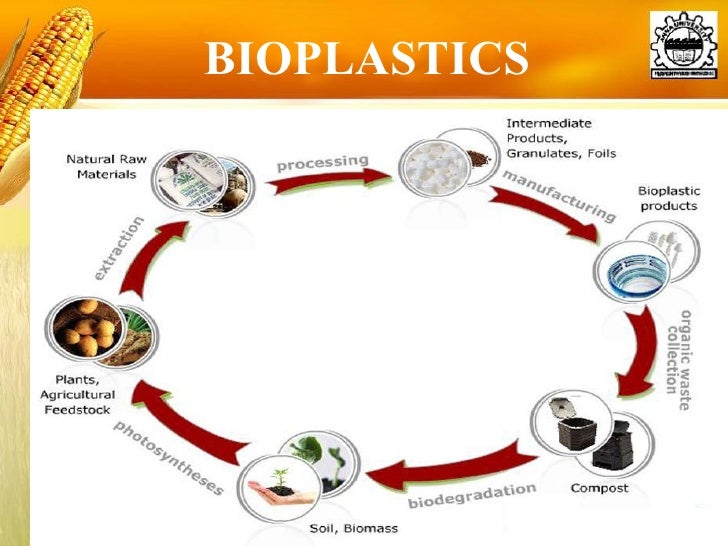
What are the pros and cons of bioplastics?
- Growing demand for bioplastics creates competition for food sources, contributing to the global food crisis. …
- Bioplastics won’t biodegrade in a landfill. …
- Bioplastics encourage people to litter more. …
- Bioplastics contaminate plastic recycling streams. …
- Bioplastics are not the answer to marine litter.
Full Answer
What are the pros of bioplastics?
The often-cited advantages of bioplastic are reduced use of fossil fuel resources, a smaller carbon footprint, and faster decomposition. Bioplastic is also less toxic and does not contain bisphenol A (BPA), a hormone disrupter that is often found in traditional plastics.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using bioplastics?
Advantages & Disadvantages - Bio-Plastics. It takes only 0.8 metric tons of CO2 to create bio-plastics which is 3.2 metric tons less than normal plastics. Bioplastics are cheaper than normal plastics especially with the soaring oil prices. Valuable raw material can be reclaimed and recycled into other products.
What are some disadvantages of bioplastics?
The Cons of BioplasticsGrowing demand for bioplastics creates competition for food sources, contributing to the global food crisis. ... Bioplastics won't biodegrade in a landfill. ... Bioplastics encourage people to litter more. ... Bioplastics contaminate plastic recycling streams. ... Bioplastics are not the answer to marine litter.
Do bioplastics harm the environment?
While the production of bioplastics produces fewer greenhouse gases, a study from the University of Pittsburgh found that they actually produce greater amounts of pollution as a result of pesticides, fertilizers and land use.
Why are bioplastics better for the environment?
In general, bioplastics contain fewer ingredients from fossil fuels. Some contain none at all. Displacing fossil fuels with renewable resources is a positive step. Under the right conditions, bioplastics produce less greenhouse gas emissions than petroleum-based plastics.
What are the disadvantages of biodegradable?
While biodegradable may aid in the environment conflict against traditional plastics, it does have some drawbacks:It may not break down completely. ... It can release harmful substances when breaking down. ... It reinforces a single-use mindset. ... It's expensive to produce.
Are bioplastics recyclable?
Bioplastics can't be recycled, and if their production rises, it will be necessary to reconsider the way we treat plastic waste. If the bioplastic is thrown in a bin with traditional plastic, it can cause problems. PET is one of the most used plastics, and the result of recycling process are PET flakes.
How long does bioplastic take to decompose?
three to six monthsIf bioplastics were to end up in the ocean, they would break down into tiny pieces similarly to traditional plastics. According to BBC Science Focus, biodegradable plastics take only three to six months to fully decompose, far quicker than traditional plastic that can take hundreds of years.
Are bioplastics more expensive?
