What are two of the products of the Krebs cycle?
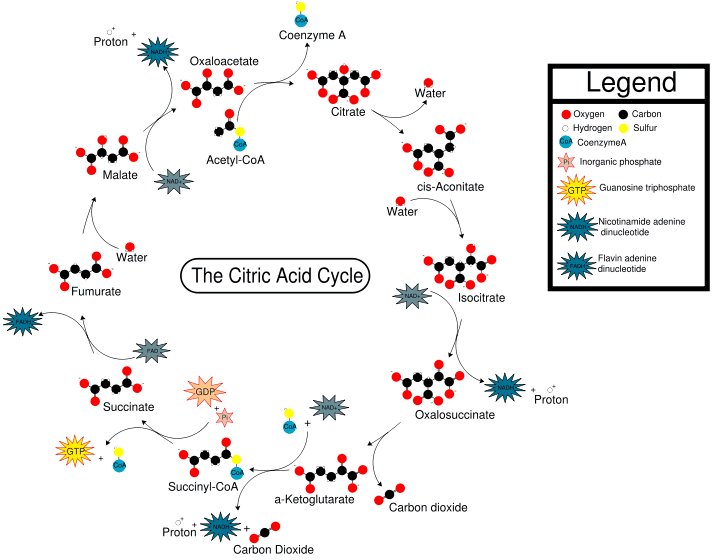
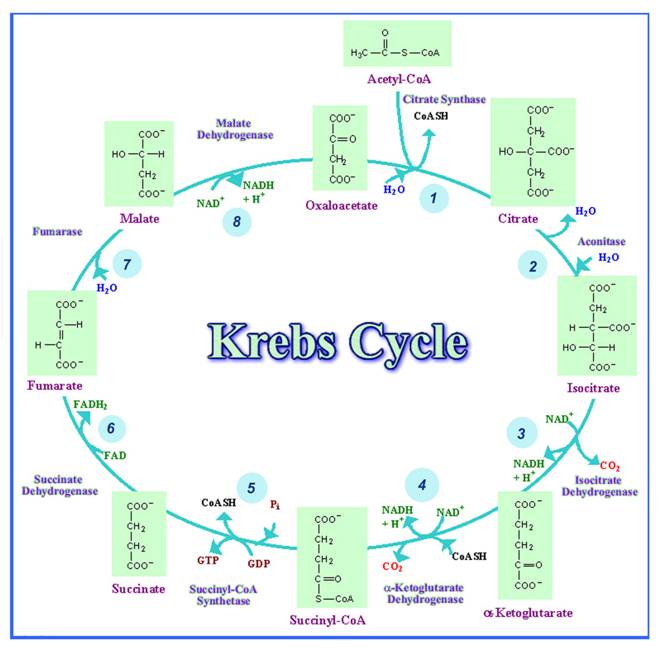
The citric acid cycle begins with the fusion of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate to form citric acid. For each acetyl-CoA molecule, the products of the citric acid cycle are two carbon dioxide molecules, three NADH molecules, one FADH 2 molecule, and one GTP/ATP molecule. Therefore, for every glucose molecule (which generates two acetyl-CoA molecules), the citric acid cycle yields four …
How much ATP is made by the citric acid cycle?
Jun 08, 2020 · Also Know, what are the products of the citric acid cycle quizlet? The citric acid cycle generates 3 molecules of NADH, 1 molecule of FADH2, and 1 molecule of GTP (ATP) per acetyl-sCoA that enters the cycle. Thus, in total, from each round of the citric acid cycle approximately 10 molecules of ATP are produced.
Which of these enters the citric acid cycle?
Mar 11, 2020 · Krebs cycle products. Each citric acid cycle forms the following products: 2 molecules of CO 2 are released. Removal of CO 2 or decarboxylation of citric acid takes place at two places: In the conversion of isocitrate (6C) to 𝝰-ketoglutarate (5C) In the conversion of 𝝰-ketoglutarate (5C) to succinyl CoA (4C)
What are the reactants and products of the Krebs cycle?
