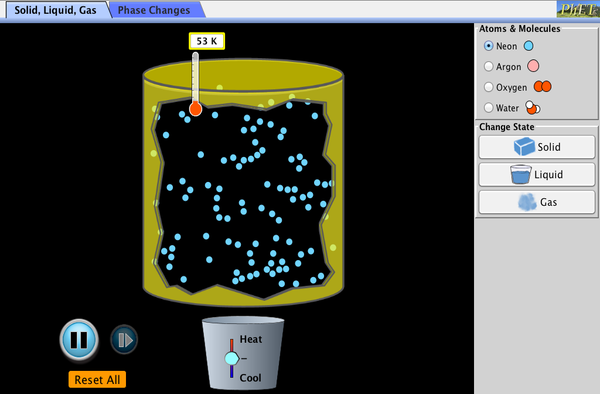
- The States of Matter. States of matter are solids, liquids, gases, and plasma. Under extreme conditions, other states exist, such as s Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter.
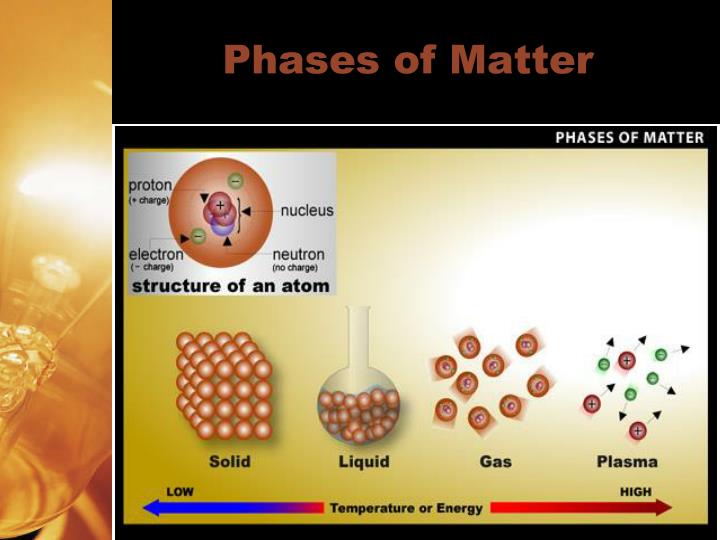
- Phases of Matter. A phase of matter is uniform with respect to its physical and chemical properties. Matter undergoes phase transitions to change from one phase to another.
- Examples. At room temperature and pressure, the state of a piece of dry ice (carbon dioxide) would be solid and gas phases.
What three states of matter can phases states exist?
The three most common phases of matter on Earth are solids, liquidsand gases. Less commonly, we can also find matter as a plasmaor Bose-Einstein (BE) condensate. Solidshave a fixed shape and volume. A solid’s particles are packed closely together. There is not much space between the particles and there is little particle movement.
What is the sixth and 7th states of matter?
Feb 15, 2014 · List of Phase Changes Between States of Matter. Melting (Solid → Liquid) Paul Taylor / Getty Images. This example shows an ice cube melting into water. Melting is the process by which a substance ... Freezing (Liquid → Solid) Vaporization (Liquid → Gas) Condensation (Gas → Liquid) Deposition (Gas → ...
What are the six changes of state of matter?
The three most common phases of matter on Earth are solids, liquids and gases. Less commonly, we can also find matter as plasma or Bose-Einstein (BE) condensate. Solids have a fixed shape and volume. A solid’s particles are packed closely together. There is not much space between the particles and there is little particle movement.
Which phase of matter is the least common on Earth?
The three fundamental phases of matter are solid, liquid, and gas (vapour), but others are considered to exist, including crystalline, colloid, glassy, amorphous, and plasma phases. When a phase in one form is altered to another form, a phase change is said to have occurred. One may also ask, are phases and states of matter the same?
What are the 4 states or phases of matter?
There are four natural states of matter: Solids, liquids, gases and plasma.Dec 13, 2021
What are the 5 phases or state of matter?
We look at five states of matter on the site. Solids, liquids, gases, plasmas, and Bose-Einstein condensates (BEC) are different states of matter that have different physical properties. Solids are often hard, liquids fill containers, and gases surround us in the air. Each of these states is also known as a phase.
What are the 3 states phases of matter?
There are three states of matter: solid; liquid and gas. They have different properties, which can be explained by looking at the arrangement of their particles.
