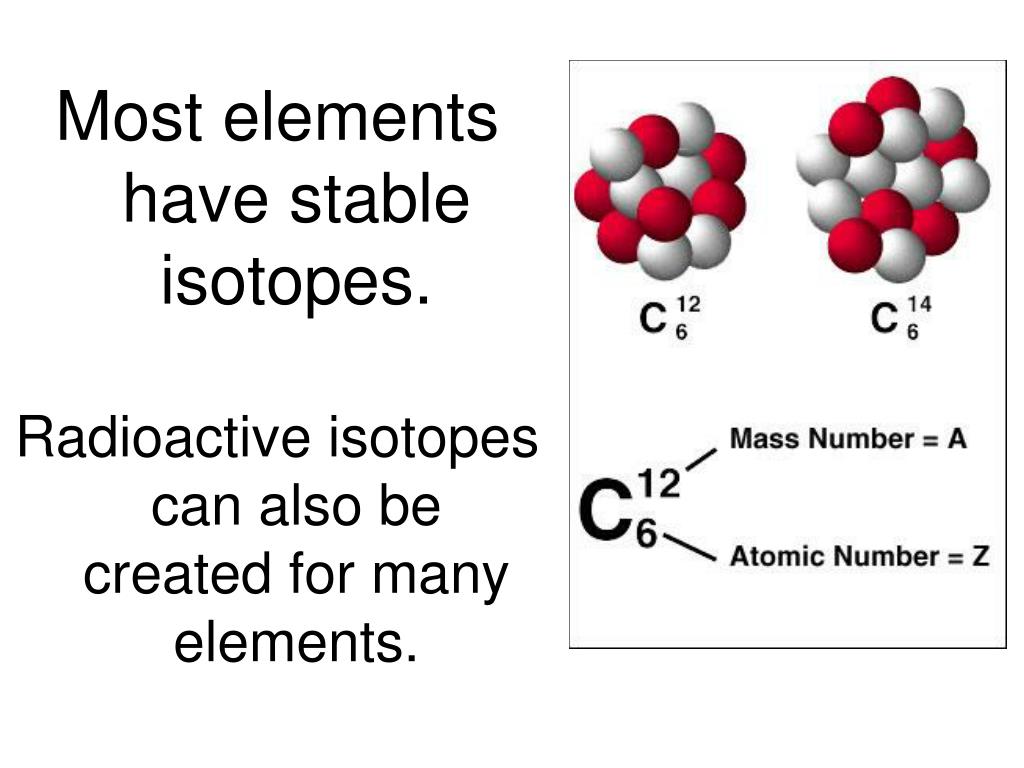
Radioactive Elements List
| Radioactive Element | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass Number | Decay Type | Half-Life |
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | 3 | Beta Decay (β –) | 12.32 years |
| Beryllium (Be) | 4 | 7 | Electron Capture (ε), Gamma Decay) | 53.12 Days |
| Beryllium (Be) | 4 | 8 | Alpha | 7 x 10 -17 sec |
| Beryllium (Be) | 4 | 10 | Beta Decay (β –) | 1,360,000 years |
What do elements tend to be radioactive?
Radioactivity is the physical phenomenon of certain elements - such as uranium - of emitting energy in the form of radiation.This energy comes from the decay of an unstable nucleus. Any nuclear species (particular configuration of protons, neutrons and energy) that exhibit radioactivity are known as radioactive nuclei.Additionally, radioactivity or simply activity can be used as a measurement ...
What periodic table elements are radioactive?
There are radioactive isotopes of elements starting with #1, hydrogen, whose naturally-occurring isotope H-3, also called tritium, is radioactive. Many more elements have naturally-occurring radioactive isotopes, such as carbon-14 and potassium-40.
What are the three types of radioactive materials?
Types of Radioactive Emissions: There are three kinds of radioactive emissions: (a) Alpha particles (α-particles) (b) Beta particles (β-particles) (c) Gamma rays (γ-rays) Alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays can be represented diagramatically as in Figure 5.9: An alpha particle: (a) is a helium nucleus.
What are all the radioactive elements on the periodic table?
The periodic table above is a visual representation of the data in the table below. How many radioactive are there? There are four major types of radiation: alpha, beta, neutrons, and electromagnetic waves such as gamma rays. They differ in mass, energy and how deeply they penetrate people and objects.