Bioplastics seem to have many benefits, but they aren't the perfect eco-friendly product we might hope for. For one thing, they're more expensive than petrochemical plastics, costing between 20 to 100 percent more [source: Dell].
Does bioplastic dissolve in water?
The bioplastic contains cassava starch, vegetable oil, and organic resins. The material is biodegradable and compostable, breaking down over a period of months on land or at sea. However, it dissolves instantly in hot water.
How do bioplastics decompose?
Biodegradable plastics: A subcategory of bioplastics To be truly labeled biodegradable, the plastic must degrade into carbon dioxide, water, biomass and / or mineral salts when exposed to air, moisture and microbes. The materials should not be toxic to the environment.
How does bioplastics reduce carbon footprint?
Notably, PLA emits 70% less greenhouse gases when it degrades in landfills [30]. Other studies have also found that substituting traditional plastic with corn-based PLA bioplastics can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 25% [110, 112].
What are the disadvantages of biopolymers?
Different biopolymers used have disadvantages such as high-water vapor permeability, oxygen permeability, fragility, low thermal resistance, low mechanical properties, vulnerability to degradation, and low processability [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19].
What is the primary disadvantage of starch as a biodegradable polymer?
Starch-based bioplastics have the disadvantages of hydrophilicity, poor mechanical properties, low water vapor barrier property, and low freeze stability during bioplastics formation [60,62,63,64,65]. However, depending on the amylose content in the polymeric starch matrix, certain bioplastics properties can change.
Can bioplastics be recycled?
Yes, bio-based plastics can be recycled. Bio-based plastics such as “BioPE” or “BioPET” are chemically identical to their fossil based versions “PE” and “PET”. That's why they are called drop-ins. Therefore they can be perfectly integrated in established recycling streams.
Are bioplastics more expensive?
Bioplastics seem to have many benefits, but they aren't the perfect eco-friendly product we might hope for. For one thing, they're more expensive than petrochemical plastics, costing between 20 to 100 percent more [source: Dell].
Why are bioplastics produced?
Several studies have shown that bioplastics production resulted in greater amounts of pollutants. This is due to the fertilizers and pesticides used in growing the crops and the chemical processing needed to turn organic material into plastic.
What are bioplastics made of?
Various bioplastics made from algae (found abundantly in seawater) using heating and cooling methods as well as mixing with e.g. calcium carbonate. We also expect to see a lot more innovation in the coming years enabling e.g. foodwaste to be turned into bioplastics.
What are biodegradable plastics made of?
Generally bioplastics are made of corn starch, cooking oil, algae or sugar although there are lots of other materials.
How do we dispose biodegradable plastics?
Biodegradable” implies that the decomposition happens in weeks to months. Bioplastics that don’t biodegrade that quickly are called “durable”.
How can we avoid bad plastics with minimal effort?
This is where biodegradable plastics can play an important role. Instead of giving up e.g. straws, single use cups or water filters we replace the existing products with something similar. The only decision or change required is to make select products with biodegradable plastic.
How much more expensive is biodegradable plastic?
Cost of Biodegradable plastics. Currently bioplastics such as PLA are about 20 to 50 percent more costly than comparable traditional plastic materials. However, prices are slowly coming down as the technology improves. As demand and production volumes increase the cost should eventually be similar to conventional plastics.
Can bioplastics be recycled?
Some bioplastics will inevitably end up in landfills where, deprived of oxygen, they may release methane. This is a greenhouse gas 23 times more potent than carbon dioxide. E. Recycling challenges. When bioplastics enter the conventional plastic recycling stream they may contaminate the recycling process.
What are the advantages of bioplastics?
As product designers look for more sustainable options to please increasingly environmentally savvy consumers, they are often looking at the advantages of bioplastics, such as lower production CO2 emissions, sustainable raw materials, biodegradability in many cases, and more…
Why are bioplastics more marketable?
Bioplastics are more marketable, for example, their usage may improve the value-add of a product through a green marketing campaign . After all, studies have shown that ‘80% of European customers want to buy products with a minimal impact on the environment,’ so bioplastics may represent a useful argument for brands.
