Fundamental Properties of Alpha Particles
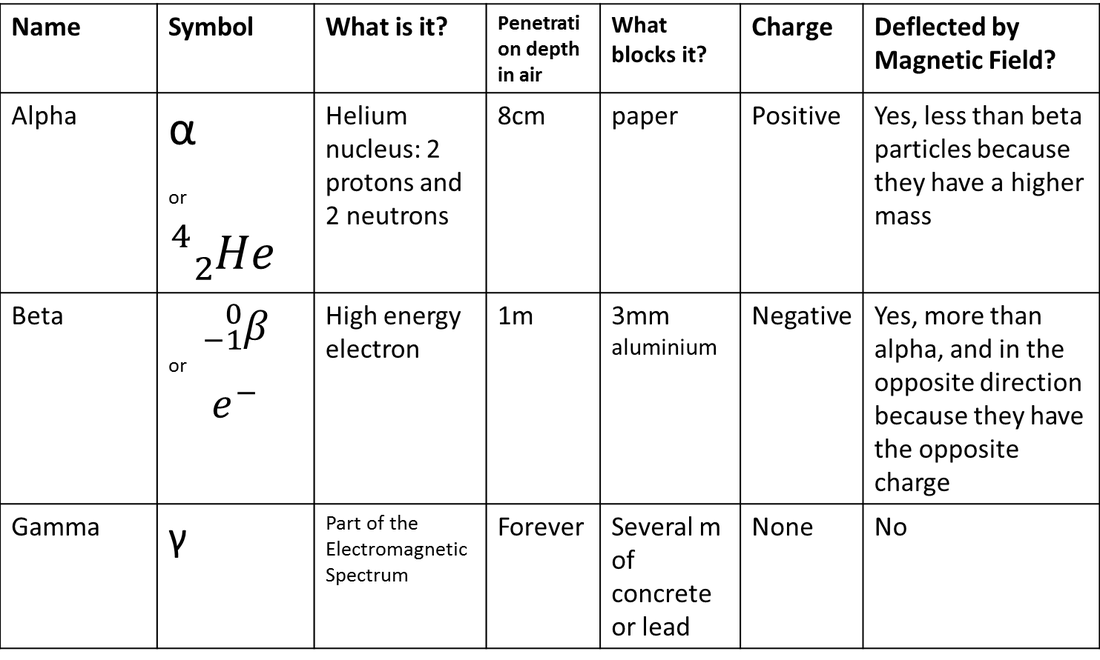
- Alpha particles carry double the positive charge of the proton, i.e., equal to the charge on the Helium nucleus.
- The mass of an α-particle is four times the mass of a Hydrogen atom, i.e., equivalent to the mass of the Helium atom.
What is an alpha particle and what do they contain?
An alpha particle is a free helium-4 nucleus. An alpha particle contains two protons and two neutrons, and no electrons. The mass of an alpha particle is therefore 4 amu, and its charge is +2. Are you a student or a teacher?
What are the characteristics of an alpha particle?
- Because of large mass and high-stepping speed, these particles have excessive ionizing efficiency. ...
- The distance an alpha particle travels in air relies on the radioactive source creating it. ...
- Alpha particles produce fluorescence in certain substances, like Barium-Platinocyanide and Zinc-Sulphide (ZnS).
Do alpha particles have the greatest penetrating power?
Because of the large mass of the alpha particle, it has the highest ionizing power and the greatest ability to damage tissue. That same large size of alpha particles, however, makes them less able to penetrate matter. Alpha particles have the least penetration power and can be stopped by a thick sheet of paper or even a layer of clothes.
What are alpha particles used for?
What are some uses of alpha particles? Alpha particles have low penetrating power but this still provides a range of useful applications: smoke detectors – americium-241 is commonly used in ionising smoke detectors. Smoke that enters the detector reduces the amount of alpha particles that are detected and triggers the alarm
See more
What are 3 characteristics of an alpha particle?
