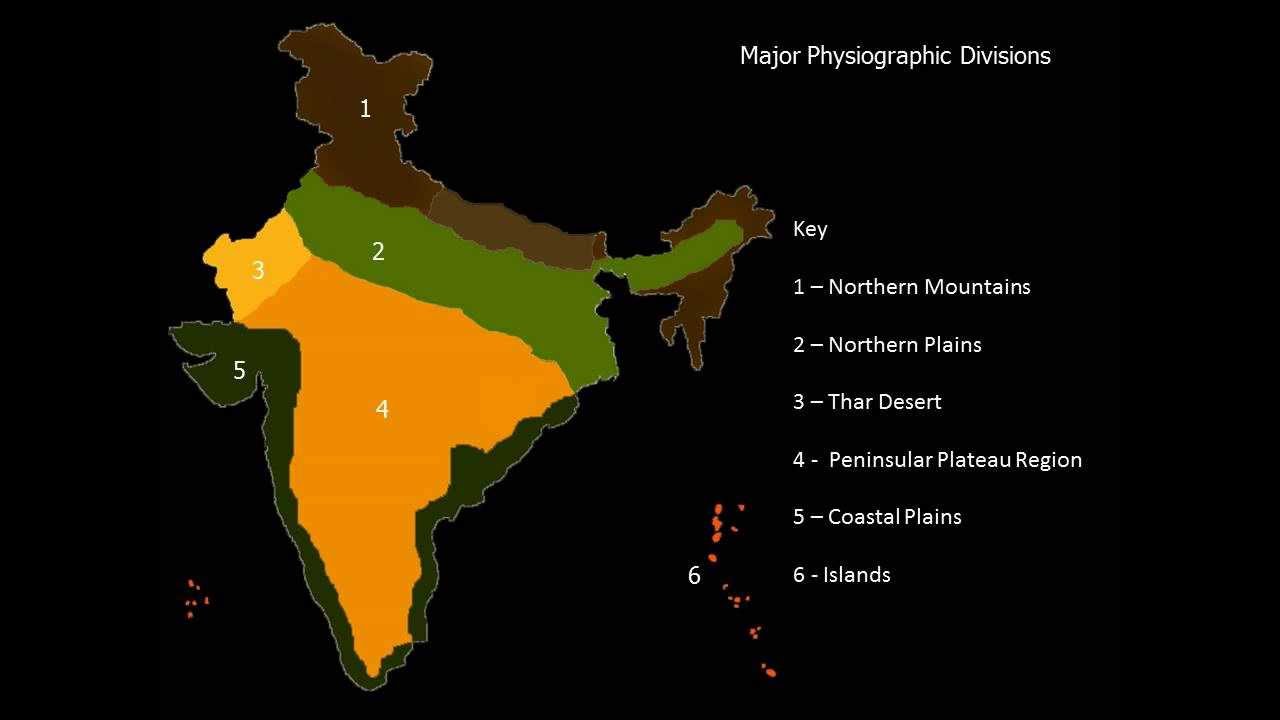
Main Physical Features of India
- Himalayan Mountains. The northernmost landscape of the country highlights the fold mountains of the Himalayas. ...
- Northern Plains. The three major river systems of India- Indus, Ganga and the Brahmaputra along with their tributaries have fed the foothills of the Himalayas.
- Peninsular Plateau. The oldest landmass of India, the Peninsular Plateau was the result of the tectonic shifts of the Gondwana Land.
- Indian Desert. The undulating sandy plains covered with sand dunes on the western fringes of the Aravali Hills comprise the Indian Desert.
- Coastal Plains. Right on the outer edges of the Indian peninsula, lies the narrow strips of the coastal plains. ...
- Islands. Two groups of islands lie on the two oceans surrounding the main landmass of the subcontinent. These most likely complete the physical features of India.
- The Himalayan Mountains. These mountain ranges run in a west-east direction from the Indus to the Brahmaputra. ...
- The Northern Plains. ...
- The Peninsular Plateau. ...
- The Indian Desert. ...
- The Coastal Plains. ...
- The Islands.
What are the 6 physiographic divisions of India?
On basis of the varied physiographic features, India is divided into six physiographic divisions: Northern and North-eastern Mountain. Northern Plain. Peninsular Plateau. Indian Desert. Coastal Plains. Islands.
