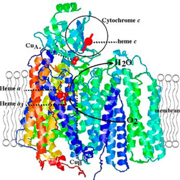
Electron transport is vital in both PHOTOSYNTHESIS and AEROBIC RESPIRATION:
- photosynthesis. Two ET systems are utilized during the LIGHT REACTIONS in the grana of the chloroplasts. ...
- aerobic respiration. A molecule of NADH from GLYCOLYSIS or the KREBS CYCLE is passed to the cristae of mitochondria where it is oxidized in the respiratory ETS, the final products being water and three molecules of ATP (= OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION ). ...
What byproduct is created during the electron transport chain?
Electron Transport Chain Products. During the course of the electron transport chain, only two things are really created. First, water is created as the electron transport chain deposits spent electrons into new water molecules. These water molecules can be reabsorbed by the body for use elsewhere or can be dispelled in the urine. Second, while ...
What are the Inhibitors of electron transport?
Inhibitors of Electron Transport
- It is the non-toxic inhibitors of Electron transport chain.
- These compounds extracted from roots of tropical plant Derris elliptica and Lonchoncarpus nicou.
- It binds at Complex I between Fe-S protein and Ubiquinone.
- This is non-toxic to mammals because poorly absorbed. Shows the toxic effect in fishes.
What is the source of energy in electron transport?
The most direct source of energy is the last complex of the electron transport chain wherein the proton gradient goes to the complex called the ATP synthase and produce ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
How many ATP are produced in the electron transport system?
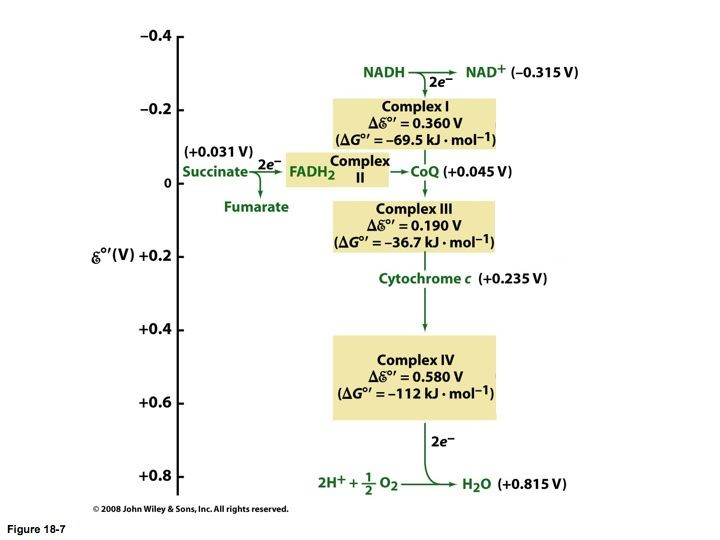
This yields about three ATP molecules. Because FADH 2 enters the chain at a later stage (Complex II), only six H + ions are transferred to the intermembrane space. This accounts for about two ATP molecules. A total of 32 ATP molecules are generated in electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation.
What are the products and reactants of the ETC?
Quiz: What are the initial reactants which start the electron transport chain?Answer 2 hydrogen ions and 2 electrons start the chain. Oxygen and ADP are also reactants.What are the final products of the chain?Answer 3 ATP and a water molecule are products.
What is produced in an electron transport chain?
The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes and electron carrier molecules within the inner membrane of mitochondria that generate ATP for energy.
How many ATP are produced from etc?
30-32 ATP moleculesThe electron transport chain is located on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. The electron transport cycle yields around 30-32 ATP molecules, according to current studies.
Is any ATP produced in the electron transport chain?
Yes, maximum ATP produced during aerobic respiration is by the electron transport chain. The process is called oxidative phosphorylation.
What does the electron transport chain produce in cellular respiration?
The electron transport chain is the last stage of the respiration pathway. It is the stage that produces the most ATP molecules.
How many FADH2 are produced in the electron transport chain?
2.5 ATP/NADH and 1.5 ATP/FADH2 are produced in the electron transport chain. Some resources will say 3 ATP/NADH and 2 ATP/FADH2, but these values are generally less accepted now.
Which process produces both NADH and FADH2?
the citric acid cycleThe process that produces both NADH and FADH2 is the citric acid cycle, the second step in aerobic cellular respiration.
