See more

What is the main part of the sun?
There are three main parts to the Sun's interior: the core, the radiative zone, and the convective zone. The core is at the center. It the hottest region, where the nuclear fusion reactions that power the Sun occur. Moving outward, next comes the radiative (or radiation) zone.
What are the 10 parts of the sun?
These are the internal parts of the Sun.Core.Radiative Zone.Convection Zone.Photosphere.Sunspots.Chromosphere.Corona.Solar Flares.More items...
What are the parts of the sun for kids?
The Sun is the largest object in our solar system. It is composed of seven layers: three inner layers and four outer layers. The inner layers are the core, the radiative zone and the convection zone, while the outer layers are the photosphere, the chromosphere, the transition region and the corona.
What are the 4 structures of the sun?
In studying the structure of the Sun, solar physicists divide it into four domains: the interior, the surface atmospheres, the inner corona, and the outer corona.
What are the 7 layers of the sun?
The inner layers are the Core, Radiative Zone and Convection Zone. The outer layers are the Photosphere, the Chromosphere, the Transition Region and the Corona. IRIS will focus its investigation on the Chromosphere and Transition Region.
What is the sun made of *?
Like any star in its prime, the sun consists mainly of hydrogen atoms fusing two by two into helium, unleashing immense energy in the process. But it's the sun's tiny concentration of heavier elements, which astronomers call metals, that controls its fate.
What are the 5 stages of the Sun?
What are the different stages of life cycle of stars?Giant Gas Cloud.Protostar.T-Tauri Phase.Main Sequence.Red Giant.The Fusion of Heavier Elements.Supernovae and Planetary Nebulae.
What are 5 features of the Sun?
Characteristics of the SunMass: 1.98892 x 1030 kg.Diameter: 1,391,000 kilometers.Radius: 695,500 km.Surface gravity of the Sun: 27.94 g.Volume of the Sun: 1.412 x 1018 km3Density of the Sun: 1.622 x 105 kg/m3
What are the 3 features of the Sun?
The main regions of the Sun include its interior, surface (photosphere), and atmosphere.
How many suns are there?
Our Sun is just one of about 200 billion stars in our galaxy.
What are 5 features of the sun?
Characteristics of the SunMass: 1.98892 x 1030 kg.Diameter: 1,391,000 kilometers.Radius: 695,500 km.Surface gravity of the Sun: 27.94 g.Volume of the Sun: 1.412 x 1018 km3Density of the Sun: 1.622 x 105 kg/m3
How many areas are there on the sun?
SunObservation dataEquatorial circumference4.379×106 km 109 × EarthFlattening9×10−6Surface area6.09×1012 km2 12,000 × EarthVolume1.41×1018 km3 1,300,000 × Earth33 more rows
How many layers the sun have?
The structure of the sun is made up of four layers. At the very center is the dense, hot core. Around the core lie two layers: a thick layer called the radiative zone and a thinner, cooler layer called the convective zone. Surrounding all of them is the sun's surface layer, known as the photosphere.
Is there gold in Sun?
Eventually, scientists calculated that the Sun contains almost 2.5 trillion tons of gold, enough to fill Earth's oceans and more. Still, that's just eight atoms of gold for every trillion atoms of hydrogen — a tiny amount when compared to the mass of the Sun.
What is the Sun made of?
The remaining amount of the Sun is made of iron, nickel, oxygen, silicon, sulfur, magnesium, carbon, neon, calcium and chromium.
Why is the Sun made of layers?
The layers of the Sun are created because the temperatures and pressures increase as you move towards the center of the Sun. The hydrogen and helium behave differently under the changing conditions.
How many solar radius does the Sun have?
Astronomers believe that the core of the Sun extends from the center out to about 0.2 solar radius. And within this region, temperatures and pressures are so high that hydrogen atoms are torn apart to form separate protons, neutrons and electrons. With all of these free floating particles, the Sun is able to reform them into atoms of helium.
What are the elements that are formed when the hydrogen in the core runs out?
Once the hydrogen in the core runs out, they switch to fusing heavier and heavier elements, like helium, lithium, oxygen. Most of the heavier metals we see in the Sun were formed in other stars at the end of their lives. The heaviest elements, like gold and uranium, were formed when stars many times more massive that our Sun detonated in supernova explosions.
Which layer of the Sun is convective?