What are the 7 different states of matter?
Matter is any thing that is made from atoms and molecules. ( Studios, 1995) . The seven states of matter that I am investigating are Solids, Liquids, Gases, Ionized Plasma, Quark-Gluon Plasma, Bose-Einstein Condensate and Fermionic Condensate. Solid Definition - Chemistry Glossary Definition of Solid.
What are the 5 phases of matter in order of increasing energy?
A notable fact about gases is that they often tend to appear in solid form until subjected to increased temperature levels. As heat (energy) is added, the solid melts and, typically, first becomes a liquid, and then, eventually, a gas. Typically, substances will go through the stages in order: solid, liquid, gas.
What are the types of phases?
The three fundamental phases of matter are solid, liquid, and gas (vapour), but others are considered to exist, including crystalline, colloid, glassy, amorphous, and plasma phases.
What are the 3 states of matter and examples?
There are three common states of matter:Solids – relatively rigid, definite volume and shape. In a solid, the atoms and molecules are attached to each other. ... Liquids – definite volume but able to change shape by flowing. In a liquid, the atoms and molecules are loosely bonded. ... Gases – no definite volume or shape.
What are the 5 phase changes?
Phase ChangesPhase ChangeNameIntermolecular Forces Increase or Decrease?solid liquidmelting or fusionincrease decreaseliquid gasvaporization or evaporationincrease decreasegas soliddepositionincrease decreasegas liquidcondensationincrease decrease3 more rows
What are the physical states of matter?
Gas can be compressed. liquid solid gas. freezing melting. evaporation condensation. sublimation deposition. These are physical states of the molecules of matter. Molecules can shift from one physical state to another without changing their molecular structure (or chemical state). Water is still H. 2.
What happens when water freezes?
When water freezes, it forms a bonded arrangement of molecules that is actually less dense than liquid water, yet takes up more space. This is an important feature of water in that when ice forms on a lake or other waterway, it is less dense than the liquid water – so forms on top of the liquid water.
Why are solids more dense than liquids?
Usually solids are more dense than liquids because their molecules are closer. Water is an important exception to this rule. When water freezes, it forms a bonded arrangement of molecules that is actually less dense than liquid water, yet takes up more space. This is an important feature of water in that when ice forms on a lake or other waterway, it is less dense than the liquid water – so forms on top of the liquid water. This allows water animals to stay alive all winter under the ice. Without this trait, many of the living things on Earth would not have survived and evolved to what we have today.
How do molecules change phase?
The six ways to change the phase (state) of matter: 1) Meltingchanges a solid to a liquid. (i.e. dripping icicles) 2) Freezingchanges a liquid to a solid.
What is the most common phase of matter?
Matter can be found in several phasesor states. The three most common phases of matter on Earth are solids, liquidsand gases. Less commonly, we can also find matter as a plasmaor Bose-Einstein (BE) condensate.
Does water change its physical state?
Water is still H. 2. 0 when it is ice, steam or a liquid – even though its physical state has changed. Physical states can be changed by adding energy(i.e. increasing temperature or pressure) or releasing energy (i.e. cooling or lowering pressure). This does not change the matter’s molecular structure.
Is there much space between particles?
There is not much space between the particles and there is little particle movement. A solid is not easily compressed. Liquidshave a fixed volume, but take the shape of the container in which they sit. There is not much space between the particles, but they can slide past each other and flow easily.
How do liquids form?
Liquids form by condensation of gases and melting of solids. Gases: Gases can ionize into plasma, condense into liquids, or undergo deposition into solids. Gases form from the sublimation of solids, vaporization of liquids, and recombination of plasma. Plasma: Plasma can recombine to form a gas.
How do states of matter change?
Another way to list phase changes is by states of matter: Solids: Solids can melt into liquids or sublime into gases. Solids form by deposition from gases or freezing of liquids. Liquids: Liquids can vaporize into gases or freeze into solids.
What is sublimation in chemistry?
Sublimation is the transition from a solid phase to a gas phase without passing through an intermediate liquid phase. Another example is when ice directly transitions into water vapor on a cold, windy winter day.
What is the opposite of evaporation?
This photo displays the process of condensation of water vapor into dew drops. Condensation, the opposite of evaporation, is the change in the state of matter from the gas phase to the liquid phase.