How is water produced in the electron transport chain?
Toward the end of the electron transport chain, the hydrogen from the coenzymes meets the oxygen that the cell has consumed and reacts with it to form water. In this way, water is created as a byproduct of the metabolism reaction.
Q.1. How many protons are required to form 1 ATP molecule?
Ans: When 2 protons get a release from the F0-F1 complex present in the inner mitochondrial membrane, 1 ATP is formed.
Q.2. How many complexes are there in an electron transport system in mitochondria?
Ans: There are five complexes in an Electron transport system embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Q.3. What is Light Reaction?
Ans: The light reaction is the first reaction in which light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules present in the reaction centre of the phot...
Q.4. In which layer of mitochondria, the Electron Transport System takes place?
Ans: The electron transport system takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
What is the electron transport chain and why is it important?
The electron transport chain is a series of oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. This process results in the formation of ATP, an important sourc...
What happens in the electron transport chain?
In the electron transport chain, electrons are transferred from one protein complex to another on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. As this o...
What is the structure of the electron transport chain?
The electron transport chain is located on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. There are five protein complexes spanning the membrane. Theses p...
What is the function of the electron transport chain?
The basic function of the electron transport chain is to move protons into the intermembrane space. ATP synthase, which is not part of the process, is also located on the mitochondrial inner membrane. This complex will use the electrochemical gradient of the protons to essentially extract energy from the pressure of the protons wanting to cross ...
Which complex transfers electrons to the final protein in the electron transport chain?
This allows for new electrons to be added, part of the reason the process is called a chain. Cytochrome C is the complex which transfers the electrons to the final protein in the electron transport chain. Complex IV has a unique function both pumping hydrogen ions as well as depositing the electrons on a final electron acceptor.
How are water molecules created in the electron transport chain?
First, water is created as the electron transport chain deposits spent electrons into new water molecules. These water molecules can be reabsorbed by the body for use elsewhere or can be dispelled in the urine.
How do electron carriers get their energy?
Electron carriers get their energy (and electrons) from reactions during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. These reactions release energy from molecules like glucose by breaking the molecules in smaller pieces and storing the excess energy in the bonds of the recyclable electron carriers.
Why does the electron transport chain stop?
This can happen from two basic scenarios. The electron transport chain can stop because it does not have a source of electrons, or it can stop because it can no longer pass electrons on. The first scenario would be caused by something like starvation.
Where do electron carriers go in the electron transport chain?
These carriers are then transported to the inner mitochondrial membrane, where they can interact with the proteins of the electron transport chain. These carriers dump their electrons and stored energy in complexes I and II. These protein units relieve the electron carriers of excess hydrogen atoms. The electrons stay with the proteins, while the hydrogen atoms are left in the matrix. The electrons from these bonds pass through complexes I and II, through coenzyme Q. This specialized protein functions solely in passing electrons from these complexes to complex III.
Which step in oxidative phosphorylation is the electron transport chain?
The electron transport chain is a crucial step in oxidative phosphorylation in which electrons are transferred from electron carriers, into the proteins of the electron transport chain which then deposit the electrons onto oxygen atoms and consequently transport protons across the mitochondrial membrane.
What are electron carriers used for?
Finally, in the electron transport chain, the electron carriers were used to donate electrons and protons that turned oxygen molecules into water and created the remainder of the 32 ATP molecules - all from one glucose molecule. Lesson Summary.
What is the last stair in the electron transport chain?
The last 'stair' of the electron transport chain is oxygen. You were wondering when we were going to use that, right? A single oxygen molecule accepts two electrons and two protons from the final protein complex. This produces a molecule of water. Why do all of us need oxygen? To complete cellular respiration!
How many ATP molecules are produced in cellular respiration?
Let's bring all this back to our formula for cellular respiration in order to summarize the reactants and products from the process as a whole. One glucose molecule was broken down in glycolysis to net two ATP molecules and electron carriers. Pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle produced two more ATP molecules, more electron carriers, and six molecules of carbon dioxide. Finally, in the electron transport chain, the electron carriers were used to donate electrons and protons that turned oxygen molecules into water and created the remainder of the 32 ATP molecules - all from one glucose molecule.
How does ATP synthase work?
