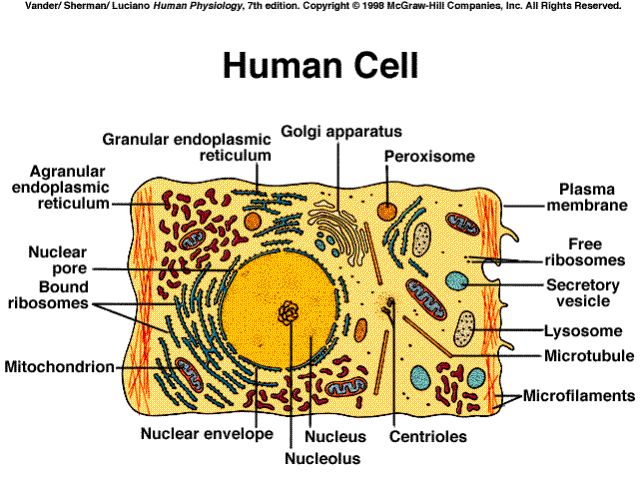
The Nucleus and Its Parts The nucleus is composed of many parts that help it function properly within the cell. The parts that make up the nucleus include the nuclear envelope, nucleolus The nucleolus is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, where it primarily serves as the site of ribosome synthesis and assembly. Nucleoli also have other important functions like assembly of signal recognition particles and playing a role in the cell's response …Nucleolus
What are all the parts of the nucleus?
The nucleus consists of the following main parts: (1) Nucleolemma or nuclear membrane (karyotheca) (2) Nuclear sap or karyolymph or nucleoplasm (3) Chromatin network or fibres (4) Nucleolus (5) Endosomes.
What are the 3 parts of the nucleus?
Parts and Function of the Nucleus. The nucleus structure is a double-membraned organelle of the eukaryotes. It has three main components: nucleolus and other chromatins (chromosomes), nuclear bodies, nuclear matrix, nucleoplasm, and nuclear envelope.
What are 5 functions of the nucleus?
Functions of NucleusNucleus contains all the genetic information in its chromatin.Nucleus take part in transmission of genetic information from parent cell to its daughter cells and from one generations to the next.Division of nucleus is pre requisite to cell division.Nucleus forms ribosomes on its nucleolus.More items...
What are the parts of the nucleus and their functions Class 8?
Its structure consists of the following important parts:The nuclear membrane- This is an aspect of the nucleus that differentiates eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells. ... Nucleoplasm- It is a type of protoplasm. ... Nucleolus- This is the most important organelle. ... Chromosomes- These are thread-like structures.More items...
What are 3 functions of the nucleus?
The primary functions of the nucleus are to store the cell's DNA, maintain its integrity, and facilitate its transcription and replication.
What is the nucleolus function?
The primary function of the nucleolus is in facilitating ribosome biogenesis, through the processing and assembly of rRNA into preribosomal particles.
What are the 10 functions of nucleus?
Functions of NucleusIt controls the heredity characteristics of an organism.It main cellular metabolism through controlling synthesis of particular enzymes.It is responsible for protein synthesis, cell division, growth and differentiation.Stores heredity material in the form of deoxy-ribonucleic acid (DNA) strands.More items...
What are the main things in a nucleus?
The nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's DNA, surrounded by a network of fibrous intermediate filaments and enveloped in a double membrane called the "nuclear envelope". The nuclear envelope separates the fluid inside the nucleus, called the nucleoplasm, from the rest of the cell.
What are the 7 functions of a cell?
What Are The 7 Functions Of The Cell Wall?Renders mechanical strength.Serve as food reservoir.It maintains the shape of the cell.It regulates the intercellular transport.It regulates the expansion of cells.Provides protection against pathogens.More items...•
What are the parts of nucleus class 9th?
The nucleus contains some thread like structures called chromatin. It exists during the resting stage of cell. The chromatin contains DNA (Deoxy-ribo nucleic acid), RNA (Ribo Nucleic acid) and proteins. The nucleus contains some rod shaped structures in a cell that contains the hereditary information.