Alpha rays are the positively charged particles. Alpha-particle is highly active and energetic helium atom that contains two neutrons and protons. These particles have the minimum penetration power and highest ionization power. They can cause serious damage if get into the body due to their high ionization power.
What are the properties of a beta particle?
Beta particles have a mass which is half of one thousandth of the mass of a proton and carry either a single negative (electron) or positive (positron) charge. As they have a small mass and can be released with high energy, they can reach relativistic speeds (close to the speed of light).
What are the properties of alpha beta and gamma particles?
Penetrating PowerAlpha is stopped by paper. Beta and gamma can pass through paper.Beta is stopped by a few millimetres of aluminium. Gamma can pass through aluminium.Gamma rays are only partially stopped by thick lead. Nothing can completely stop gamma radiation.
What are the properties of gamma particles?
Gamma radiation is highly penetrating and interacts with matter through ionisation via three processes; photoelectric effect, Compton scattering or pair production. Due to their high penetration power, the impact of gamma radiation can occur throughout a body, they are however less ionising than alpha particles.
What is the symbol of alpha particle?
The Greek letter “α” is used to symbolise alpha particles.
What is the charge of alpha particle?
+2A positively charged particle ejected spontaneously from the nuclei of some radioactive elements. It is identical to a helium nucleus that has a mass number of 4 and an electrostatic charge of +2.
What are the two properties of beta rays?
Property 1: Beta particles (β – particles) are fast-moving electrons or positrons with high energy emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus. Property 2: Penetrating power of beta particles is higher than α-particles. They can penetrate through a thin metal foil.
What is the difference between alpha and beta particles?
Beta particles are more penetrating than alpha particles, but are less damaging to living tissue and DNA because the ionizations they produce are more widely spaced. They travel farther in air than alpha particles, but can be stopped by a layer of clothing or by a thin layer of a substance such as aluminum.
What is alpha particle made of?
alpha particle, positively charged particle, identical to the nucleus of the helium-4 atom, spontaneously emitted by some radioactive substances, consisting of two protons and two neutrons bound together, thus having a mass of four units and a positive charge of two.
Who discovered alpha rays?
Ernest RutherfordIn 1899 Ernest Rutherford demonstrated that there were at least two distinct types of radiation: alpha radiation and beta radiation.
What is alpha radiation used for?
Alpha emitter radiation therapy is used to treat prostate cancer that has spread to the bone, and it is being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer.
What are two properties of gamma radiation?
10 Properties of gamma raysGamma, γ-rays are not deflected by electric and magnetic fields. ... Gamma, γ-rays are electromagnetic waves like X-rays. ... The rest mass of a Gamma, γ-ray photon is zero. ... Gamma, γ-rays travel with the speed of light.Gamma, γ-rays have very large penetrating power.More items...
Which best describes a beta particle?
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay.
What charge does beta particle have?
negatively charged electronsBeta particles are negatively charged electrons emitted by the nucleus on decay (splitting of a neutron).
What is the difference between an electron and a beta particle?
The main difference between a beta particle and an electron is that a beta particle can have either charge or charge whereas electron has a charge.
What is a beta particle also known as?
Beta particles, also known as beta rays, are a high speed, high energy electron (β-) or positron(β+) emitted from the radioactive decay of the atomic nucleus. This process is called beta decay. An unstable atomic nucleus with an excess of neutrons will emit electrons (β-) during the β decay.
What are the properties of alpha particles?
Fundamental Properties of Alpha Particles. Alpha particles carry double the positive charge of the proton, i.e., equal to the charge on the Helium nucleus. The mass of an α-particle is four times the mass of a Hydrogen atom, i.e., equivalent to the mass of the Helium atom. (The above two properties proves that an alpha particle is equal to ...
What is an Alpha Particle?
Radiation is one of the forms of energy that occurs when an unstable parent nucleus undergoes radioactive decay. Radiations travel a certain distance from its source in the form of energized waves/particles. The particles are alpha, beta, and gamma; these particles have different attributes and effects. We will focus on the alpha particle. Now, let’s understand what alpha particles are.
