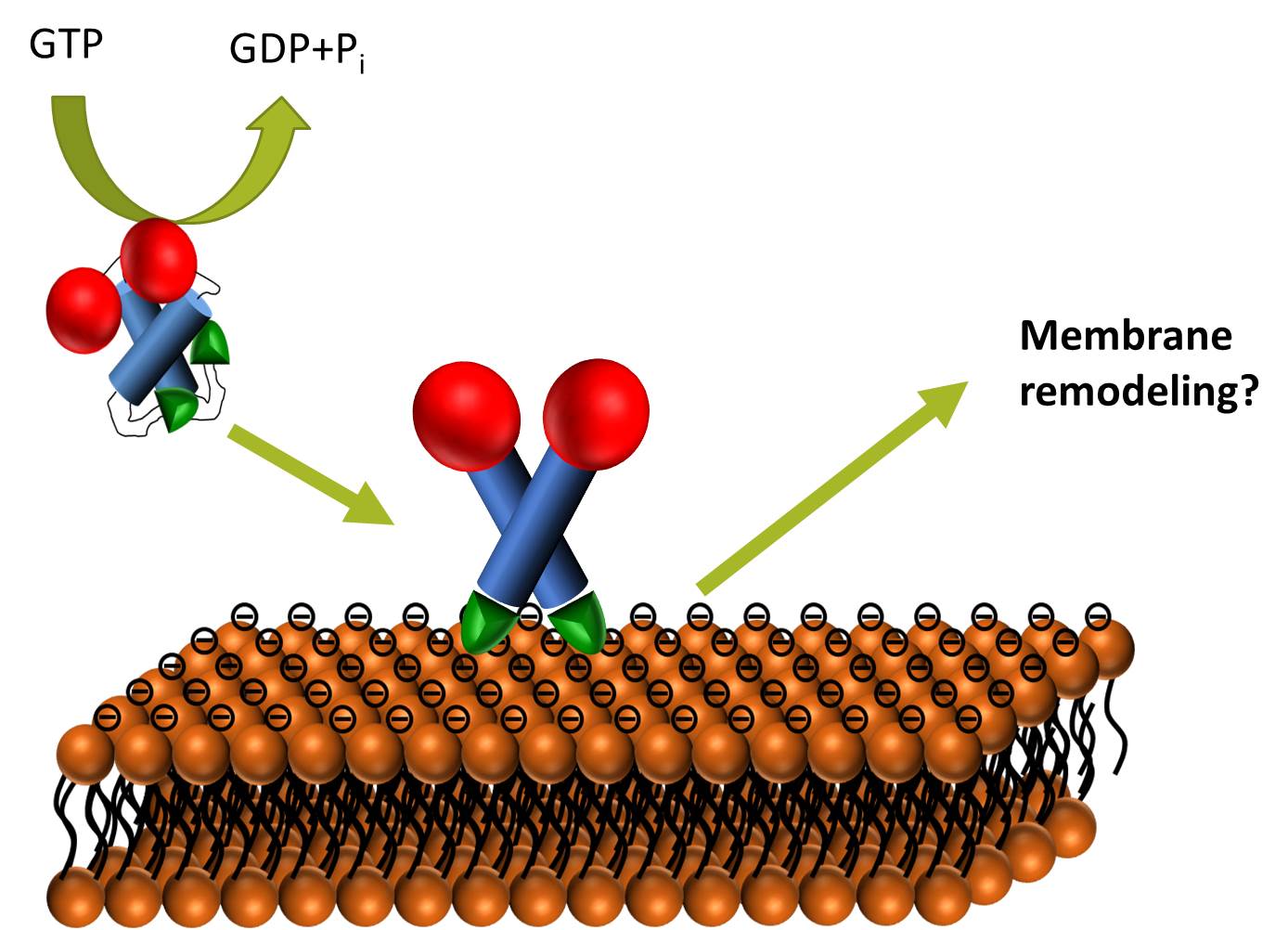
.PNG)
In summary:
- The cell membrane is a physical and chemical barrier which separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment
- Structure of the cell membrane Liquid bilayer of lipid with embedded proteins (a "fluid mosaic"), 5 nm thick ...
- Physical properties of the cell membrane: Impermeable to water-soluble molecules (but not to water) ...
- Composition of the cell membrane: Lipids (50% by weight) ...
What are three characteristics of a cell membrane?
The main functions of the cell membrane are:
- Controls movement of fluids, ions, and other substances, such as organic molecules, in and out of the cells and organelles.