Why are bioplastics so fragile?
For instance, some algae-based bioplastics will break down in a matter of hours when in the water – this makes them very biodegradable, but also fragile.
How much CO2 is released from oil based plastics?
The refinement of oil to create the petrochemical building blocks for oil-based plastics uses a lot of energy and releases a lot of CO2 during production, perhaps as much as 500 million tonnes of CO2 per year. Common bioplastics, such as starch-based PLA and PHB, are non-toxic and of ‘no health concern’.
What are the requirements for bioplastics?
Crop-based bioplastics require fertile land, water, fertilizers, and are reliant on weather conditions . This means that the supply of raw materials for bioplastics are at risk of natural phenomena, such as drought.
What is the difference between microplastics and oil based plastics?
The difference is that they do not cause the same level of harm to the environment as their oil-based cousins. For instance, we’ve all heard of the damage that microplastics do to animal life.
Is bioplastics cheaper than oil?
First, bioplastics are generally NOT cost-competitive compared to their oil-based counterparts. They are generally two or three times more expensive than the major conventional plastics such as PE or PET, and their production is plagued by low yields and being expensive .
What are some of the advantages and disadvantages of bioplastics?
In one article, without complex discussion of all of the different types of bioplastic, it’s impossible to categorically list all of the advantages and disadvantages of bioplastics. As such, this is very much an overview and generalisation, picking five pros and cons of bioplastic.
Why is it important to break down bioplastics?
This is because some are better for the environment than others, either in terms of how they are manufactured, or in terms of how they degrade, or both.
What is bioplastic made of?
The fundamental concept of bioplastic is that, instead of petroleum sources, other renewable biomass sources are used to make the plastic materials, such as corn starch.
How long does it take for bioplastics to be biodegradable?
Microorganisms do the work. Many would agree that to use the term ‘biodegradable’, this process should happen relatively quickly, over weeks or months. It also won’t happen in your home compost, but requires industrial conditions. Not all bioplastics are therefore truly biodegradable.
How much of the marine debris is made up of plastic?
It’s notorious and no one can claim ignorance about it today. With plastics making up 80% of all marine debris and killing over 1 million sea birds every year, these statistics are just the tip of the iceberg. Plastics create masses of carbon dioxide in their manufacture and they don’t biodegrade.
Which is more sustainable, bio or fossil fuels?
2. Bio materials are more renewable and sustainable: Fossil fuels are, by nature, finite. Plant sources for plastic materials are renewable and therefore inherently more sustainable, if farmed with care.
Can turtles be strangled by bioplastic bags?
A turtle can still be strangled by a bioplastic bag. 4. Production of bioplastics may not be eco-friendly: Whilst on the face of it bioplastics should be greener than petroleum based plastics, this is dependent on the agricultural process.
What are some of the advantages and disadvantages of bioplastics?
In one article, without complex discussion of all of the different types of bioplastic, it’s impossible to categorically list all of the advantages and disadvantages of bioplastics. As such, this is very much an overview and generalisation, picking five pros and cons of bioplastic.
What is bioplastics?
There are a huge number of bioplastics being manufactured, and many claim the name ‘bioplastics’ for anything which doesn’t fully use petroleum sources, even if the bulk of the plastic material still relies on fossil fuels and a petroleum base.
Is bioplastic biodegradable?
With all of these different types of bioplastic, this isn ’t an easy question to answer. Generally speaking, the quick answer is sort of, and with caveats!
How much of the world's plastics are bioplastics?
Globally, bioplastics make up nearly 331,000 tons (300,000 metric tons) of the plastics market [source: European Bioplastics ]. That may sound like a lot, but it only accounts for less than 1 percent of the 200 million tons (181 million metric tons) of synthetic plastics the world produces each year [source: Green Council ].
Can bioplastic be recycled?
In fact, a relatively small amount of bioplastic can contaminate conventional plastic recycling, preventing the salvaged plastic from being reused and stopping recycling companies from profiting from one of their more lucrative recyclables.