Apr 04, 2020 · During the citric acid cycle, acetate derived from carbohydrates, proteins and fats is oxidized in a step-by-step process that yields ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, the molecule that transports the chemical energy that cells need for metabolism. In plants and animals, this series of reactions take place in the mitochondria of the cell.
/citricacidcycle-57ff98d45f9b5805c267d2ec.jpg)
What is the Krebs Cycle?
Also known as the citric acid cycle, the Krebs cycle is a chain of reactions occurring in the mitochondria, through which almost all living cells p...
How Many ATPs are Produced In the Krebs Cycle?
2 ATPs are produced in one Krebs Cycle. For complete oxidation of a glucose molecule, the Krebs cycle yields 4 CO2, 6NADH, 2 FADH2 and 2 ATPs.
Where Does Krebs Cycle Occur?
Mitochondrial matrix. In all eukaryotes, mitochondria are the site where the Krebs cycle takes place. The cycle takes place in a mitochondrial mat...
How The Krebs Cycle Works?
It is an eight-step process 1) Condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate (4C) forming citrate (6C), coenzyme A is released. 2) Conversion of Ci...
Why Is Krebs Cycle Called As Amphibolic Pathway?
It is called amphibolic as in the Krebs cycle both catabolism and anabolism take place. The amphibolic pathway indicates the one involving both cat...
How Many NADH are Produced In The Krebs Cycle?
3 NADH molecules In one turn of the Krebs cycle, 3 molecules of NADH are produced. For complete oxidation of a glucose molecule, Krebs cycle yield...
What Is The Krebs Cycle Also Known As?
Krebs cycle is also known as Citric acid cycle (CAC) or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)
Why Krebs Cycle Is Called the Citric Acid Cycle?
Krebs cycle is also referred to as the Citric Acid Cycle. Citric acid is the first product formed in the cycle.
What are the inputs of the citric acid cycle?
Citric acid cycle inputs are derived from glycolysis outputs. Glycolysis produces pyruvate molecules, , and ATP. The pyruvate molecules undergo reactions that convert the three carbon pyruvate to a two carbon acetyl CoA and an one carbon carbon dioxide.
What is the end product of glycolysis?
Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis. After glycolysis, the three-carbon molecule pyruvate is converted into the two-carbon molecule acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA). This is carried out by a combination of three enzymes collectively known as the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA also produces one molecule ...
How many carbons are in acetyl-CoA?
As mentioned, acetyl-CoA has two carbons; therefore, most of the intermediates in this cycle have six carbons, or four more carbons than acetyl-CoA. One turn of citric acid cycle produces , , (carbon dioxide) and one GTP molecule (s). Report an Error.
What is the third carbon of pyruvate?
The third carbon of pyruvate is lost as carbon dioxide () during the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA. The citric acid cycle begins when the four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate combines with acetyl-CoA (a two carbon molecule) via an aldol condensation, yielding the six-carbon molecule citrate. Report an Error.
What is the name of the enzyme that produces pyruvate?
Acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate. Explanation: Pyruvate is produced in the last step of glycolysis, then, it is converted to the two-carbon molecule acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA). This is carried out by a combination of three enzymes collectively known as the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
How does succinate dehydrogenase convert to fumarate?
During the conversion of succinate into fumarate by succinate dehydrogenase, a single molecule of is reduced to as it accepts the hydrogens from succinate. then feeds its electrons into the electron transport chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
How many molecules does acetyl-coa produce?
Each acetyl-CoA molecule produces three and one in the citric acid cycle. This means that two acetyl-CoA (derived from one glucose molecule) produces six and two molecules in the citric acid cycle. Report an Error.
What are the components of the citric acid cycle?
Vitamins play an important role in the citric acid cycle. Riboflavin, niacin, thiamin and pantothenic acid as a part of various enzymes cofactors (FAD, NAD) and coenzyme A. Regulation of Krebs cycle depends on the supply of NAD + and utilization of ATP in physical and chemical work.
What is the role of vitamin in the citric acid cycle?
It plays an important role in gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis and interconversion of amino acids. Many intermediate compounds are used in the synthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, cytochromes and chlorophylls, etc. Vitamins play an important role in the citric acid cycle.