Pumping all these protons outside across the inner membrane of the mitochondria creates a high concentration of protons between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes and, therefore, a concentration gradient of protons. In the last step of the electron transport chain, an enzyme called ATP synthase is used. This is a channel protein in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The protons flow through this pump at max speed, back into the mitochondrial matrix; this causes part of the enzyme to spin in circles like a whirling dervish. This spinning motion provides the final dance and song number of cellular respiration. ATP synthase catalyzes the phosphorylation of ADP, creating the last 28 molecules of ATP. How's that for a final act?
What proteins are oxidized?
NADH + H+ and FADH2 become oxidized, donating electrons to the first and second protein complex respectively. These complex proteins now become electron carriers themselves and are now reduced. They become oxidized as they pass these electrons down the electron transport chain.
What is the process that converts food into chemical energy?
You can think of the steps of cellular respiration as the opening acts to the main event. We've been doing a dance of cellular respiration for a few lessons now, building up to the finale. Remember that cellular respiration is the process that converts food into chemical energy.
Where are protons pumped to?
They are pumped to the other side of the inner mitochondrial membrane through the protein complexes I, III, and IV. They are moved by active transport from the mitochondrial matrix to the space between the inner membrane and outer membrane of the mitochondria. They do this by using the energy derived from the electrons that flow down the electron transport chain stairs.
What is the electron transport system?
Definition of Electron Transport System. It refers to the mechanism of cellular respiration that occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It is the third and last stage of cellular respiration. Electron transport chain or Respiratory chain is the alternative terms of the electron transport system. ETS follows an aerobic pathway.
What is the mechanism of electron transport?
The electron transport chain sometimes refers to the “ Respiratory chain ”, which is the third or final stage of cellular respiration. It requires the presence of oxygen to carry out cellular respiration. The energy is produced during the transfer of electrons from one carrier to the other.
How do electrons pass from one complex to the other?
Electrons pass from one complex to the other by redox reactions. The free energy during electron transfer is captured as a proton gradient and used up by the ATP synthase to derive ATP. The electron carrier Co-Q receives the electrons formed by the reduction of FADH 2 and NADH.
How does ETS work?
ETS involves electron transfer through a series of protein complexes from higher (NADH +) to lower energy state (O 2) by releasing protons into the cytosol. A movement of proton or H + from a matrix to cytosol generates a proton motive force and creates an electrochemical gradient.
How is energy produced in a cell?
The energy is produced during the transfer of electrons from one carrier to the other. A cell harnesses the energy loss during electron transport to pump protons into the cytosol. It creates a chemiosmotic gradient. A chemiosmotic gradient becomes charged by the potential energy of the electrons.
What are the steps of the electron transport chain?
The electron transport system can be summarized into the following steps: Step 1: Generation of proton motive force. In the first step of the electron transport chain, the NADH + and FADH 2 molecule of glycolysis and Kreb’s cycle is oxidized into NAD + and FAD, respectively, along with the release of high energy electrons and protons.
How many ATP molecules are produced in the electron transport chain?
In the electron transport chain, per molecule of glucose can produce 34 molecules of ATP, as given in the equation below: Thus, the net production of energy in the electron transport chain is 34 ATP molecules.
Where does the electron transport system occur?
Electron Transport System. The electron transport system occurs in the cristae of the mitochondria, where a series of cytochromes (enzymes) and coenzymes exist. These cytochromes and coenzymes act as carrier molecules and transfer molecules. They accept high-energy electrons and pass the electrons to the next molecule in the system.
What is the final electron acceptor in cellular respiration?
In cellular respiration, the final electron acceptor is an oxygen atom. In their energy-depleted condition, the electrons unite with an oxygen atom. The electron-oxygen combination then reacts with two hydrogen ions (protons) to form a water molecule (H 2 O). The role of oxygen in cellular respiration is substantial.
How many protons are transported by NADH?
Each NADH molecule is highly energetic, which accounts for the transfer of six protons into the outer compartment of the mitochondrion.
What is the electron transport system?
The Electron Transport System also called the Electron Transport Chain, is a chain of reactions that converts redox energy available from oxidation of NADH and FADH 2, into proton-motive force which is used to synthesize ATP through conformational changes in the ATP synthase complex through a process called oxidative phosphorylation.
