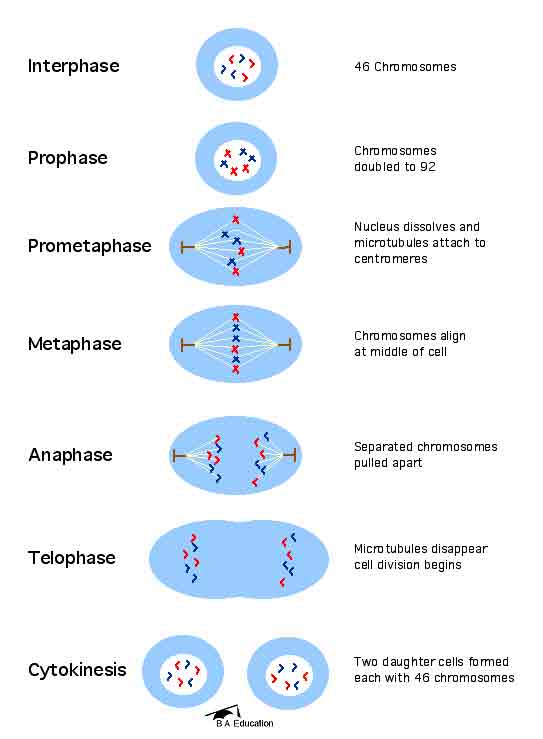
Both stages of meiosis 1 and 2 consist of four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Homologous tetrads are divided into two daughter cells at the meiosis 1. The resulting bivalent chromosomes in one daughter cell are divided into two daughter cells, containing single sister chromatids in each.
What are the 10 stages of meiosis?
The ten stages of meiosis are two separate instances of P.M.A.T., or prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. These phases occur during meiosis I and meiosis II. The 10 stages are as follows: Are you a student or a teacher?
What happens in each stage of meiosis?
The stages of meiosis 2 are as follows:
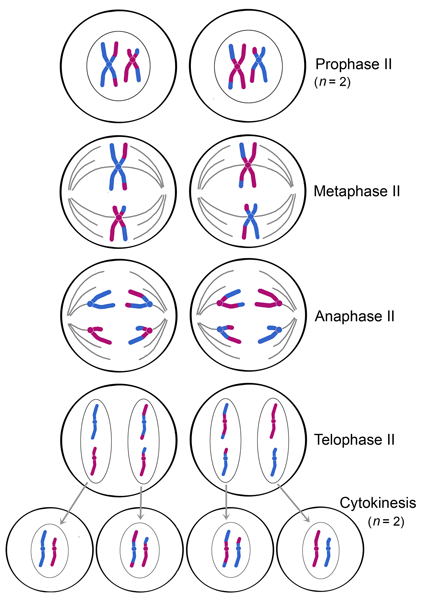
- Prophase 2: Here, we see the nucleoli and nuclear membrane disappear again. ...
- Metaphase 2: The centrosomes have two kinetochores that attach to spindle fibres from the centrosomes at opposite ends of the cell.
- Anaphase 2: Here, the spindle fibres contract and separate from non-sister chromatids. ...
What are the divisions of meiosis?
‘Meiosis’ consists of two successive divisions of the diploid mother nucleus, that are: (i) meiosis division I in which the diploid chromosome number (2n) is reduced to haploid chromosome number n, and (ii) meiosis division II which is a mitotic division.
Does meiosis 2 have a prophase stage?
The four aspects of Meiosis 2 are Prophase 2, Metaphase 2, Anaphase 2 and Telophase 2. The stages of meiosis 2 are as follows: Prophase 2: Here, we see the nucleoli and nuclear membrane disappear again. The chromatids get shorter and thicker. Chromosomes condense and centrosomes move to the opposite sides of the cell.
What are the phases for meiosis 1?
Meiosis 1 separates the pair of homologous chromosomes and reduces the diploid cell to haploid. It is divided into several stages that include, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
What are the phases for meiosis 2?
