What is the difference between primary and secondary lymphoid organs?
• Primary lymphoid organs are the thymus and bone marrow, whereas secondary lymphoid organs are the lymphoid nodes, Peyer’s patches, tonsils, adenoids and spleen. • Primary lymphoid organs are the site of maturation for T and B cells, whereas secondary lymphoid organs are the sites of cell function for mature T and B cells.
What is lymphoid tissue and where is it found?
The most highly organized lymphoid tissues are in the thymus and lymph nodes, which are well-defined encapsulated organs with easily identifiable architectures. In the spleen (a soft, purplish organ lying high in the abdomen), the lymphoid tissue is a cylinder of loosely organized cells surrounding small arteries.
What is a primary lymphoid organ in a human?
The primary (or central) lymphoid organs generate lymphocytes from immature progenitor cells. The thymus and the bone marrow constitute the primary lymphoid organs involved in the production and early clonal selection of lymphocyte tissues.
What is primary lymphoid organ?
The primary lymphoid organs or central are the organs responsible for creating a specialized microenvironment for the production of cells of the immune system and blood (hematopoiesis) and for the maturation of lymphocytes, where they acquire specific receptors that enable them to respond to an antigen. The primary lymphoid organs are the bone marrow and the thymus.

What are the secondary lymphoid tissues?
Secondary lymphoid organs (SLOs) include lymph nodes (LNs), spleen, Peyer's patches (PPs) and mucosal tissues- the nasal associated lymphoid tissue (NALT), adenoids, and tonsils.
What are the four types of lymphoid tissue?
The histological structure of four different types of secondary lymphoid tissue; lymph nodes, tonsils, Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue and the spleen, and how their structure is adapted to their different functions. The involvement of the lymphoid tissues in some common medical conditions.
How many primary lymphoid organs are there?
two primary lymphoid organsThere are only two primary lymphoid organs – the thymus and the bone marrow (bursa analogue). These are the sites where immature T and B cells, respectively, mature before they leave to circulate through the body to interact with their cognate antigen in the secondary lymphoid organs.
What are the major cell types of lymphoid tissue?
The most common cell type in the lymphoid tissue is the lymphocyte. Like macrophages, lymphocytes are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and then circulated in the blood to the lymphoid tissue. T lymphocytes mature in the thymus before proceeding to the other lymphoid organs, such as the spleen.
What are the 7 main parts of the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system is a network of very small tubes (or vessels) that drain lymph fluid from all over the body. The major parts of the lymph tissue are located in the bone marrow, spleen, thymus gland, lymph nodes, and the tonsils. The heart, lungs, intestines, liver, and skin also contain lymphatic tissue.
What is the majority of secondary lymphoid tissue?
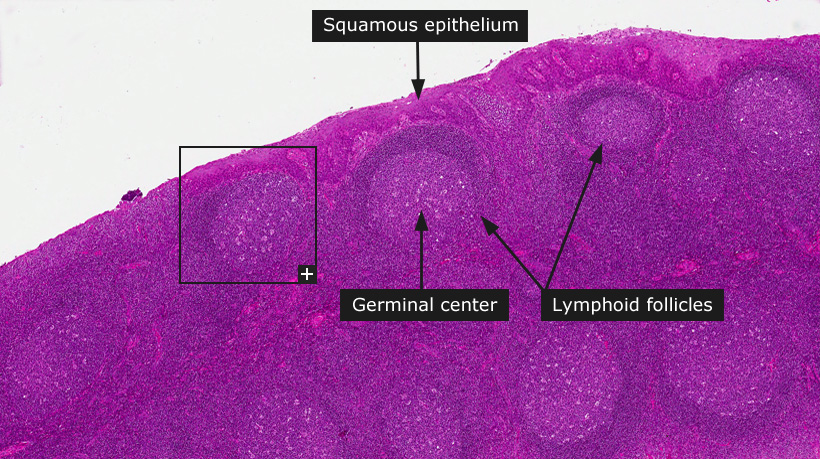
Secondary lymphoid tissue provides the environment for the antigens to interact with the lymphocytes. It is found mainly in the lymph nodes, but also in the lymphoid follicles in tonsils, Peyer's patches, spleen, adenoids, skin, and other areas associated with the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT).
Is malt a primary lymphoid tissue?
Primary lymphoid organs (bone marrow and thymus) and. Secondary lymphoid organs (including the spleen, lymph nodes, and MALT)
Which of the following is not a primary lymphoid organ?
So, the correct option is 'Appendix'.
Is liver a primary lymphoid organ?
The liver primarily operates as a metabolic center to maintain homeostasis that includes processing of gut-derived nutrients, the clearance of toxins, and the production of the bile (1). Besides these well-known functions, it is also considered as a lymphoid organ (2).
What is the lymphoid tissue made of?
It consists of connective tissue formed of reticular fibers, with various types of leukocytes (white blood cells), mostly lymphocytes enmeshed in it, through which the lymph passes. Regions of the lymphoid tissue that are densely packed with lymphocytes are known as lymphoid follicles.
What is the difference between primary and secondary lymphoid centers in the human body?
The main difference between primary and secondary lymphoid organs is that primary lymphoid organs allow the lymphoid stem cells to proliferate, differentiate, and mature whereas secondary lymphoid organs allow lymphoid cells to become functional.
What are the 4 main functions of the lymphatic system?
They include protecting your body from illness-causing invaders, maintaining body fluid levels, absorbing digestive tract fats and removing cellular waste.
What type of connective tissue is lymphoid tissue?