What are the functions of nucleus class 9?
Function of Nucleus Class 9Nucleus plays an important role in cellular reproduction. ... It Determines the cell development and maturity by directing the chemical activities of the cell.It helps in the transmission of hereditary traits from the parent to offspring.It controls all metabolic activities of the cell.
What is the function of nucleolus for Class 8?
Nucleolus Function Primarily, it takes part in the production of subunits that unites to form ribosomes. Hence, nucleolus plays an important role in the synthesis of proteins and in the production of ribosomes in eukaryotic cells.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The key function of the nucleus is to control cell growth and multiplication. This involves regulating gene expression, initiating cellular reproduction, and storing genetic material necessary for all of these tasks. In order for a nucleus to carry out important reproductive roles and other cell activities, it needs proteins and ribosomes.
What is the cell nucleus?
Updated November 06, 2019. The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains a cell's hereditary information and controls its growth and reproduction. It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is usually the most notable cell organelle in both size and function.
What is the nucleus membrane?
Nuclear Envelope and Nuclear Pores. The cell nucleus is bound by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. This membrane separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm, the gel-like substance containing all other organelles. The nuclear envelope consists of phospholipids that form a lipid bilayer much like that of the cell membrane.
What is the nucleoplasm?
The nucleolus and chromosomes are surrounded by nucleoplasm, which cushions and protects nuclear contents. Like the nuclear envelope, the nucleoplasm supports the nucleus to hold its shape.
What is the nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope consists of phospholipids that form a lipid bilayer much like that of the cell membrane. This lipid bilayer has nuclear pores that allow substances to enter and exit the nucleus, or transfer from the cytoplasm to the nucleoplasm. The nuclear envelope helps to maintain the shape of the nucleus.
What is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope?
Nucleoplasm is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope. Also called karyoplasm, this semi-aqueous material is similar to cytoplasm in that it is composed mainly of water with dissolved salts, enzymes, and organic molecules suspended within.
What is the name of the structure that houses chromosomes?
Chromatin. The nucleus houses chromosomes containing DNA. DNA holds heredity information and instructions for cell growth, development, and reproduction. When a cell is "resting", or not dividing, its chromosomes are organized into long entangled structures called chromatin .
What are the parts of the nucleus?
The nucleus is composed of many parts that help it function properly within the cell. The parts that make up the nucleus include the nuclear envelope, nucleolus, and chromosomes/ chromatin.
What is the structure of a chromosome?
Structure: Chromosomes are composed of nucleotides, which bond together to form a double helix. Th is double helix is tightly wrap around a protein to form a c h romosome . The unraveled material from a chromosome that fl oats around in the nucleus is known as chromatin.
Where is the N ucleolus located?
Location: The n ucleolus is located inside of the nucleus. It is surrounded by the nuclear envelope. It is NOT membrane- bound. Structure: The nucleolus is a dense region in the nucleus composed of DNA, RNA, and proteins. Function: The nucleolus makes r ibosomes. This is a very important job inside of the cell.
What is the role of the nucleus in the cell?
The nucleus has very important roles to play. As it contains genetic material , it coordinates cell activities like protein synthesis and cell division. Anatomically the nucleus is made up of several components: nuclear envelope, nuclear lamina, nucleolus, chromosomes, nucleoplasm are some of these components.
What is the nucleus?
Key facts about the cell nucleus. Definition. A membranous organelle of the eukaryotic cell that contains the cellular genetic material. Parts. Nuclear envelope, nuclear lamina, nucleolus, chromosomes, nucleoplasm. Function. Control of the genetical information, protein and enzyme synthesis, cell division and cell growth;
What is the most important organelle in eukaryotic cells?
The cell nucleus is the most noticeable organelle within the eukaryotic cell, and perhaps the most important and defining feature of the eukaryotic cells. Most of the genetic material (DNA) is contained in the nucleus, while a small amount of it is found in mitochondria. The majority of human cells have a single nucleus, ...
How big is the nucleus?
The nucleus is normally around 5-10 μm in diameter in many multicellular organisms, and the largest organelle in the cell. The smallest nuclei are approximately 1 μm in diameter and are found in yeast cells.