Why do alpha particles burn?
Though alpha particles have low perforating power, they can cause burns on the human body. Because of large mass and high-stepping speed, these particles have excessive ionizing efficiency. It means a single alpha particle can bring forth thousands of ions before being absorbed.
What is the effect of alpha radiation on the air molecules?
Alpha radiations ionize the air molecules, allowing a small current to flow between electrodes. This current rings an alarm.
How far does an alpha particle travel?
At the normal pressure in air, the range of alpha particles deviates from 3 to 8 cm.
What is the velocity of an alpha particle?
The velocity of alpha particles ranges between 1.4 х 10⁷ m/s to 2.1 х 10⁷ m/s , relying on the source emitting/radiating it.
Which angle do particles deflect?
Most of the particles were disordered at small angles; however, a few of them deflected at an angle greater than the right angle.
What is the symbol for an alpha particle?
Alpha particles are named after the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α. The symbol for the alpha particle is α or α 2+. Because they are identical to helium nuclei, they are also sometimes written as He2+. indicating a helium ion with a +2 charge (missing its two electrons ).
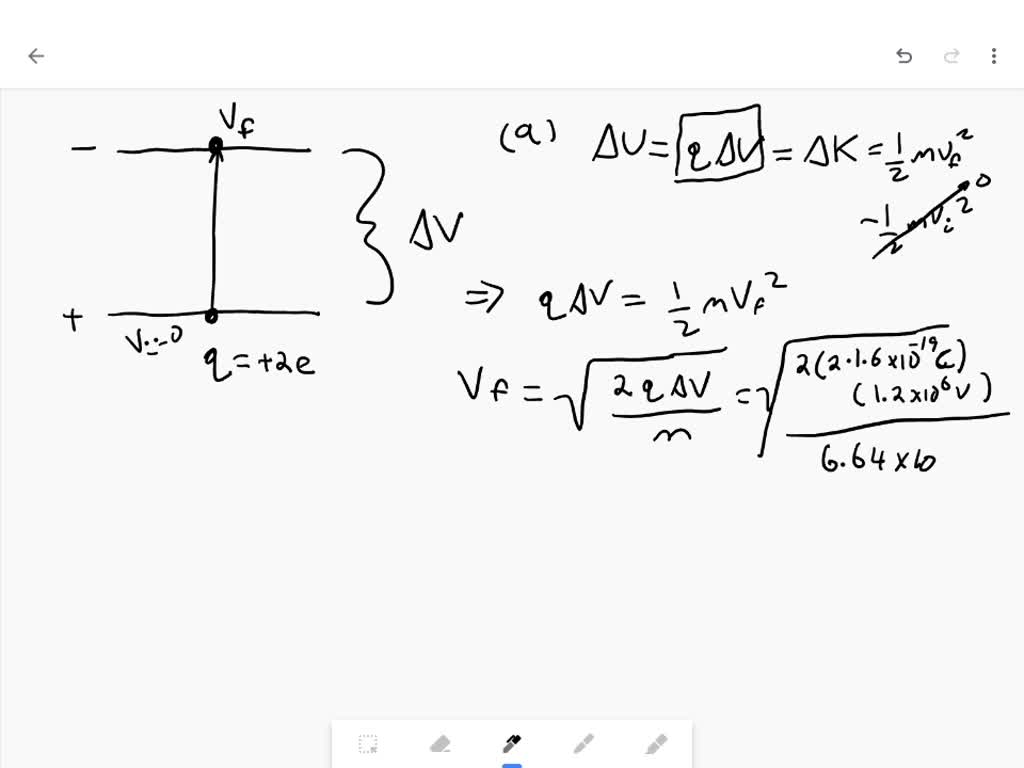
How much energy does an alpha particle emit?
The energy of alpha particles emitted varies, with higher energy alpha particles being emitted from larger nuclei, but most alpha particles have energies of between 3 and 7 MeV (mega-electron-volts), corresponding to extremely long and extremely short half-lives of alpha-emitting nuclides, respectively.