Can bioplastics be used for sports?
This approach means that bioplastics could conceivably be used to great effect at sports games and other events where foods are purchased and consumed on the premises in bulk. As with corn ethanol, corn plastic has also drawn criticism for depending on the industrial farming of large fields of crops.
Can bioplastics be incinerated?
On the other hand, if incinerated, bioplastics don't emit toxic fumes like their oil-based counterparts. To avoid the complications of mixed plastics, commercial composters in the Northwestern United States only accept bioplastics from food service operations, not households.
Is PET plastic a commodity?
PET plastics are a mature commodity, with years of production fine-tuning behind it. Bioplastics advocates argue that, in time, PLA costs will go down, all while petroleum-based plastics costs continue to fluctuate due to unstable production regions and dwindling resources.
Can you use genetically modified corn to make plastic water bottles?
Nevertheless, even if genetically modified corn was used to make your plastic water bottle, NatureWorks insists that you don't have to worry about consuming modified proteins, as these are destroyed in the transformation from plant to PLA plastic [source: Jewell ].
Can you compost corn plastic?
What's wrong with putting corn plastics in your recycling bin? To the uninformed eye, one may look very much like the other, but their chemical composition is very different. In fact, a relatively small amount of bioplastic can contaminate conventional plastic recycling, preventing the salvaged plastic from being reused and stopping recycling companies from profiting from one of their more lucrative recyclables.
Why are plastics biodegradable?
1. Biodegradable plastics offer reduces carbon dioxide levels.# N#We are producing more waste plastic today than ever before in human history. These items are finding their way into our oceans and even contaminating our drinking water. Scientists estimate that there could be more waste plastic in the ocean than fish by the year 2050, with tap water containing microplastics up to 80% of the time. Researchers at the University of Bath have created a plastic that only uses sugar and carbon dioxide, resulting in polycarbonates that no longer need to use petrochemicals and their CO2 emissions necessary for refinement. Plastics like these break down naturally, only depositing the amount of gas back into the environment that was used to create it in the first place.
Why are biodegradable plastics good for the environment?
Biodegradable plastics must follow a specific disposal procedure.#N#We can definitely benefit from the presence of biodegradable plastics because they can decompose effectively in our environment without creating a pollutive effect. This advantage can only occur if the items are disposed of properly, meaning that these items must be treated in a manner that is similar to compost. If we throw out these plastics in the landfill last we would the traditional items, then they will follow a path that is similar to the non-biodegradable option. That is why we must be mindful of recycling programs and waste-reduction initiatives to ensure that we can all take advantage of the benefits that the natural products offer.
How are biodegradable plastics broken down?
Biodegradable plastics are broken down by naturally-occurring bacteria. After plastics are formed, the traditional products will hold their carbon. When you dispose of them and they begin to decompose in some way, then that gas is released into the atmosphere.
What are biodegradable plastics made of?
Numerous plant materials are useful in the making of biodegradable plastics today. Manufacturers can create items using plants, starches, corn oil, or even the peels from citrus fruits. That means we no longer need to use the chemical fillers that are found in the traditional items, which then enter the environment when the plastic is melted to release them. Biodegradable plastics offer a substance that is made from a natural source, so the risks of breaking down are much fewer.
Why is biodegradable plastic considered eco friendly?
This outcome is achievable because the microorganisms in the environment are able to break down the structures which make the biodegradable plastic. It creates a result which is believed to be eco-friendly compared to the traditional plastics that we throw away every day.
How much would we save by recycling plastic?
If we were to recycle our plastics each year, then our net carbon savings alone would be up to 30%, which some researchers suggesting the savings could be as high as 80%. Switching to biodegradable plastics would help to reduce the number of greenhouse gas emissions produced by the industry even further, despite the initial financial costs that would be required to make the transition.
What happens when plastics break down?
When they begin to break down in the environment, bacteria in the soil begin to consume the components. That leaves us with less waste to manage over all, reducing the potential for pollution in every biome. 4. Biodegradable plastics do not release other dangerous items upon decomposition.