What are the important physical features of India?
Oldest and most stable landmass of India, general elevation from West to East. Important physiographic features are tors, block mountains, rift valleys, spurs, bare rocky structures, series of hummocky hills and wall-like quartzite dykes offering natural site for water storage.
What are the physical features of India class 9 Geography?
CBSE Notes Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 - Physical Features of India. India has all major physical features of the earth, i.e., mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands. The land of India displays great physical variation. Geologically, the Peninsular Plateau constitutes one of the ancient land masses on the earth’s surface.
What is the physiography of India?
The physiography of India is unique and is responsible for development of distinctive features in the sub-continent. The Indian Mainland extends from 8°4′ north and 37°6′ North in length (latitudes). And between 68°7′ East and 97°25′ East in width (longitudes).

What are 6 physical features of India?
The six physical features of India are:(1) The Himalayan mountains.(2) The Northern plains.(3) Indian Desert.(4) Peninsular plateau.(5) Coastal Plains.(6) Islands.
What are the physiographic division of India Class 9?
They are: The great Himalayas, the northern plains, the peninsular plateau, the coastal plains, the Indian desert, and the Islands. All the physiographic divisions are different from each other in various contexts.
How many physical features are there in India?
Hint: India is mainly divided into 5 physical divisions, such as the northern mountainous region, north Indian plain, peninsular plateau, islands, and the coastal plain.
What are the physical features of India explain Class 9?
In fact, our country has practically all major physical features of the earth, i.e., mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands. The land of India displays great physical variation. Geologically, the Peninsular Plateau constitutes one of the ancient landmasses on the earth's surface.
What is the importance of physical features of India Class 9?
Answer. In fact, India has every possible landscape that the earth has. From cold mountains to arid deserts, vast plains, hot and humid plateau and wide sea shores and tropical islands, the physical features of India cover every terrain.
What are the main physiographic regions of India?
India can be divided into the following physiographic divisions: (i) The Northern and Northeastern Mountains (ii) The Northern Plain (iii) The Peninsular Plateau (iv) The Indian Desert (v) The Coastal Plains (vi) The Islands.
What are known as physical features?
Human and physical features are things that you can see all around you. Physical features like seas, mountains and rivers are natural. They would be here even if there were no people around. Human features are things like houses, roads and bridges. They have been built by people.
Which is the largest physiographic division of India?
The Peninsular PlateauThe Peninsular Plateau or Deccan Plateau It covers an area of about 16 lakh sq km forms the largest and oldest physiographic division of India.
What are the physiographic division of India?
India can be divided into the following physiographic divisions: (i) The Northern and Northeastern Mountains (ii) The Northern Plain (iii) The Peninsular Plateau (iv) The Indian Desert (v) The Coastal Plains (vi) The Islands. Was this answer helpful?
Which of the following is not a physiographic division of India Class 9?
Therefore, from the above discussion, we may say that the Elevated peninsula region is not a part of the Indian physiographic division.
How do different physiographic regions of India complement each other Class 9?
Answer: (i) Each region complements the other and makes the country richer in its natural resources. (ii) The northern mountains are the major source of water and forest wealth. (iii) The northern plains are the granaries of the country.
What are physical divisions of India?
The major physical divisions of India: (i) The Himalayas (ii) The Northern Indian Plains (iii) The Great Indian Desert (iv) The Peninsular Plateau (v) The Coastal plains (vi) The two groups of Islands.
How many km is the coastline of India?
Of the total coastline of India (7517 km), that of the peninsula is 6100 km between the peninsular plateau and the sea. The peninsular plateau of India is flanked by narrow coastal plains of varied width from north to south.
How many mountains are there in Satpura range?
Satpura range is a series of seven mountains (‘Sat’ = seven and ‘pura’ = mountains).
Why did the northern part of the Indian Peninsula get subsided?
Due to the uplift of the Himalayas in the Tethys Sea, the northern part of the Indian Peninsula got subsided and formed a large basin.
What are the two regions of the Himalayas?
The Regional Divisions of Himalayas – the Western and Eastern Himalayas.
What is the climatic influence of the Himalayas?