In meiosis II, the phases are, again, analogous to mitosis: prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II (see figure below). As shown in the figure below, meiosis II begins with two haploid (n = 2) cells and ends with four haploid (n = 2) cells.
What is difference between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2?
Meiosis I includes crossing over or recombination of genetic material between chromosome pairs, while meiosis II does not. This occurs in meiosis I in a long and complicated prophase I, split into five sub-phases. The equatorial plane in meiosis II is rotated 90° from the alignment of the equatorial plane in meiosis I.
How many chromosomes are at the end of meiosis 1 and 2?
Each daughter cell will have half of the original 46 chromosomes, or 23 chromosomes. Each chromosome consists of 2 sister chromatids. The daughter cells now move in to the third and final phase of meiosis: meiosis II. At the end of meiosis I there are two haploid cells.
What are the 4 phases of meiosis?
Meiosis I consists of four phases: prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, and telophase I.
What are the 8 phases of meiosis in order?
In this video Paul Andersen explains the major phases of meiosis including: interphase, prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, cytokinesis, interphase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II.
What is meiosis and its phases?
Meiosis is the process in which a single cell divides twice to form four haploid daughter cells. These cells are the gametes – sperms in males and egg in females. The process of meiosis is divided into 2 stages. Each stage is subdivided into several phases.
What are the 5 stages of meiosis?
Therefore, meiosis includes the stages of meiosis I (prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I) and meiosis II (prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II).
How many phases does meiosis 2 take?
Meiosis 2 proceeds through four sequential phases: prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2 and telophase 2. During prophase 2, nuclear envelop and nucleolus disappear, thickening the chromatids to form chromosomes. A new pair of centrosomes appears in the opposite poles of the second cell equator, which is in a rotated position by 90 degrees relative ...
What are the stages of meiosis?
Both stages of meiosis 1 and 2 consist of four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Homologous tetrads are divided into two daughter cells at the meiosis 1. The resulting bivalent chromosomes in one daughter cell are divided into two daughter ...
How are separated chromosomes pulled to the opposite poles?
The separated chromosomes are pulled to the opposite poles by the kinetochore microtubule contraction at the telophase 1. After the completion of telophase 1, new nuclear envelopes are formed surrounding the chromosomes in the opposite poles.
What happens during prophase 1?
During prophase 1, homologous chromosomes are paired by an event known as synapsis. During synapsis, genetic variation is allowed by two ways. First is the independent orientation of the pairs of the homologous chromosomes in the cell equator.
What is the first phase of meiosis?
What is Meiosis 1. Meiosis 1 is the initial period of the cell cycle and is followed by meiosis 2. During meiosis 1, homologous chromosomes are separated into two daughter cells, reducing the chromosome number by half, relative to the parent cells’ chromosome number. Meiosis 1 is composed of four phases: prophase 1, metaphase 1, ...
Why are cohesins cleaved in meiosis 2?
Meiosis 2: Cohesins at the centromeres are cleaved in order to separate the two sister chromatids.
What is the second division of meiosis?
The second division of meiosis is meiosis 2 which is involved in the equal segregation and separation of bivalent chromosomes. Meiosis 2 is only physically similar to the mitosis (vegetative cell division), not genetically since it produces haploid cells, which are used as gametes later, starting from diploid cells.
What is the phase of meiosis?
Interphase. Ed Reschke/Getty Images. There are two stages or phases of meiosis: meiosis I and meiosis II. Before a dividing cell enters meiosis, it undergoes a period of growth called interphase. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. G1 phase: The period prior to the synthesis of DNA.
What phase of meiosis is the nucleus bounded by?
At the end of interphase, the cell enters the next phase of meiosis: Prophase I.
What is the function of microtubules in meiosis?
Similar to mitosis, microtubules such as the kinetochore fibers interact to pull the chromosomes to the cell poles. Unlike in mitosis, sister chromatids remain together after the homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles. At the end of anaphase I of meiosis, the cell enters into telophase I.