How many phases are there in plasma?
The most commonly known phase changes are those six between solids, liquids, and gasses. However, plasma also is a state of matter, so a complete list requires all eight total phase changes.
What is the ionization energy of an aurora?
Ionization may be observed inside a plasma ball novelty toy. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion .
What is the process of vaporization?
Vaporization, or evaporation, is the process by which molecules undergo a spontaneous transition from a liquid phase to a gas phase.
Why are solids more dense than liquids?
Usually solids are more dense than liquids because their molecules are closer. Water is an important exception to this rule. When water freezes, it forms a bonded arrangement of molecules that is actually less dense than liquid water, yet takes up more space.
How does heat change the state of matter?
The six ways to change the phase (state) of matter: 1) Melting changes a solid to a liquid. (i.e. dripping icicles) 2) Freezing changes a liquid to a solid. (i.e. lake freezing over)
What is the difference between liquid and solid?
Solids have a fixed shape and volume . A solid’s particles are packed closely together. There is not much space between the particles and there is little particle movement. A solid is not easily compressed. Liquid s have a fixed volume, but take the shape of the container in which they sit.
What are the three phases of matter?
Matter can be found in several phases or states. The three most common phases of matter on Earth are solids, liquids and gases.
Is gas a liquid or a gas?
A liquid is not easily compressed. Gas fills the shape and volume of the container in which it sits. There is a lot of free space between its particles and they flow easily past each other. Gas can be compressed. These are physical states of the molecules of matter.
When you research information, do you cite the reference?
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
Is water a physical state?
Molecules can shift from one physical state to another without changing their molecular structure (or chemical state). Water is still H 2 0 when it is ice, steam or a liquid – even though its physical state has changed.
Why do particles in a solid have low kinetic energy?
In a solid, particles are packed tightly together so they don't move much. The electrons of each atom are constantly in motion, so the atoms have a small vibration, but they are fixed in their position. Because of this, particles in a solid have very low kinetic energy. Solids have a definite shape, as well as mass and volume, ...
Why is liquid a shape?
In a liquid, the particles are more loosely packed than in a solid and are able to flow around each other, giving the liquid an indefinite shape. Therefore, the liquid will conform to the shape of its container. Much like solids, liquids (most of which have a lower density than solids) are incredibly difficult to compress.
Why do atoms clump together?
Since there is almost no kinetic energy being transferred from one atom to another, the atoms begin to clump together. There are no longer thousands of separate atoms, just one "super atom.". A BEC is used to study quantum mechanics on a macroscopic level.
What is the difference between a gas and a particle?
Gases. In a gas, the particles have a great deal of space between them and have high kinetic energy. A gas has no definite shape or volume. If unconfined, the particles of a gas will spread out indefinitely; if confined, the gas will expand to fill its container.
What is the energy that holds atoms and molecules together?
Both atoms and molecules are held together by a form of potential energy called chemical energy . Unlike kinetic energy, which is the energy of an object in motion, potential energy is the energy stored in an object.
What is the shape of a solid?
Solids have a definite shape, as well as mass and volume, and do not conform to the shape of the container in which they are placed. Solids also have a high density, meaning that the particles are tightly packed together.
What happens when a solid is heated?
Melting and freezing. When heat is applied to a solid, its particles begin to vibrate faster and move farther apart. When the substance reaches a certain combination of temperature and pressure, its melting point, the solid will begin to melt and turn into a liquid.
What is matter in science?
Updated July 03, 2019. The matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. States of matter are the physical form taken by the phases of matter. Although the state and phase don't mean quite the same thing, you'll often hear the two terms used interchangeably.
What are the primary phases of matter?
Matter undergoes phase transitions to change from one phase to another. The primary phases of matter are solids, liquids, gases, and plasma.
What are the states of matter?
States of matter are solids, liquids, gases, and plasma. Under extreme conditions, other states exist, such as s Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter. The state is the form taken by matter at a given temperature and pressure.
Who is Anne Marie Helmenstine?
Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. our editorial process. Facebook Facebook. Twitter Twitter. Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D. Updated July 03, 2019.
Is carbon dioxide a solid or gas?
At room temperature and pressure, the state of a piece of dry ice (carbon dioxide) would be solid and gas phases. At 0 °C, the state of water can be the solid, liquid, and/or gas phase. The state of water in a glass is the liquid phase. Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph.D.