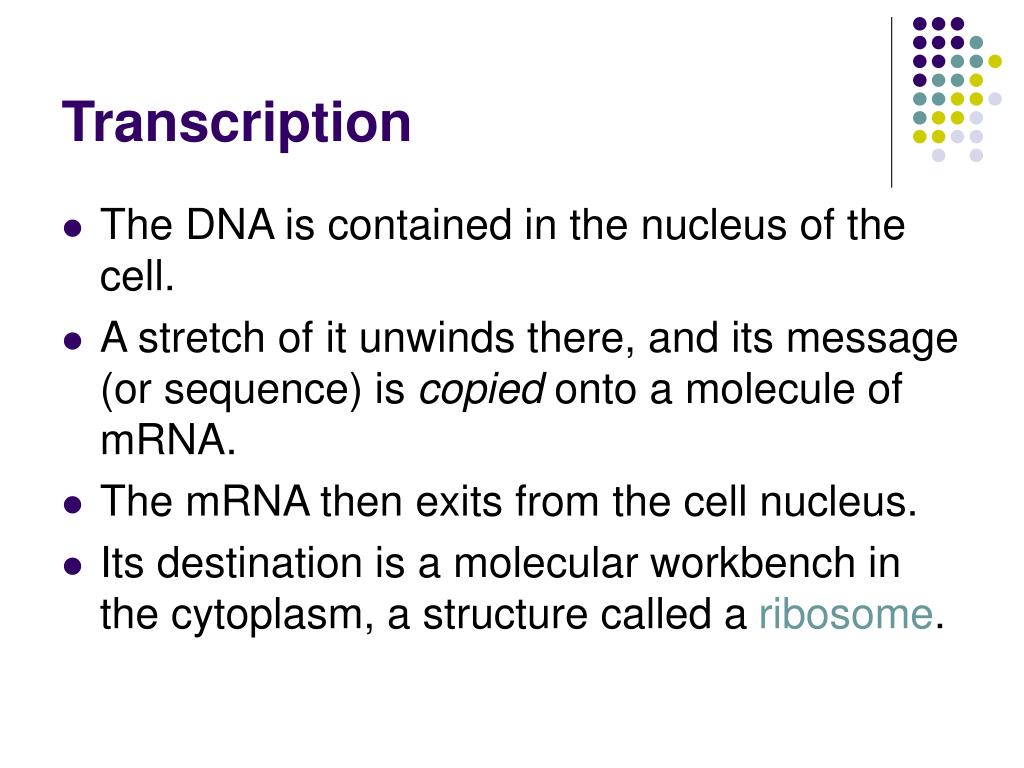
What are the 4 steps in the process of transcription?
Transcription is the name given to the process in which DNA is copied to make a complementary strand of RNA. RNA then undergoes translation to make proteins. The major steps of transcription are initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination.
What are the three processes of transcription?
Transcription is performed by enzymes called RNA polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an RNA strand (using a DNA strand as a template). Transcription has three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination.
What are the processes of transcription and translation?
Transcription is the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template where the code in the DNA is converted into a complementary RNA code. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mRNA template where the code in the mRNA is converted into an amino acid sequence in a protein.
How many stages does transcription have?
This process is divided into 3 stages: initiation, elongation Elongation Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) , and termination. Transcription begins at a region known as the promoter. An enzyme called RNA.
What begins the process of transcription?
The process of transcription begins when an enzyme called RNA polymerase (RNA pol) attaches to the template DNA strand and begins to catalyze production of complementary RNA.
What are the 6 steps of transcription?
These steps are also involved in DNA replication.Initiation. Transcription is catalysed by the enzyme RNA polymerase, which attaches to and moves along the DNA molecule until it recognises a promoter sequence. ... Elongation. ... Termination. ... 5' Capping. ... Polyadenylation. ... Splicing.
What is the process of translation?
Listen to pronunciation. (trans-LAY-shun) In biology, the process by which a cell makes proteins using the genetic information carried in messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA is made by copying DNA, and the information it carries tells the cell how to link amino acids together to form proteins.
What is the process of transcription and translation in protein synthesis?
Cell uses the genes to synthesize proteins. This is a two-step process. The first step is transcription in which the sequence of one gene is replicated in an RNA molecule. The second step is translation in which the RNA molecule serves as a code for the formation of an amino-acid chain (a polypeptide).
What is the process of translation?
Listen to pronunciation. (trans-LAY-shun) In biology, the process by which a cell makes proteins using the genetic information carried in messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA is made by copying DNA, and the information it carries tells the cell how to link amino acids together to form proteins.
What are the steps of transcription in prokaryotes?
The mechanism of transcription in prokaryotes typically occurs in three stages: initiation elongation and termination. Through the help of both DNA and mRNA, a pre mRNA molecule, which is then transformed into a mature mRNA molecule, is formed.
What are the 6 steps of transcription?
These steps are also involved in DNA replication.Initiation. Transcription is catalysed by the enzyme RNA polymerase, which attaches to and moves along the DNA molecule until it recognises a promoter sequence. ... Elongation. ... Termination. ... 5' Capping. ... Polyadenylation. ... Splicing.
What is the process of translation in DNA?
Translation is the process that takes the information passed from DNA as messenger RNA and turns it into a series of amino acids bound together with peptide bonds.