Lymphoid tissue is not one of the primary or basic tissue types of the body but is a variety of connective tissue or, in the case of the thymus, epithelial tissue. Lymphoid tissue is divided into central and peripheral types, which are either encapsulated or unencapsulated.
What are the functions of the lymphoid tissues?
Lymphoid tissues are found in all vertebrates and are essential for adaptive immunity. Primary lymphoid tissues (thymus, fetal liver and bone marrow) nurture lymphocyte development, whereas secondary lymphoid organs support lymphocyte maturation, survival and activation.
How many types of lymph nodes are there?
Lymph nodes are clustered throughout the body, including the neck (cervical lymph nodes), groin (inguinal lymph nodes), armpits (axillary lymph nodes). There are also internal lymph nodes in the abdomen (mesenteric and retroperitoneal), chest cavity (mediastinal), and lower abdomen (pelvic).
What are the primary lymphoid organs?
The primary lymphoid organs are the bone marrow and the thymus. Once the cells are produced in the bone marrow and have completed their maturation process in the marrow itself or in the thymus, they are ready to be directed towards the secondary lymphoid organs. This is how vertebrate organisms have developed a ubiquitous and specialized tissue ...
Which organ is responsible for the production of cells in the immune system?
The primary lymphoid organ or central are the organ reponible for creating a pecialized microenvironment for the production of cell of the immune ytem and blood (hematopoiei) and for the maturation of.
Why is the thymus important?
The thymus is an important organ from the first years of life for the development of a successful immune function. This organ maintains homeostasis by controlling defense and permanent vigilance functions. It is able to remotely control the functioning of secondary or peripheral lymphoid organ tissues through thymic hormones.
How are self-reactive B lymphocytes eliminated?
Self-reactive B lymphocytes are eliminated by apoptosis. Those that survive are carried by the circulation to the secondary lymphoid organs where they are activated and come into contact with some foreign antigen.
What are the two compartments of bone marrow?
In the bone marrow two compartments are clearly distinguished: the vascular and the hematopoietic.
Which cells are able to interact with their own tissue?
Both lymphocytes and dendritic cells express gene-encoded determinants of the major histocompatibility system on their surfaces, which allow intimate contact between them. In this process, T cells capable of reacting with their own tissue are detected through a process called negative selection.
What is the immune system?
This is how vertebrate organisms have developed a ubiquitous and specialized tissue and cellular system, strategically distributed throughout the body, known as the immune system . The classification of the organs that are part of this system has been established according to their functions.
Primary Lymphoid Organs
They are the centers of the immune system where lymphocyte development and maturation occur i.e., they are responsible for lymphocyte proliferation, differentiation, and maturation. Therefore, the initial cells in the primary lymphoid organs are the undifferentiated stem cells in the lymphoid.
Secondary Lymphoid Organs
They are the locations of the immune system, where lymphocytes are functionally specialized by allowing them to come into contact with different antigens. Hence, secondary lymphoid organs form an array of filters to collect antigens, which always track the contents of the extracellular fluid including blood, tissue fluid, and lymph.
Things to Remember
Lymph fluids are formed when the interstitial fluid is collected through tiny lymph capillaries located throughout the body.
Intravital three-photon microscopy allows visualization over the entire depth of mouse lymph nodes
Choe and colleagues show that intravital three-photon microscopy can be used to visualize the popliteal LN in…
Single-cell transcriptional profiling of splenic fibroblasts reveals subset-specific innate immune signatures in homeostasis and during viral infection
Joern Pezoldt et al. analyze mouse spleen fibroblasts using single cell RNA sequencing, revealing 11 distinct…
Specialized transendothelial dendritic cells mediate thymic T-cell selection against blood-borne macromolecules
T cells are selected in the thymus, through interaction with self-antigens, to remove autoreactive cells. Here…
T-bet and RORα control lymph node formation by regulating embryonic innate lymphoid cell differentiation
Romagnani and colleagues discover an unexpected role for T-bet and RORα during embryonic ILC function and…
Inflammatory stromal cells in the myeloma microenvironment
Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies an inflammatory subpopulation of mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with multiple myeloma.
Gremlin neighbours for DCs
A paper in Nature Immunology describes a new subset of fibroblastic reticular cells, defined by expression of…
Lymphoid stromal cells pro Grem dendritic cell homeostasis
Single-cell technologies reveal the building blocks of secondary lymphoid organs, identifying Grem1 + fibroblastic…
Which organ is the main lymphoid organ?
ADVERTISEMENTS: (a) Bone Marrow: It is the main lymphoid organ, where all the lymphocytes and all the body cells are produced and T-lymphocytes are developed. (b) Thymus: It is a lobed organ, located near the heart and beneath the breast bone.
Which organs are also part of the secondary lymphoid organs?
Peyer’s patches of small intestine and appendix are also some of the secondary lymphoid organs. (a) Spleen: It is a large bean-shaped organ containing lymphocytes and phagocytes. It filters the blood by trapping the pathogens in it. ADVERTISEMENTS: (b) Lymph Nodes:
What is the function of lymph nodes?
Their function is to trap the microorganisms or other antigens, that enter the lymph and tissue fluid. Therefore, the antigens trapped in the lymph nodes are responsible for the activation of lymphocytes present there and cause the immune response. (c) Mucosal Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT):
Which organelle provides micro-environments for the development and maturation of T-lymphocytes?
Both bone marrow and thymus provide micro-environments for the development and maturation of T-lymphocytes.
What organs differentiate into antigen sensitive lymphocytes?
Primary Lymphoid Organs: In primary lymphoid organs, immature lymphocytes differentiate to mature ones into an antigen sensitive lymphocytes and after maturation, lymphocytes migrate to secondary lymphoid organs.