cell produces electricity as a redox reaction occurs. The voltage of a voltaic cell can be determined by the reduction potentials of the half reactions. Voltaic cells are fashioned into batteries, which are a convenient source of electricity. Exercises.
Why is the anode considered the negative electrode of the cell?
Because electrons are coming from the anode , the anode is considered the negative electrode of the cell, while the cathode is considered the positive electrode of the cell. Finally, because electrons are moving from one half cell to the other, a charge imbalance builds up as the reaction proceeds.
Why are absolute voltages unnecessary?
Because the voltage of a redox reaction is determined by the difference of the tendencies of the individual half reactions, absolute voltages are unnecessary; only relative voltages of each half reaction are needed.
What is the tendency for electrons to go from one half cell to another called?
The tendency for electrons to go from one half cell to another is called the voltage.
Which half cell contains the reduction reaction?
The half cell that contains the oxidation reaction is called the anode, while the half cell that contains the reduction reaction is called the cathode . The cathode and anode collectively are the electrodes of the voltaic cell.
What is the apparatus that allows electrical work to be extracted from a redox reaction?
The apparatus as a whole, which allows useful electrical work to be extracted from a redox reaction, is called a voltaic (galvanic) cell.
What are the different types of voltaic cells?
The commonly used cells are the dry cell, lead- acid accumulator, mercury cell, alkaline cell and nickel-cadmium cell. The uses, advantages and disadvantages of these cells are summarised in Table.
What is a voltaic cell?
The production of electricity in the cell will cause the bulb to light up, and make the needle of voltmeter or galvanometer to deflect. A voltaic cell is also called a galvanic cell. The mechanism of a magnesium-copper simple cell ...
What are the two electrolytes that are connected by a salt bridge?
The two electrolytes, zinc sulphate solution and copper (II) sulphate solution, are connected by a salt bridge or a porous pot. Functions of a salt bridge or a porous pot are as follows: (a) To prevent the two electrolytes from mixing. (b) To allow the flow of the ions so that the electric circuit is completed.
What are some examples of voltaic cells?
A zinc-copper cell or Daniell cell is another example of a voltaic cell. Figure shows the two structures of Daniell cells. In the cell, zinc and copper metals are used as the electrodes. Each of the metals is immersed into a solution of its ions. The two electrolytes, zinc sulphate solution and copper (II) sulphate solution, ...
How many electrons does magnesium have?
Each magnesium atom donates two electrons to form a Mg 2+ ion. The Mg 2+ ions are released into the sodium chloride solution while the electrons go onto the magnesium ribbon to make it negative. At the negative terminal: Mg (s) → Mg 2+ (aq) + 2e –.
How does a voltaic cell work?
A voltaic cell is a device which converts chemical energy to electrical energy. The chemical reactions that take place inside the cell cause the flow of electrons and hence, electricity is produced. A simple voltaic cell is made by placing two different metals in contact with an electrolyte. The metals act as the electrodes for the voltaic cell. ...
Which ion is lower than the Mg 2+ ion?
These electrons can be accepted by the positive ions in the electrolyte like Mg 2+ ions, H+ ions and Na + ions. The H + ion is lower than the Mg 2+ ion and Na + ion in the electrochemical series.