What happens to chromosomes in meiosis?
Chromosomes thicken and detach from the nuclear envelope. Similar to mitosis, the centrioles migrate away from one another and both the nuclear envelope and nucleoli break down. Likewise, the chromosomes begin their migration to the metaphase plate. At the end of prophase I of meiosis, the cell enters into metaphase I.
What happens at the end of metaphase I of meiosis?
At the end of metaphase I of meiosis, the cell enters into anaphase I.
What happens at the end of telophase?
At the end of telophase I and cytokinesis, two daughter cells are produced, each with one-half the number of chromosomes of the original parent cell. Depending on the kind of cell, various processes occur in preparation for meiosis II. There is, however, a constant: The genetic material does not replicate again.
What happens to the sister chromatids in meiosis?
In anaphase II of meiosis, the following events occur: Sister chromatids separate and begin moving to opposite ends (poles) of the cell. Spindle fibers not connected to chromatids lengthen and elongate the cell. Once the paired sister chromatids separate from one another, each is considered a full chromosome.
What is meiosis 1?
Meiosis I : Reductional Cell Division. Sexual reproduction in organisms takes place through the fusion of male and female gametes, the sperm and the egg respectively. Gametes are haploid in nature, i.e., they contain only half the number of chromosomes. This genetic content makes them different from other body cells.
How many cells are produced in meiosis?
Meiosis is the process in which a single cell divides twice to produce four cells with half the original amount of chromosomes.
What is a pair of synapsed homologous chromosomes called?
A pair of synapsed homologous chromosome forms a complex known as bivalent or tetrad. At pachytene stage, crossing over of non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes occurs at the recombination nodules. The chromosomes remain linked at the sites of crossing over.
How are homologous chromosomes different in meiosis?
In meiosis 1 the homologous chromosomes separate from each other, whereas, in meiosis 2 the sister chromatids separate. In meiosis 1 two diploid daughter cells are produced, whereas, in meiosis 2 four haploid daughter cells are produced.
What is the name of the process that separates homologous chromosomes and reduces the diploid?
Meiosis 1 separates the pair of homologous chromosomes and reduces the diploid cell to haploid. It is divided into several stages that include, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Also Read: Significance of Meiosis.
What is the name of the structure formed during separation of homologous chromosomes?
The X-shaped structures formed during separation are known as chiasmata.
How many times does DNA replication occur?
It occurs in two stages of the nuclear and cellular division as Meiosis I and Meiosis II. DNA replication occurs, however, only once . It involves the pairing of homologous chromosomes and recombination between them. Four haploid daughter cells are produced at the end, unlike two diploid daughter cells in mitosis.
How many divisions are there in meiosis?
There are two divisions in meiosis; the first division is meiosis I: the number of cells is doubled but the number of chromosomes is not. This results in 1/2 as many chromosomes per cell. The second division is meiosis II: this division is like mitosis; the number of chromosomes does not get reduced. The phases have the same names as those of mitosis.
How does meiosis reduce chromosomes?
Meiosis functions to reduce the number of chromosomes to one half. Each daughter cell that is produced will have one half as many chromosomes as the parent cell.
How many daughter cells are there in meiosis 2?
In meiosis 2, the two cells produced in meiosis 1 will now divide again to form 2 more cells bringing the total to 4 daughter cells.
What is the purpose of meiosis?
The main function of meiosis is to produce gametes (sex cells) such as the male gamete (known as Spermatozoa) and the female gametes ( ova ). The process for the production of male gametes is called Spermatogenesis, and the process of producing the female gametes is called Oogenesis. The general name for the production of gametes (both the female and male gametes) is called Gametogenesis. Whatever is going on during oogenesis or spermatogenesis is the process of meiosis. Without these cells, reproduction will not be possible. Therefore, it can occur in both animals and plants.