What is the role of fatty acids in the Krebs cycle?
Fatty acids undergo 𝞫-oxidation to form acetyl CoA, which enters the Krebs cycle. It is the major source of ATP production in the cells. A large amount of energy is produced after complete oxidation of nutrients. It plays an important role in gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis and interconversion of amino acids.
What reactants are produced in the Krebs cycle?
Krebs cycle reactants: Acetyl CoA , which is produced from the end product of glycolysis, i.e. pyruvate and it condenses with 4 carbon oxaloacetate, which is generated back in the Krebs cycle
What is the first step in the formation of acetyl CoA?
Step 1: The first step is the condensation of acetyl CoA with 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate to form 6C citrate, coenzyme A is released. The reaction is catalysed by citrate synthase. Step 2: Citrate is converted to its isomer, isocitrate. The enzyme aconitase catalyses this reaction.
How many steps are there in acetyl-CoA?
It is a series of eight-step processes, where the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form two molecules of CO 2 and in the process, one ATP is produced. Reduced high energy compounds, NADH and FADH 2 are also produced.
What is the Krebs cycle?
Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle is the final pathway of oxidation of glucose, fats and amino acids. Many animals are dependent on nutrients other than glucose as an energy source. Amino acids (metabolic product of proteins) are deaminated and get converted to pyruvate and other intermediates of the Krebs cycle.
What is the citric acid cycle?
The citric acid cycle is a series of chemical reactions whereby acetate molecules from food are broken down into carbon dioxide, water and energy. It is the principal method by which all aerobic organisms generate energy.
Who discovered the citric acid cycle?
Sometimes called the Krebs cycle, the citric acid cycle was discovered by Sir Hans Adolf Krebs, a British biochemist, in 1937. ADVERTISEMENT.
What is the molecule that transports the chemical energy that cells need for metabolism?
During the citric acid cycle, acetate derived from carbohydrates, proteins and fats is oxidized in a step-by-step process that yields ATP , or adenosine triphosphate, the molecule that transports the chemical energy that cells need for metabolism.
What is the citric cycle?
Whatever you prefer to call it, the citric cycle is a central driver of cellular respiration. It takes acetyl —produced by the oxidation of pyruvate and originally derived from glucose—as its starting material and, in a series of redox reactions, harvests much of its bond energy in the form of , , and molecules.
What happens in the third step of the citric acid cycle?
In the third step, isocitrate is oxidized and releases a molecule of carbon dioxide, leaving behind a five-carbon molecule—α-ketoglutarate. During this step, is reduced to form . The enzyme catalyzing this step, isocitrate dehydrogenase, is important in regulating the speed of the citric acid cycle. Step 4.
How many acetyl molecules are produced in a glucose cycle?
These figures are for one turn of the cycle, corresponding to one molecule of acetyl . Each glucose produces two acetyl molecules, so we need to multiply these numbers by if we want the per-glucose yield. Two carbons—from acetyl —enter the citric acid cycle in each turn, and two carbon dioxide molecules are released.
How many steps are there in the citric acid cycle?
The citric acid cycle is a closed loop; the last part of the pathway reforms the molecule used in the first step. The cycle includes eight major steps. Simplified diagram of the citric acid cycle.
How many carbons enter the acetyl cycle?
In a single turn of the cycle, two carbons enter from acetyl , and two molecules of carbon dioxide are released; three molecules of and one molecule of are generated; and. one molecule of or is produced. These figures are for one turn of the cycle, corresponding to one molecule of acetyl .
What is the starting molecule of acetyl?
At the end of this series of reactions, the four-carbon starting molecule, oxaloacetate, is regenerated, allowing the cycle to begin again. In the first step of the cycle, acetyl combines with a four-carbon acceptor molecule, oxaloacetate, to form a six-carbon molecule called citrate.
What happens to the remaining four carbons in a molecule?
The remaining four-carbon molecule undergoes a series of additional reactions , first making an molecule—or, in some cells, a similar molecule called —then reducing the electron carrier to , and finally generating another . This set of reactions regenerates the starting molecule, oxaloacetate, so the cycle can repeat.