Convective Zone: Outside the radiative zone is another layer, called the convective zone, where heat from inside the Sun is carried up by columns of hot gas. Most stars have a convective zone. In the case of the Sun, it starts at around 70% of the Sun’s radius and goes to the outer surface (the photosphere).
How many degrees is the Sun's core?
Astronomers believe that the core of the Sun extends from the center out to about 0.2 solar radius.
Why is the Sun's surface brighter?
Bright spots and short-lived magnetic regions – The surface of the Sun has many brighter and dimmer spots caused by changing temperature. The temperature changes from the constantly shifting magnetic field.
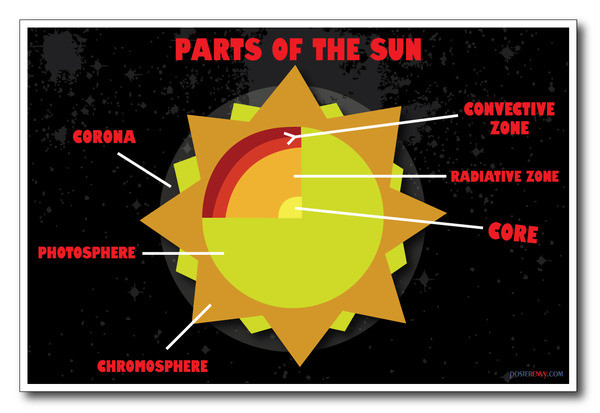
What are the parts of the Sun?
There are three main parts to the Sun's interior: the core, the radiative zone, and the convective zone.
Where is the core of the Sun?
The core is at the center. It the hottest region, where the nuclear fusion reactions that power the Sun occur. Moving outward, next comes the radiative (or radiation) zone. Its name is derived from the way energy is carried outward through this layer, carried by photons as thermal radiation. The third and final region of ...
What is the solar interior?
The solar interior includes the core, radiative zone and convective zone. The photosphere is the visible surface of the Sun. The solar atmosphere includes the chromosphere and corona. Credit: SOHO (ESA & NASA)
What is the lower part of the solar system called?
The lower region of the solar atmosphere is called the chromosphere. Its name comes from the Greek root chroma (meaning color), for it appears bright red when viewed during a solar eclipse. A thin transition region, where temperatures rise sharply, separates the chromosphere from the vast corona above. The uppermost portion of the Sun's atmosphere ...
What is the third and final region of the solar interior?
The third and final region of the solar interior is named the convective (or convection) zone. It is also named after the dominant mode of energy flow in this layer; heat moves upward via roiling convection, much like the bubbling motion in a pot of boiling oatmeal. The boundary between the Sun's interior and the solar atmosphere is called ...
What is the photosphere?
Did you know that the Sun has an atmosphere? The lower region of the solar atmosphere is called the chromosphere.
What is the uppermost part of the Sun called?
The uppermost portion of the Sun's atmosphere is called the corona, and is surprisingly much hotter than the Sun's surface (photosphere)! The upper corona gradually turns into the solar wind, a flow of plasma that moves outward through our solar system into interstellar space. The solar wind is, in a sense, just an extension ...
What part of the Sun is the surface?
The part of the Sun we see from Earth – the part we call the surface – is the photosphere. The Sun doesn’t actually have a solid surface because it’s a ball of plasma.
Which planets orbit the Sun?
The planets orbit the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The dwarf planets Pluto, Ceres, Makemake, Haumea, and Eris also orbit the Sun.
What is the largest object in our solar system?
The Sun is the largest object in our solar system. The Sun’s volume would need 1.3 million Earths to fill it. Its gravity holds the solar system together, keeping everything from the biggest planets to the smallest bits of debris in orbit around it. The hottest part of the Sun is its core, where temperatures top 27 million degrees Fahrenheit (15 million degrees Celsius). The Sun ’s activity, from its powerful eruptions to the steady stream of charged particles it sends out, influences the nature of space throughout the solar system.
What is the only star in our solar system?
The Sun is the only star in our solar system. It is the center of our solar system, and its gravity holds the solar system together. Everything in our solar system revolves around it – the planets, asteroids, comets, and tiny bits of space debris.
What spacecraft monitors the Sun?
Sun-exploring spacecraft include Parker Solar Probe, Solar Orbiter, SOHO, ACE, IRIS, WIND, Hinode, Solar Dynamics Observatory, and STEREO.
How old is the Sun?