What is the term for a type of cell division that occurs only in sex cells or gametes?
Definition. Meiosis is a type of cell division occurring only in sex cells or gametes (such as spermatozoa and ova) that involves a single parent cell dividing to produce four daughter cells that are genetically different and each of the daughter cells having half of the number of chromosomes of the parent cell ...
What is the term for the exchange of genetic components between chromosomes in a sex cell?
Crossing over: refers to the exchange of genetic components by the chromosomes in a sex cell (gamete) before the cell division. Crossing over leads to genetic variability and occurs in the interphase and prophase 1 of meiosis. It is started in interphase and continued in prophase 1 stage.
What are the daughter cells?
Each daughter cell contains half of the parent’s number of chromosomes. This process occurs only in the sex cells which are spermatozoa and ova. These two gametes (spermatozoa and ova) differentiate to form the various cells and tissues of the body. This is the reason why they are called Germ cells ...
What are the two types of cells in the human body?
There are two types of cells in the body: the sex cells (involve in the production of the spermatozoa in males and also involved in the production of ova or eggs in females) and the somatic cells (the body cells that make up different cells and tissues of the body ).
Which phase of the chromosome is bivalent?
Bivalent chromosomes: these are chromosomes from male and female parents which normally line up to form synapsis or exchange points (chiasmata) in the prophase 1 phase.
What are the two parts of meiosis?
The process of Meiosis is divided into two parts: meiosis I and meiosis II which are further separated into Karyokinesis I and Cytokinesis I and Karyokinesis II and Cytokinesis II respectively. The preparatory steps that lead up to meiosis are similar in pattern and name to interphase of the mitotic cell cycle.
What is the longest stage of meiosis?
Prophase I is the longest stage of meiosis. During the phase of prophase, I, homologous chromosomes pair and exchange DNA (homologous recombination). This frequently results in a chromosomal hybrid. The new combination of DNA made during hybrid is a critical source of hereditary variation and result in new mixes of alleles, which might be beneficial. The combined and duplicated chromosomes are called bivalents or quadruplicates, which have two chromosomes and four chromatids, with one chromosome originating from each parent. The method of pairing the homologous chromosomes is called synapsis. At this stage, non-sister chromatids traverse at areas called chiasmata. Prophase I has historically been divided into sub-stages which are named as per the appearance of chromosomes.
What stage of meiosis do chromosomes assemble?
Chromosomes assemble further during the diakinesis stage; from Greek words signifying "moving through". This is the main point in meiosis where the four sections of the quadruplicates are really distinguishable. Regions of crossing-over entangle here, successfully covering, making chiasmata distinguishable.
How does meiosis produce gamete hereditary diversity?
Meiosis produces gamete hereditary diversity in two ways: (1) Law of Independent Assortment of homologous chromosome matches along the metaphase plate during metaphase I and introduction of sister chromatids in metaphase II, this is the resulting division of homologs and daughter chromatids during anaphase I and II, it permits an arbitrary and free distribution of chromosomes to every daughter cell (and at last to gametes); The physical trade of homologous chromosomal regions by homologous recombination during prophase I result in a new combination of DNA inside chromosomes .
How many daughter cells are there in meiosis?
Meiosis I isolate homologous chromosomes, each still made up of two sister chromatids, into two daughter cells, subsequently decreasing the chromosome number by half. In the process of meiosis II, sister chromatids decouple, and the resultant daughter chromosomes are segregated into four daughter cells. For diploid organisms, the daughter cells ...
What is the process of producing gametes?
Meiosis is the process of producing gametes—sex cells, or sperm and eggs in the human body. In a human being, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm and eggs. At the point when a sperm and an egg participate in of fertilization, the two haploid arrangements of chromosomes create a complete diploid set: another genome.
Which stage of meiosis is the sister chromatids not yet consolidated into the thickly?
• Growth 2 (G2) stage: G2 stage as observed before mitosis is absent in meiosis.