- Facilitate cell adhesion
- Regulate ion conductivity
- Cell signaling
- Attach to glycoproteins and an intracellular network of protein fibers, collectively called the cytoskeleton
What are the 5 components of the cell membrane?
Cell Membrane Structure
- Phospholipids. Phospholipids are referred to as glycerophospholipids, these phospholipids are part of the cell membrane of living beings as well as a group of lipid compounds; i.e. ...
- Protein. This protein itself is derived from the Greek word “Protos” which means “most importantly”. ...
- Glycolipids and glycoproteins. ...
- Oligosaccharides. ...
- Cholesterol. ...
What property does the cell membrane have?
The cell membrane is semi-permeable, ie, it allows some substances to pass through it and does not allow others. It is thin, flexible and a living membrane, which consists of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins/ The cell membrane has large content of proteins, typically around 50% of membrane volume.
What are the functions of cell membrane?
What are 4 functions of the cell membrane?
- A Physical Barrier.
- Selective Permeability.
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis.
- Cell Signaling.
- Phospholipids.
- Proteins.
- Carbohydrates.
- Fluid Mosaic Model.

What is the property of the cell membrane?
Cell membranes serve as barriers and gatekeepers. They are semi-permeable, which means that some molecules can diffuse across the lipid bilayer but others cannot. Small hydrophobic molecules and gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide cross membranes rapidly.
What is the most important property of the cell membrane?
The most important property of the cell membrane -selective permeability. This means some substances can pass through it freely, but others cannot. Small and nonpolar (hydrophobic) molecules can freely pass through the membrane, but charged ions and large molecules such as proteins and sugars are barred passage.
What are the properties of the cell?
3 Properties of a CellMembrane. A cellular membrane, also called a plasma membrane, surrounds all cells. ... Nucleus. The nucleus, a spherical organelle surrounded by a membrane, is the information center of the cell. ... Cytoplasm.
What are the 4 main functions of the cell membrane?
The four main functions of the plasma membrane include identification, communication, regulation of solute exchange through the membrane, and isolation of the cytoplasm from the external environment.
What are the 5 functions of the cell membrane?
Terms in this set (5)protects the cell by acting as a barrier.regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell.receives chemical messengers from other cell.acts as a receptor.cell mobility, secretions, and absorptions of substances.
What are 3 functions of the cell membrane?
Biological membranes have three primary functions: (1) they keep toxic substances out of the cell; (2) they contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules, such as ions, nutrients, wastes, and metabolic products, that mediate cellular and extracellular activities to pass between organelles and between the ...
Which is not a property of cell membrane?
Final Answer: Proline is not a constituent of the cell membrane.
What are the properties of membrane proteins?
Membrane protein functionsEnzymatic functions. All enzymes are a type of protein. ... Transportation. Membrane proteins can allow hydrophilic molecules to pass through the cell membrane. ... Signal transduction. Some membrane proteins can feature a binding site. ... Cell recognition. ... Intercellular joining. ... Attachment.
What are the basic structural features of cell membrane?
Lipids and proteins make up the majority of the cell membrane. Phospholipids are large lipids that form a bilayer with hydrophobic saturated hydrocarbon tails on the inside and polar heads on the outside. It is made up of both integral and peripheral proteins. The membrane also contains cholesterol.
What are the 10 functions of cell membrane?
Functions of the Cell MembraneMechanical Structure. Defines/encloses the Cell. Re. Cytoskeleton. Extracellular Matrix. Protection.Selective Permeability.Active Transport.Bulk Transport: Exocytosis and Endocytosis.Markers & Signalling. (for communication with other cells & the external environment)Metabolic Activities.
Which of the following best describes the cell membrane?
The correct answer is (C) A flexible lipid double layer. The cell membrane is often referred to as a "fluid mosaic," a flexible structure containing phospholipids as well as some proteins and other important molecules.
What are some functions of a cell membrane select all that apply?
Select all that apply. The cell membrane allows some materials to enter the cell while blocking others. The cell membrane helps the cell maintain homeostasis. The cell membrane allows waste materials to exit the cell.
What is the most important feature of the cells phospholipid membrane?
Phospholipid bilayers are critical components of cell membranes. The lipid bilayer acts as a barrier to the passage of molecules and ions into and out of the cell. However, an important function of the cell membrane is to allow selective passage of certain substances into and out of cells.
What is cell membrane and its function?
The cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane. It provides protection for the cell and its cellular components from the external environment. It is selectively permeable and regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell.
What is a characteristic of cell membranes quizlet?
All cells are surrounded by a membrane. Which is a characteristic of a cell membrane? It is semipermeable.