Which chain of enzymes catalyzes the transfer of electrons through different electron carriers to the molecular?
A chain of four enzyme complexes is present in the electron transport chain that catalyzes the transfer of electrons through different electron carriers to the molecular oxygen.
What is the final step in the electron transfer chain?
The final step in the electron transfer chain is catalyzed by complex IV (cytochrome oxidase) where electrons are transferred from cytochrome c to molecular oxygen. Since two electrons are required to reduce one molecule of oxygen to water, for each NADH oxidized half of oxygen is reduced to water.
How many electrons does each cytochrome transfer?
Each cytochrome transfers one electron each and thus two molecules of cytochrome are reduced for the transfer of electrons for every NADH oxidized.
What is the name of the electron carrier that is not bound to a protein?
Ubiquinone (Co-enzyme-Q) Between the flavoproteins and cytochromes are other electron carriers termed ubiquinone (UQ). Ubiquinone is the only electron carrier in the respiratory chain that is not bound attached to a protein. This allows the molecule to move between the flavoproteins and the cytochromes.
How many sets of electron transport chains are there in the mitochondria?
The number of electron transport chains in the mitochondria depends on the location and function of the cell. In the liver mitochondria, there are 10, 000 sets of electron transport chains while the heart mitochondria have three times the number of electron transport chain as in the liver mitochondria.
Which complex in the electron transport chain is formed of NADH dehydrogenases and the Fe-S centers?
Complex I in the electron transport chain is formed of NADH dehydrogenases and the Fe-S centers that catalyzes the transfer of two electrons from NADH to ubiquinone (UQ).
Where Does the Electron Transport Chain Occur?
During the process, a proton gradient is created when the protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space of the cell, which also helps in driving ATP production. Often, the use of a proton gradient is referred to as the chemiosmotic mechanism that drives ATP synthesis since it relies on a higher concentration of protons to generate “proton motive force”. The amount of ATP created is directly proportional to the number of protons that are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
How do electrons move in the electron transfer chain?
In the electron transfer chain, electrons move along a series of proteins to generate an expulsion type force to move hydrogen ions, or protons, across the mitochondrial membrane. The electrons begin their reactions in Complex I, continuing onto Complex II, traversed to Complex III and cytochrome c via coenzyme Q, and then finally to Complex IV. The complexes themselves are complex-structured proteins embedded in the phospholipid membrane. They are combined with a metal ion, such as iron, to help with proton expulsion into the intermembrane space as well as other functions. The complexes also undergo conformational changes to allow openings for the transmembrane movement of protons.
How many electrons does NADH have?
The NADH now has two electrons passing them onto a more mobile molecule, ubiquinone (Q), in the first protein complex (Complex I). Complex I, also known as NADH dehydrogenase, pumps four hydrogen ions from the matrix into the intermembrane space, establishing the proton gradient.
What is the ATP synthase?
As the proton gradient is established, F 1 F 0 ATP synthase, sometimes referred to as Complex V, generates the ATP. The complex is composed of several subunits that bind to the protons released in prior reactions. As the protein rotates, protons are brought back into the mitochondrial matrix, allowing ADP to bind to free phosphate to produce ATP. For every full turn of the protein, three ATP is produced, concluding the electron transport chain.
What is the mechanism that drives ATP synthesis?
Often, the use of a proton gradient is referred to as the chemiosmotic mechanism that drives ATP synthesis since it relies on a higher concentration of protons to generate “proton motive force”. The amount of ATP created is directly proportional to the number of protons that are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane. ...
Which protein transfers electrons to the last complex?
ISP and cytochrome b are proteins that are located in the matrix that then transfers the electron it received from ubiquinol to cytochrome c1. Cytochrome c1 then transfers it to cytochrome c, which moves the electrons to the last complex. (Note: Unlike ubiquinone (Q), cytochrome c can only carry one electron at a time).
What is the name of the protein that is oxidized into fumarate?
In the next protein, Complex II or succinate dehydrogenase, another electron carrier and coenzyme, succinate is oxidized into fumarate, causing FAD (flavin-adenine dinucleotide) to be reduced to FADH 2. The transport molecule, FADH 2 is then reoxidized, donating electrons to Q (becoming QH 2 ), while releasing another hydrogen ion into the cytosol.