Climatic Influence – The altitude of the Himalayas, their sprawl and extension intercept the summer monsoon. They also prevent the cold Siberian air masses from entering into India.
How many zones are there in the Northern Plains?
From the north to the south, the northern plains can be divided into three major zones:
What is the width of the Western Coastal Plains?
1. Extent: The Western Coastal Plains are a thin strip of coastal plains with a width of 50 km between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats.
What are the physical features of India?
V. Coastal Plains – Physical features of India: The coastal plains in India are situated parallel to the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal. On the basis of location and active geomorphic processes, it is divided into Western and eastern Coastal Plains. 1.
What are the features of India?
Important physiographic features are tors, block mountains, rift valleys, spurs, bare rocky structures, series of hummocky hills and wall-like quartzite dykes offering natural site for water storage.
What are the two major rivers in the Himalayas?
Darjiling and Sikkim Himalayas: It consists of Nepal Himalyas in the west and Bhutan himalyas in east. Though this part is small but significant. Tista is the fast flowing river here. Kanchenjunga peak (Kanchengiri) and deep valleys. Lepcha tribes in high up regions. This area is characterised by absence of Shiwalik formations. In place of them, there are ‘duar formations’ which are useful for tea garden development.
What is the northernmost part of Himachal?
The Northernmost part of Himacahl Himalayas is an extension of ladakh cold desert, in Spiti sub-division of Lahul and Spiti. It consists of Great Himalayan, the Lesser Himalayas and Shiwalik range from north to south, locally called Dhaoladhar in Himachal Pradesh and Nagtibha in Uttarakhand. ‘Shiwalik’ and ‘Dun formations’ are features of this part of Himalayas. All five Prayags are located here.
What direction are the Himalayas?
The general orientation of great Himalayas is from North-west to Southwest direction (in Northwestern region). In Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram, the himalyas are oriented in North-South direction. Himalyas are physical as well as Climatic, drainage and cultural divide.
What is the physiography of India?
The physiography of India is unique and is responsible for development of distinctive features in the sub-continent. The Indian Mainland extends from 8°4′ north and 37°6′ North in length (latitudes). And between 68°7′ East and 97°25′ East in width (longitudes). This makes the North-south extension of 3214 km and East-west extension of 2933 km.
What are the two major islands in India?
The Islands in India : In the physiography of India, there are two major Island groups. They are in Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea. The Bay of Bengal Island group are 204 in number known as Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The Andaman is in North and Nicobar is in South of each other, they are separated by “Ten degree Channel”.
Why are the physical features of India important?
The diverse physical features of India have immense future possibilities of development because of the following reasons. The mountains are the major sources of water and forest wealth. The northern plains are the granaries of the country. They provide the base for early civilisations.
What are the most recent landforms in India?
Geologically, the Peninsular Plateau constitutes one of the ancient land masses on the earth’s surface. The Himalayas and the Northern Plains are the most recent landforms. The northern plains are formed of alluvial deposits. The CBSE Notes Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 on Physical Features ...
What is the outermost range of the Himalayas?
The outermost range of the Himalayas is called the Shiwaliks. These ranges are composed of unconsolidated sediments. The longitudinal valley lying between lesser Himalaya and the Shiwaliks are known as Duns. DehraDun, Kotli Dun and Patli Dun are some of the well-known Duns.
What is the role of the plateau in India?
They provide the base for early civilisations. The plateau is a storehouse of minerals, which has played a crucial role in the industrialisation of India. The coastal region and island groups provide sites for fishing and port activities. We hope CBSE Notes for Class 9 Geography helped you in your studies.
Which mountain range is the easternmost boundary of the Himalayas?
Beyond the Dihang gorge, the Himalayas bend sharply to the south and spread along the eastern boundary of India, which is known as the Purvachal or the Eastern hills and mountains.
How many regions are there in the Northern Plains?
According to the variations in elevation points, the Northern plains can be divided into 4 regions.
How is the Northern Plain formed?
The northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the 3 major river systems – the Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra along with their tributaries. It spreads over an area of 7 lakh sq. km.
How many lakes are there in India?
India also has a variety of lagoons and other bodies of water associated with coastal environments as well as over sixty lakes.
What are the wetlands in India?