Why did Rutherford study alpha particles?
Because alpha particles occur naturally, but can have energy high enough to participate in a nuclear reaction, study of them led to much early knowledge of nuclear physics. Rutherford used alpha particles emitted by radium bromide to infer that J. J. Thomson 's Plum pudding model of the atom was fundamentally flawed. In Rutherford's gold foil experiment conducted by his students Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, a narrow beam of alpha particles was established, passing through very thin (a few hundred atoms thick) gold foil. The alpha particles were detected by a zinc sulfide screen, which emits a flash of light upon an alpha particle collision. Rutherford hypothesized that, assuming the " plum pudding " model of the atom was correct, the positively charged alpha particles would be only slightly deflected, if at all, by the dispersed positive charge predicted.
How much of the cosmic rays are made up of alpha particles?
In addition, extremely high energy helium nuclei sometimes referred to as alpha particles make up about 10 to 12% of cosmic rays. The mechanisms of cosmic ray production continue to be debated.
How fast does an alpha particle travel?
With a typical kinetic energy of 5 MeV; the speed of emitted alpha particles is 15,000 km/s, which is 5% of the speed of light. This energy is a substantial amount of energy for a single particle, but their high mass means alpha particles have a lower speed than any other common type of radiation, e.g. β particles, neutrons.
What is the kinetic energy of an alpha particle?
Due to the mechanism of their production in standard alpha radioactive decay, alpha particles generally have a kinetic energy of about 5 MeV, and a velocity in the vicinity of 4% of the speed of light. (See discussion below for the limits of these figures in alpha decay.)
Which element has the smallest alpha nucleus?
The smallest nuclei that have to date been found to be capable of alpha emission are beryllium-8 and the lightest nuclides of tellurium (element 52), with mass numbers between 104 and 109. The alpha decay sometimes leaves the nucleus in an excited state; the emission of a gamma ray then removes the excess energy .
What are the characteristics of alpha particles?
The production of alpha particles is termed alpha decay. Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutronsbound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus. Alpha particles are relatively large and carry a double positive charge.
What is the energy of an alpha particle?
Alpha particlesare energetic nuclei of heliumand they are relatively heavy and carry a double positive charge. Typical alpha particle have kinetic energy about 5 MeV. This is due to the nature of alpha decay. Pure alpha decay is very rare, alpha decay is frequently accompanied by gamma radiation.
What are the elements that are produced in nuclear reactors?
Alpha particles are commonly emitted by all of the heavy radioactivenuclei occuring in the nature (uranium, thorium or radium), as well as the transuranic elements (neptunium, plutonium or americium). Especially energeticalpha particles(except artificially ...
How many charged particles are in the nucleus of uranium?
In this process, the nucleus of uranium is splitted into three charged particles(fission fragments) instead of the normal two. The smallest of the fission fragments most probably (90% probability) being an extra energetic alpha particle. Characteristics of Alpha Particles. Key characteristics of alpha particles are summarized in few ...
Is alpha decay rare?
Pure alpha decay is very rare, alpha decay is frequently accompanied by gamma radiation. Alpha particles interact with matterprimarily through coulomb forces (ionization and excitation of matter) between their positive charge and the negative charge of the electrons from atomic orbitals.
What are the properties of an alpha particle?
An alpha particle. is the same thing as the nucleus of a helium atom. What are the Properties of an Alpha P article? 1. An alpha particle has a positive charge. because the 2 protons have a positive charge. 2. An alpha particle has by far the most mass of the. three types of radioactivity .
Why is an alpha particle positive?
because the alpha particle has a bigger mass. An alpha particle has a positive charge and will be. deflected in the opposite direction. from a beta particle which has a negative charge.
Which type of particle is most likely to collide with other atoms?
It is the type most likely. to collide with other atoms which means that. (i) alpha particles have the least penetrating ability of the three types. and are easily absorbed by paper, skin or a few centimetres of air. (ii) alpha particles are the most ionising of the three types.