What is the inner nuclear membrane?
The inner nuclear membrane is internally lined by protein filaments meshwork organised in a net-like fashion, called nuclear lamina. The proteins that make up the nuclear lamina are known as lamins, which are intermediate filament proteins. These support the nuclear envelope, ensuring that the overall shape and structure of the nucleus is maintained.
What is the control of the genetical information of the cell?
control of the genetical information of the cell and thus the heredity characteristics of an organism, regulation of the transcription of the mRNA to protein. When a cell is histologically stained, the nucleus normally appears as a large, dark organelle, mostly at or near the centre of a cell .
What is the mass of DNA and proteins inside a chromosome called?
Mitosis. The mass of DNA and proteins inside a chromosome is referred to as chromatin. When a cell is not dividing, it is difficult to see the chromosomes within a cell, even when it is stained. However, when DNA prepares and begins to divide, the chromosomes can be visualised more clearly.
What are the parts of the nucleus?
The nucleus consists of the following main parts: (1) Nucleolemma or nuclear membrane (karyotheca) (2) Nuclear sap or karyolymph or nucleoplasm (3) Chromatin network or fibres (4) Nucleolus (5) Endosomes.
Which structure is able to leave the nucleus?
On the other hand, very large structures such as ribosomal subunits, which are assembled in the nucleolus, are able to leave the nucleus through the nuclear pore complexes. The unit membranes of karyotheca are composed of protein and lipid, like plasma membrane.
When does the nucleolus disappear?
During cell division the nucleolus generally disappears during the first stage or prophase stage, but it reappears in the daughter cells. Morphologically, two components may be defined in a nucleolus:
How many nuclear pores are there in the nucleus?
Nuclear pores: The nuclear membrane possesses a number of nuclear pores or annuli, which vary from 40 to 145 per square micro-meter in nuclei of various plants and animals. Watson (1959) stated the number of pores in mammalian cells as 10 percent of the total surface of the nucleus.
What is the membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm?
The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a limiting membrane called as karyotheca or nuclear membrane. This membrane plays an important role for the transport of the material between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Which contractile proteins are found in the nucleus?
A considerable amount of the contractile proteins actin, myosin, tropomyosin and tubulin are said to be present. Nonhistone proteins have a more rapid turnover than histones do. Both histones and nonhistone proteins are synthesized in the cytoplasm and enter the nucleus through the nuclear envelope.
Which part of the nucleus controls the passage of some molecules and particles?
The materials exchanged between nucleus and cytoplasm must traverse the nuclear pore complexes. Thus, annuli or pores control the passage of some molecules and particles, even some ribosome components, between nucleus and cytoplasm.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The main function of the cell nucleus is to control gene expression and mediate the replication of DNA during the cell cycle.
What is the structure of a nucleus?
The structure of a nucleus encompasses the nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, chromosomes, and nucleolus.
What is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope?
Nucleoplasm. Nucleoplasm is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope. Also called karyoplasm, this semi-aqueous material is similar to the cytoplasm and is composed mainly of water with dissolved salts, enzymes, and organic molecules suspended within. The nucleolus and chromosomes are surrounded by nucleoplasm, ...
What is the role of the nucleoplasm in the nucleus?
Nucleoplasm also supports the nucleus by helping to maintain its shape. Additionally, nucleoplasm provides a medium by which materials, such as enzymes and nucleotides (DNA and RNA subunits), can be transported throughout the nucleus. Substances are exchanged between the cytoplasm and nucleoplasm through nuclear pores.
What is the space between the nucleus and the cytoplasm?
Such nuclear pores are the sites for the exchange of large molecules (proteins and RNA) between the nucleus and cytoplasm. A fluid-filled space or perinuclear space is present between the two layers of a nuclear membrane.
How many nuclei does an eukaryotic cell have?
In general, a eukaryotic cell has only one nucleus. However, some eukaryotic cells are enucleated cells (without a nucleus), for example, red blood cells (RBCs); whereas, some are multinucleate (consists of two or more nuclei), for example, slime molds. The nucleus is separated from the rest of the cell or the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane.