Wetlands in India include the Chandertal Wetland in Himachal Pradesh, the Keoladeo National Park in Rajasthan, and the Bandhavgarh National Park in Madhya Pradesh, which contains wetlands that are famous for their swamp tigers (aka Bengal tigers). Plateaus, Plains & Deserts.
What are some examples of mountain ranges?
Here are three examples of major mountain ranges: The Himalayas: Mount Everest is the highest peak in the Himalayas with an elevation of 29,035 feet; the Himalaya's lie to the north and sit on India's border with the country of Nepal. The Western Ghats: Anai Mudi is the highest peak in the Western Ghats at 8,842 feet above sea level ...
What is the Lakshadweep Islands?
Lakshadweep Islands (Arabian Sea), an archipelago with only a few inhabited islands. Visitors are limited and must have permits. Lesson Summary. India is a land of diverse geography. India is surrounded by three large bodies of water with nearly 4,350 miles of coastline. India also has many lakes, wetlands, and rivers.
Which river is the longest in India?
The longest river that is completely within India's borders is the Ganga (Ganges), which has a length of approximately 1,560 miles. However, the longest river in India that spans the borders of other countries is the Indus River, which is around 2,000 miles long. The Ganges River Delta separates India from Bangladesh and is formed by ...
Where is Anai Mudi?
The Western Ghats: Anai Mudi is the highest peak in the Western Ghats at 8,842 feet above sea level and is located near India's western coast on the Arabian Sea.
Which river separates India from Bangladesh?
The Ganges River Delta separates India from Bangladesh and is formed by the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers and associated streams. It is the largest delta of its kind in the world.
What are the physiographic units of India?
On the basis of origin and structure, the Indian sub-continent can be divided into five physiographic units: 1. The Himalayas 2.
Which river forms the plain of India?
The vast plain of India, between the Himalayas to the north and the peninsular plateau to the south is formed by the Indus-Ganga-Brahmaputra Rivers. The surface of the plain has resulted by the works of Himalayan Rivers.
How many phases did the Himalayas develop?
Geological studies reveal that the Himalayas came into the present stage as results of the development during three geological phases or epoch. During the first phase, the middle Himalayan range was raised during the Oligocene Epoch or era. This range is formed of the old crystalline and old sedimentary rocks.
What are the relief features of the Himalayas?
The relief features of the Himalayas exhibit striking youthfulness. A complex nature of folding and deformation of the strata has taken place in this region. The mountains are of tectonic origin, with deep river valleys, gorges, and waterfalls.
How long is the Himalayas?
It has been recognised as a natural guard on the north of the sub-continent. The total length of the Himalayas is about 2415 kilometres and is considered to have consisted of four main sections separated by the gorges of different rivers. The Himalayas is the highest mountain range in the world.
What are the tilted beds of the lake deposits of Kashmir called?
The occurrences of the tilted beds of the lake deposits of Kashmir are called the Karewas. This clearly suggests that the Himalayas were in the process of uplift as late as the Pliocene era. Fossils of some mammals of Post—Tertiary era have been also found in the foothills of the sub-Himalayan region.
How were the Himalayan mountains formed?
The Himalayan Mountain ranges were formed by the sediment collected on the bed of the Tethys Sea for millions of years. The sediments might have been derived from the two stable land masses—Angara land to the north and peninsular landmass to the south.
What is the coastal plain of India?
The coastal plains in India run parallel to the Arabian Sea & Bay of Bengal alongthe Peninsular Plateau.The western coastal plain is a narrow belt along the Arabianseaestern of about coastal 10-20km plains wide. comprises It stretches of three from sectors Rann (i) of Kachchhonkan C to astKanyaKumari. (Mumbai to
How many islands are there in India?
India has two main groups of Islands. There are 204 islands in Bay of Bengal calledas Andaman and Nicobar islands and 43 islands in Arabian Sea called asLakshadweep islands The Andaman & Nicobar island extend from north to southin Bay of Bengal. They are bigger in size. An active volcano is located on the BarrenIsland in Andaman & Nicobar group of islands. Lakshadweep islands are locatednear Malabar coast of Kerala in the Arabian sea. They cover an area of 32 sq km.Kavarati is the capital of Lakshdweep. Thes These islands islands are areimportant formed tourist by corals attraction and