What is a heavy nucleus?
heavy nuclei which have a large number of protons and neutrons. After an a lpha particle has been emitted the atomic number and the. mass number changes and a new element is made ( see examples ).

Fundamental Properties of Alpha Particles
- Alpha particles carry double the positive charge of the proton, i.e., equal to the charge on the Helium nucleus.
- The mass of an α-particle is four times the mass of a Hydrogen atom, i.e., equivalent to the mass of the Helium atom.
Uses of Alpha Radiations
- Alpha radiations are very popular in day-to-day applications. Some of its uses are: 1. For Treating Cancer Patients We use alpha particles in cancer treatment. While treating the cancer patient, doctors use a technique called Unsealed Source Radiotherapy. This technique involves inserting alpha particles like Radium-226 in tiny amounts into cancerous masses. We use Radium-223 to t…
Conclusion
- Thus after reading this write-up on alpha particles we have understood what alphas particles are, how they are generated, their properties and characteristics and their uses. It has also helped us understand how important alpha particles are from the application point of view. As a Physics student who will be handling such devices in the future, one must remember these particles are …
Also by Vedantu
- Vedantu suggests you go ahead and learn about beta particles (formed during beta decay) and gamma decaywhich produces gamma particles. Vedantu can also help you understand the topic of applications of Radioactivity in detail.
Overview
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be produced in other ways. Alpha particles are named after the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α. The symbol for the alpha particle is α or α . Because they ar…
Name
Some science authors use doubly ionized helium nuclei (He ) and alpha particles as interchangeable terms. The nomenclature is not well defined, and thus not all high-velocity helium nuclei are considered by all authors to be alpha particles. As with beta and gamma particles/rays, the name used for the particle carries some mild connotations about its production process and energy, but these are not rigorously applied. Thus, alpha particles may be loosely used as a ter…
Sources of alpha particles
The best-known source of alpha particles is alpha decay of heavier (> 106 u atomic weight) atoms. When an atom emits an alpha particle in alpha decay, the atom's mass number decreases by four due to the loss of the four nucleons in the alpha particle. The atomic number of the atom goes down by two, as a result of the loss of two protons – the atom becomes a new element. Examples of this …
Energy and absorption
The energy of the alpha particle emitted in alpha decay is mildly dependent on the half-life for the emission process, with many orders of magnitude differences in half-life being associated with energy changes of less than 50%, shown by the Geiger–Nuttall law.
The energy of alpha particles emitted varies, with higher energy alpha particle…
Biological effects
Due to the short range of absorption and inability to penetrate the outer layers of skin, alpha particles are not, in general, dangerous to life unless the source is ingested or inhaled. Because of this high mass and strong absorption, if alpha-emitting radionuclides do enter the body (upon being inhaled, ingested, or injected, as with the use of Thorotrast for high-quality X-ray images prior to the 1950s), alpha radiation is the most destructive form of ionizing radiation. It is the most str…
History of discovery and use
In 1899, physicists Ernest Rutherford (working in McGill University in Montreal, Canada) and Paul Villard (working in Paris) separated radiation into three types: eventually named alpha, beta, and gamma by Rutherford, based on penetration of objects and deflection by a magnetic field. Alpha rays were defined by Rutherford as those having the lowest penetration of ordinary objects.
Anti-alpha particle
In 2011, members of the international STAR collaboration using the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory detected the antimatter partner of the helium nucleus, also known as the anti-alpha. The experiment used gold ions moving at nearly the speed of light and colliding head on to produce the antiparticle.
Applications
• Some smoke detectors contain a small amount of the alpha emitter americium-241. The alpha particles ionize air within a small gap. A small current is passed through that ionized air. Smoke particles from fire that enter the air gap reduce the current flow, sounding the alarm. The isotope is extremely dangerous if inhaled or ingested, but the danger is minimal if the source is kept sealed. Many municipalities have established programs to collect and dispose of old smoke det…