What is the nucleus made of?
Nucleolus. Contained within the nucleus is a dense, membrane-less structure composed of RNA and proteins called the nucleolus. Some of the eukaryotic organisms have a nucleus that contains up to four nucleoli.
How many parts does the nucleus have?
The structure of the nucleus can be divided into four main parts. The nuclear envelope: The nucleus is bound by a double membrane layer that forms the capsule or the envelope. The two layers of this envelope stay separated from each other by a space known as the perinuclear space.
What is the membrane of the nucleus?
The nuclear membrane has tiny gaps called pores. These pores allow the selective passage of substances between the nucleus and the cytoplasm (the matrix containing various organelles in the cell). The chromatin: The DNA is organized in the nucleus to form chromatin.
What is the most prominent organelle in the cell?
The nucleus (pleural nuclei) is the most prominent and largest organelle in the cell. This membrane-bound (encapsulated) organelle contains the genetic material inside it. It stores all the information that is required to reconstruct the organism. The nucleus is present in every cell of the human body except some cells, ...
What are the organs of the human body?
The cell further contains several tiny well-defined structures called the organelles, such as the nucleus , mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. The nucleus (pleural nuclei) is the most prominent and largest organelle in the cell.
Why is the outer layer of the nuclear envelope rough?
The outer layer of the nuclear envelope is rough because of the presence of ribosomes on its surface. The outer membrane may be continuous with other organelles, such as the Golgi apparatus and the endoplasmic reticulum. The nuclear membrane has tiny gaps called pores.
What is the function of protein fibers in the nucleus?
The protein fibers form a crisscross matrix within the nucleus. This helps maintain the shape and structure of the nucleus. The nucleoplasm is the main site for enzyme activity within the nucleus. The appearance of nucleoplasm may vary during the different phases of the cell cycle.
What is the nucleolus?
The nucleolus: The nucleolus is a well-defined spherical structure within the nucleus. It is the site for the synthesis and assembly of the ribosomes. The ribosomes act as the site of protein synthesis within the cell.
What is the cell nucleus?
The cell nucleus is a small structure with a spheroid or oval appearance that is found (usually) in the center of the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and that contains all the genetic material of the organism.
Structure and elements of the cell nucleus
The outer membrane has a rough appearance due to the presence of ribosomes.
Where is the nucleolus located?
The nucleolus is found in close association of a specific chromosome at a fixed point called nucleolus-organising region (Fig. 8.5).
How many nucleolus are there in a plant?
In many plants and animals, there is only one nucleolus for each haploid set of chromosomes.
How many nucleoli are in a vicia faba?
In vicia faba, for example, each diploid nucleus contains two nucleoli. ADVERTISEMENTS: In some organisms there may be two or more nucleoli for each haploid set of chromosomes and in some others the number of nucleoli within the nucleus changes with the advancement in the age of the cell.
What is the most characteristic structural feature of the nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope possesses special circular structures, the annuli (singular-annulus) through which certain materials can pass. The presence of annuli is the most characteristic structural feature of the nuclear envelope (Fig. 8.2).
What is the undifferentiated protoplasm inside the nuclear envelope called?
Nuclear Sap or Nucleoplasm: The undifferentiated protoplasm or ground substance present inside the nuclear envelope is called nuclear sap or nucleoplasm or karyolymph. The nucleoplasm seems to contain granules of various sizes and densities and is yet of unknown composition and function. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is the term for a thickened, electron dense ring of material set into the nuclear envelope?
Thus, it seems preferable to use the term ‘annulus ’, in precise sense, signifying a thickened, electron dense ring of material set into the nuclear envelope and functioning by some unknown mechanism to control the passage of particles in and out of the nucleus.
How many parts are in an annulus?
The structure of each annulus is eight-partite. Somewhat more specifically, 8 spheroid particles have been found to be arranged around the circumference of each annulus in the nuclear envelope of amoeba (Fig. 8.4) and of pea seedlings. Annulus shows contraction and relaxation.