Which property of the cell membrane has resulted in the observations?
Answer: The correct answer is option c) Selectively permeable nature.
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell.
What are the proteins that interact with other cells?
Another is that the membrane of the cell, which would be the plasma membrane, will have proteins on it which interact with other cells. Those proteins can be glycoproteins, meaning there's a sugar and a protein moiety, or they could be lipid proteins, meaning that there's a fat and a protein.
Is the cell wall tougher than the plasma membrane?
In fact, they have a cell wall outside of them, and that cell wall is much tougher and is structurally more sound than a plasma membrane is. William Gahl, M.D., Ph.D.
Is cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
And there are different types of plasma membranes in different types of cells, and the plasma membrane has in it in general a lot of cholesterol as its lipid component. That's different from certain other membranes from within the cell.
Why is membrane potential difference not entirely due to the membrane acting as a separator between two electrolyte solutions?
The generation of the membrane potential difference is not entirely due to the membrane acting as a separator between two electrolyte solutions, but also due to the collection of charged ions at the membrane surface ( Tamagawa et al, 2014 ).
Why is the whole membrane thicker than the whole membrane?
The whole membrane, of course, ends up appearing thicker than this (hence the 7-10 nm estimates) because it is packed full of proteins and polysaccharides, such that the entire membrane probably resembles a "cobblestone pavement" ( Takamori et al, 2006 ) with the lipid bilayer acting as a thin mortar between large thick clusters of transmembrane proteins. Again borrowing (stealing) shamelessly from Phillips (2018), the diagram below demonstrates the relative sizes of these transmembrane structures.
How are surface proteins and transmembrane proteins divided?
Historically, the division of surface proteins and transmembrane proteins was by whether or not they were soluble in polar solvents. Peripheral proteins would dissolve and drift away, they would say, and integral transmembrane proteins would remain stuck in the membrane until you use a non-polar solvent or detergent to disrupt the lipid bilayer.
What are the physical properties of a bilayer?
Physical properties of the cell membrane: Impermeable to water-soluble molecules (but not to water) Soft and flexible. Spontaneously prone to forming self-repairing pores.
What attracts phospholipids to the membrane?
Attracted to the membrane by the intrinsic negative charge of the phospholipid heads
Which bilayer is hydrophilic?
The lipid bilayer consists of phospholipids, which are amphipathic molecules (i.e. where one end of the molecule is hydrophilic and the other end is hydrophobic)
What are glycolipids and glycoproteins?
Glycosylated components of glycolipids and glycoproteins. These form the cellular glycocalyx. Water. Present between lipid molecules in a highly organised form, as well as bulk water in pores and channels. Ions. . Adsorbed ions (eg. calcium, sodium)
What are the functions of membranes?
It is well known that membranes play an essential role in various biological processes, such as communication, cell interactions, signal transduction, active transport, as well activity of various hormones, drugs, and other molecules that occur on membranes [1–6].
What is the operating temperature of a proton exchange fuel cell?
The practical attractions of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) all stem from the low-temperature operating regime of these cells: 60–80 °C in the case of sulfonated perfluorocarbon membranes such as the commercially available Nafion® (Dupont) and Aciplex (Asahi Chemical) polymers. This attribute leads to system designs that allow for a small footprint and flexible geometries; rapid start-up and rapid power output stabilization; projected low system maintenance and long-term chemical stability; and a high safety factor allowing other system components and humans to be in close proximity to the operating fuel cell. The low operational temperature of these cells is especially impressive when compared with solid-oxide cells that are presently available or under development with operational temperatures in the 700–1000 °C range, or the commercially available phosphoric acid cell that operates at 200 °C.
What is the deformability of RBCs?
RBC deformability describes the ability of RBCs to change their shape and subsequently return to their original biconcave disc shape. The deformability is directly related to the RBC membrane properties such as stiffness, rigidity and elasticity [26,32,52,53]. Whole blood analysis provides little information on the behaviour of individual RBCs. A direct measurement of individual cell deformability would offer valuable information on the influence of aging, diseases and pharmacological agents on the circulation efficiency of blood [54]. Various methods have been used to measure the deformability of RBCs including filtration [55], rheoscopy [56], ektacytometry [57], cell poking [58], optical tweezers [59,60], microaspiration [61] and flicker spectroscopy [62]. However, most of these methods require large samples, have large variation in measured mechanical moduli values, and only the last three methods mentioned produced a quantitative estimation of the elastic modulus of the RBC's membrane-skeleton complex [26,63,64].
What temperature should a fuel cell be operating?
