Which bone has the head located on the distal end?
Jan 16, 2020 · The enlarged proximal and distal ends of long bones are called epiphyses, and the middle shaft area composed of compact bone is called the diaphysis. Popular Trending
What does proximal end mean?
Dec 26, 2010 · Epiphyses is the word used for the distal and proximal ends of The epiphysis contains red bone marrow. What are the distal and proximal ends of long bones called? epiphyses Where is the metatarsus?...
What is the difference between lateral and distal?
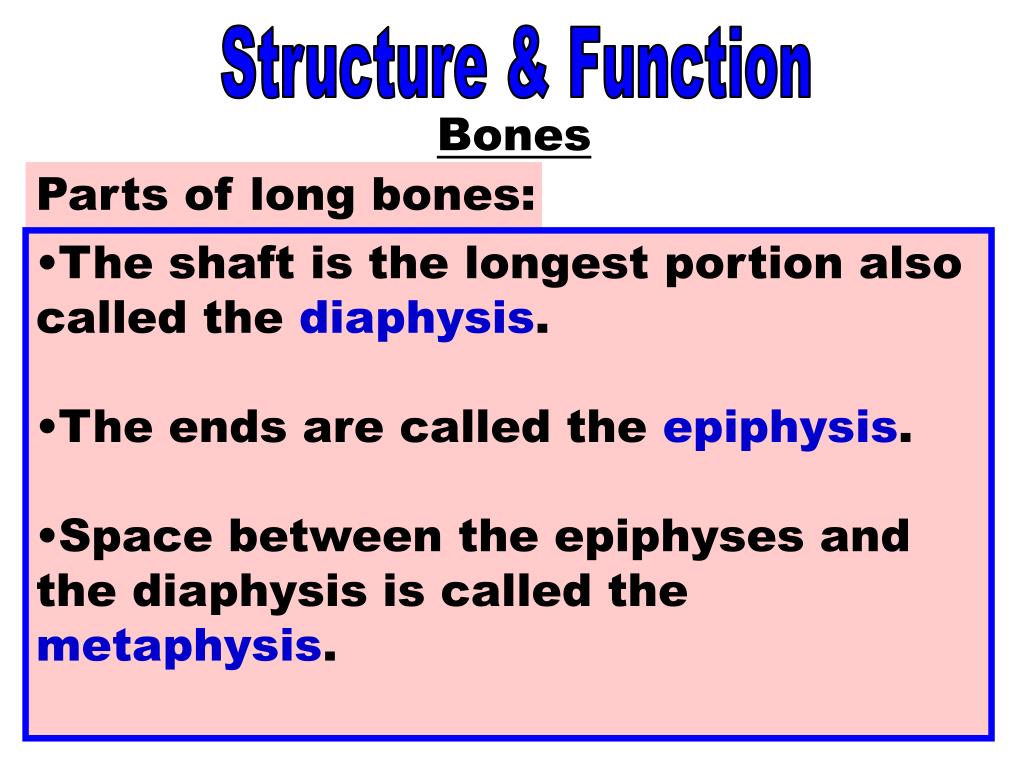
A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The wider section at each end of the bone is called the epiphysis (plural = epiphyses), which is filled with spongy bone.A long bone has two parts: the diaphysisdiaphysisThe diaphysis is the main or midsection (shaft) of a long bone.
What bone is distal to the femur?
The intervening cancellous tissue is called the diploë. What are the regions of a long bone? A long bone has two main regions: the diaphysis and the epiphysis (Figure 6.3. 1). The diaphysis is the hollow, tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone.

What are the proximal and distal ends of a long bone?
What are the ends of a long bone called?
Where is compact bone located?
Compact bone – Also known as cortical bone, compact bone is thick and strong, situated just beneath the periosteum and meeting at the endosteum (the border of the medullary cavity). In the illustration, a portion of periosteum has been peeled back to reveal compact bone beneath.
What is compact bone?
Compact bone is comprised of numerous passages allowing for blood vessels and nerves. A layer of osteoblast and osteoclast cells surround cortical bone along the cambrium. Osteoblasts produce a combination of minerals to form additional layers of cortical bone when stress is applied. Medullary cavity – The medullary cavity is the central part ...
What is the role of the periosteum in bone growth?
Periosteum – You can think of the periosteum as a thin double-layered skin or membrane that covers the surface of all bones. The periosteum plays a crucial role in bone growth and repair. This essential membrane is attached to bones by strong collagenous fibers called Sharpey’s fibres.
Where is the yellow bone marrow?
Yellow bone marrow can be found in the medullary cavity in the shaft of long bones like the femur. Yellow bone marrow contains mesenchymal stem cells producing skeletal tissues, cartilage, bone, and fat. Yellow bone marrow has a gelatinous, sponge-like consistency and carotenoid is responsible for the yellow color.
What is spongy bone?
Spongy bone with red bone marrow – Spongy bone is intricate in appearance. It’s a vast and nearly seamless pattern of tissue that remains strong against multidirectional lines of force. Although extremely porous, spongy bone makes up the majority of interior bone density and is highly vascularized. In adults, all red marrow is found only in ...
Where is red bone marrow found?
In adults, all red marrow is found only in the proximal ends of the long bones of the limbs like the femur (as shown in the illustration) and in the breastbone, spine, ribs, shoulder blades, pelvis, and skull. In babies, all bone marrow is red. 1.
Why are long bones important?
Besides having a significant length vs width when compared to most other bones, long bones are also responsible for supporting weight and are facilitators of motion. These combined characteristics set long bones apart from other bones in the human body.
What is a long bone?
Long bone anatomy. A long bone is a bone that has greater length than width. A long bone has a shaft and 2 ends. Long bones have a thick outside layer of compact bone and an inner medullary cavity containing bone marrow. The ends of a long bone contain spongy bone and an epiphyseal line. The epiphyseal line is a remnant ...
What is the structure of a long bone?
Long bone structure. A typical long bone consists of the following parts: The diaphysis (growing between) is the shaft of a long bone — the long, cylindrical, main portion of the bone. The epiphyses (growing over; singular is epiphysis) are the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The metaphyses (between; singular is metaphysis) ...
How long does it take for a greenstick fracture to heal?
Most greenstick fractures require four to eight weeks for complete healing, depending on the break and the age of the child.
What is it called when a bone breaks?
Open fracture or compound fracture. If a bone breaks in such a way that bone fragments stick out through the skin or a wound penetrates down to the broken bone, the fracture is called an open or compound fracture . Open fractures often involve much more damage to the surrounding muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
What is the epiphyseal line?
The epiphyseal line is a remnant of an area that contained hyaline cartilage that grew during childhood to lengthen the bone. Long bones contain yellow bone marrow and red bone marrow, which produce blood cells. The thigh bone (femur) is a long bone.
What is the metaphysis?
The metaphyses (between; singular is metaphysis) are the regions between the diaphysis and the epiphyses. In a growing bone, each metaphysis contains an epiphyseal (growth) plate, a layer of hyaline cartilage that allows the diaphysis of the bone to grow in length. When a bone ceases to grow in length at about ages 14–24, ...
What is the articular cartilage?
The articular cartilage is a thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering the part of the epiphysis where the bone forms an articulation (joint) with another bone. Articular cartilage reduces friction and absorbs shock at freely movable joints.