Our Sun is a 4.5 billion-year-old star – a hot glowing ball of hydrogen and helium at the center of our solar system. The Sun is about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) from Earth, and without its energy, life as we know it could not exist here on our home planet.
How much bigger is the Sun than the Earth?
The Sun is about 100 times wider than Earth and about 10 times wider than Jupiter, the biggest planet. If the Sun were as tall as a typical front door, Earth would be about the size of a nickel.
What are the layers of the Sun?
Layers of the Sun. This graphic shows a model of the layers of the Sun, with approximate mileage ranges for each layer: for the inner layers, the mileage is from the sun's core; for the outer layers, the mileage is from the sun's surface. The inner layers are the Core, Radiative Zone and Convection Zone. The outer layers are the Photosphere, the ...
Which layer of the Sun is covered by granulation?
Most of the photosphere is covered by granulation. Chromosphere - The chromosphere is a layer in the Sun between about 250 miles (400 km) and 1300 miles (2100 km) above the solar surface (the photosphere).
Which layer of the Sun is the deepest?
Photosphere - The photosphere is the deepest layer of the Sun that we can observe directly. It reaches from the surface visible at the center of the solar disk to about 250 miles (400 km) above that.
What are the outer layers of the photosphere?
The inner layers are the Core, Radiative Zone and Convection Zone. The outer layers are the Photosphere, the Chromosphere, the Transition Region and the Corona. IRIS will focus its investigation on the Chromosphere and Transition Region. More detail on the outer layers follows:
What are the two elements that make up the Sun?
1. Hydrogen and Helium - Major Components of the Sun. The sun is chemically composed of hydrogen and helium. The two elements came from the Big Bang process and account for 98% of the celestial object's mass.
How did the Sun form?
The celestial body was formed from a collapse of a giant cloud that consisted mainly of hydrogen and helium. It is the brightest component of the solar system and the primary source of energy for life on earth (Aller, L.H).
What happens to the Earth if the core of the star doesn't absorb radiation?
Radiations from the core lose a lot of energy when passing through this zone to the earth. Life would be unbearable or there would be no life on the earth if this region doesn't absorb some of the radiations' energy. The region takes 70% of the star's radius, making it the largest in the celestial body (Tobias, S.M, Mullan, D.J, Cohen, H, Zirker J.B, Aller, L.H).
What is the hottest part of the Sun?
The Core. According to astrophysicists, this is the hottest zone/part of the sun. It is believed to be at a temperature in the region of 15.7 million Kelvin and under a very high pressure. The high temperature and pressure cause nuclear fusion which involves the atoms of hydrogen and helium combining together.
What is the temperature of the Sun's core?
This is the second hottest zone of the star, after the core. Its temperature ranges between 1million Kelvin and 20 million Kelvin, and it consists of darker, less hot regions known as coronal holes or sunspots (Parker, E.N).
Why is the center of the Sun brighter than the edges?
Studies show that there exist some water and carbon monoxide molecules in the cooler region.
Which layer of the atmosphere is filled with particles?
Heliosphere. This is the outermost layer of the solar atmosphere. It is filled with energetic particles as well as the solar wind, and is believed to be felt in all planets (Space Ref, Rusell, C.T). 7. Other Features and Components. Neutrinos- Micro particles produced during the fusion reactions.
What are the layers of the Sun's surface called?
Surrounding all of them is the sun’s surface layer, known as the photosphere. Above this lies the sun’s thin atmosphere, which is made up of the chromosphere and the corona.
What is the atmosphere of the Sun made of?
Above this lies the sun’s thin atmosphere, which is made up of the chromosphere and the corona. Most of the sun is made up of hydrogen in the form of a glowing-hot gas called plasma. Everysecond, the sunreleases1 million timesmore energythan everyone onEarthuses in ayear. Quiz. Take the solar system quiz.
Which layer of the Sun is made of hydrogen gas squeezed very tightly together?
This process allows heat to move from the sun’s heart to its outer surface. Radiative. zone. Radiative. zone. This layer is made of hydrogen gas squeezed very tightly together. Energy from the core seeps very slowly through the radiative zone toward the sun’s surface.
How long does it take for a ray of light to pass through the Sun's core?
It can take 100,000 years for a ray of light to pass through this thick, dense layer. Core. Core. Inside the dense, hot core of the sun, particles of a gas called hydrogen merge together to create another gas, called helium.