Most or all of the PEMFC shortcomings noted here can be ameliorated by raising the operating temperature of the fuel cell stack to the 120–150 °C range. Operating at temperatures greater than 100 °C can eliminate the flooding problem and simplify water management in the electrode portion of the fuel cell. Elevated-temperature operation also simplifies the required cooling system owing to the increased temperature difference between the fuel cell stack and the environment. Operating temperature of around 120 °C and 25% relative humidity (RH) have been set as reasonable standards for the optimization of thermal balance and water management. Somewhat higher temperatures of 130–150 °C are useful in the mitigation of the carbon monoxide poisoning problem. At these temperatures, hydrogen starts to successfully compete with carbon monoxide for electrocatalytic platinum surface sites. While carbon monoxide poisoning at 80 °C becomes intolerable around 10 ppm, PEMFCs operating at 130–140 °C provide good current–voltage output in the presence of as much as 1000–1500 ppm of carbon monoxide.
Is elevated temperature PEMFC compatible with presently available membranes?
The temperature regime of interest, however, is not compatible with presently available membranes. New membrane materials that can withstand elevated temperature/low-humidity operating conditions while maintaining high proton conductivity, chemical stability, and good impermeability with regard to hydrogen and oxygen feeds are required. This chapter reviews recent advances in elevated-temperature PEMFCs based on neoteric membranes, such as composite sulfonated perfluorocarbon membranes formed from mixing Nafion and an inorganic phase, membranes composed of the thermally tolerant polybenzimidazole (PBI) polymer systems, and the recently reported purely inorganic solid-acid membranes.
Why is the cell membrane important?
Thus the cell membrane also serves to help support the cell and help maintain its shape.
What is the cell membrane made of?
Cell Membrane Structure. The cell membrane is primarily composed of a mix of proteins and lipids. Depending on the membrane’s location and role in the body, lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the membrane, with the remainder being proteins.
What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes?
Cholesterol molecules are selectively dispersed between membrane phospholipids. This helps to keep cell membranes from becoming stiff by preventing phospholipids from being too closely packed together. Cholesterol is not found in the membranes of plant cells.
What are the functions of cell membrane receptor proteins?
Cell membrane receptor proteins help cells communicate with their external environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling molecules.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus and mitochondria are two examples. Another function of the membrane is to regulate cell growth through the balance of endocytosis and exocytosis. In endocytosis, lipids and proteins are removed from the cell membrane as substances are internalized. In exocytosis, vesicles containing lipids and proteins fuse with ...
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and ...
Which bilayer of lipids is hydrophobic?
Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and extracellular fluid.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Cell membranes protect and organize cells. All cells have an outer plasma membrane that regulates not only what enters the cell, but also how much of any given substance comes in. Unlike prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells also possess internal membranes that encase their organelles and control the exchange of essential cell components. Both types of membranes have a specialized structure that facilitates their gatekeeping function.
What is the most important feature of a cell?
The cell membrane could be considered the single most important feature of a living cell (with perhaps the exception of DNA/RNA). It's composed of several types of triacyglyerides and other molecules that form a bilayer separating the cell from the extra cellular space around it.
Why are membrane transport proteins important?
Membrane transport proteins are specific and selective for the molecules they move, and they often use energy to catalyze passage. Also, these proteins transport some nutrients against the concentration gradient, which requires additional energy. The ability to maintain concentration gradients and sometimes move materials against them is vital to cell health and maintenance. Thanks to membrane barriers and transport proteins, the cell can accumulate nutrients in higher concentrations than exist in the environment and, conversely, dispose of waste products (Figure 3).
What molecules help maintain the fluidity of the membrane?
There are also cholesterol molecules which maintain the fluidity of the membrane. When the outside temperatures drop, the phospholipids molecules tend to get closer to each other. This increases membrane rigidity. Cholesterol prevents this close packing of phospholipds, and keeps the membrane fluid. The opposite takes place during warm external temperatures.
Why is a phospholipid membrane described as fluid?
It is described as fluid mosaic. It is described as “fluid” because the individual phospholipid molecules are free to move around within their layer. It is described as “mosaic”, because of the mosaic like pattern produced by individual, scattered proteins, when the membrane is viewed from above.
Why is the bilayer mosaic?
The Bilayer is mosaic in appearance due to present of Proteins and Glycoproteins. It is asymmetric as both the layers have a different composition of Lipids and proteins.
What are the proteins that are found in the membrane?
Intrinsic proteins can be transmembrane proteins (cross both layers) or proteins that only cross one layer. These proteins can act as transport proteins, enzymes, etc.