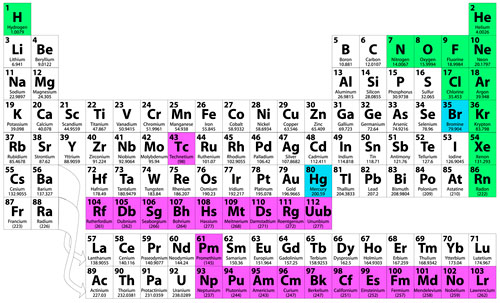
Where are the radioactive elements on the periodic table?
Keep in mind, all elements can have radioactive isotopes. If enough neutrons are added to an atom, it becomes unstable and decays....Radioactive Elements.ElementMost Stable IsotopeHalf-life of Most Stable IsotopePromethiumPm-14517.4 yearsPoloniumPo-209102 yearsAstatineAt-2108.1 hoursRadonRn-2223.82 days33 more rows•Jul 30, 2019
What are the most radioactive elements called?
Polonium. Because it is a naturally-occurring element that releases a huge amount of energy, many sources cite polonium as the most radioactive element. Polonium is so radioactive it glows blue, which is caused by excitation of the gas particles by radiation.
How many radioactive elements are there?
There are 38 radioactive elements.
Can u touch uranium?
With a half-life of 4 billion years, uranium is only very weakly radioactive. In fact, since uranium is a heavy metal, its chemical toxicity is actually more of a danger than its radioactivity. If you touch it directly with your hands, you should wash your hands afterwards. You should not eat it.
What is the strongest radioactive element?
PoloniumAtomic number (Z)84Groupgroup 16 (chalcogens)Periodperiod 6Blockp-block42 more rows
What's the most radioactive thing on Earth?
The Most Radioactive Places on EarthUranium: 4.5 billion years.Plutonium 239: 24,300 years.Plutonium 238: 87.7 years.Cesium 137: 30.2 years.Strontium-90: 28-years.
Is uranium the most radioactive element?
The radioactivity of radium then must be enormous. This substance is the most radioactive natural element, a million times more so than uranium.
Which element has the most isotopes?
All elements have a number of isotopes. Hydrogen has the fewest number of isotopes with only three. The elements with the most isotopes are cesium and xenon with 36 known isotopes.
What is a radioactive element?
Some elements of atomic nuclei are unstable because of the presence of excess nuclear charge inside it so these nuclei undergo radioactive decay to...
What are the 4 radioactive elements?
The common 4 radioactive elements are Uranium, Radium, Polonium, Thorium etc.
Are smokers lungs radioactive?
Cigarettes made from tobacco contain radioactive materials: polonium-210 and lead-210. These radioactive particles settle in smokers’ lungs, where...
What is uranium used for?
U-235 and U-238 occur naturally in nearly all rock, soil, and water. Uranium is now used to power commercial nuclear reactors that produce electric...
What are the examples of radioactive waste?
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Any activity related to the nuclear fuel cycle that produces or...
Where are radioactive elements produced?
These radioactive elements are produced in nuclear reactors and accelerators . There are different strategies used to form new elements. Sometimes elements are placed within a nuclear reactor, where the neutrons from the reaction react with the specimen to form desired products.
Which isotopes can decay to form secondary radionuclides?
For example, primordial isotopes thorium-232, uranium-238, and uranium-235 can decay to form secondary radionuclides of radium and polonium. Carbon-14 is an example of a cosmogenic isotope. This radioactive element is continually formed in the atmosphere due to cosmic radiation.
Where Do Radionuclides Come From?
Radioactive elements form naturally, as a result of nuclear fission, and via intentional synthesis in nuclear reactors or particle accelerators.
How do radionuclides affect organisms?
Radioactivity exists in nature, but radionuclides can cause radioactive contamination and radiation poisoning if they find their way into the environment or an organism is over-exposed. 1 The type of potential damage depends on the type and energy of the emitted radiation.
What is the name of the product produced by nuclear fission?
Nuclear fission from nuclear power plants and thermonuclear weapons produces radioactive isotopes called fission products. In addition, irradiation of surrounding structures and the nuclear fuel produces isotopes called activation products. A wide range of radioactive elements may result, which is part of why nuclear fallout and nuclear waste are so difficult to deal with.
What are some examples of radionuclides?
In other cases, particle accelerators bombard a target with energetic particles. An example of a radionuclide produced in an accelerator is fluorine-18. Sometimes a specific isotope is prepared in order to gather its decay product. For example, molybdenum-99 is used to produce technetium-99m.
Which element has no stable isotopes?
A good example of this is tritium, a radioactive isotope of hydrogen naturally present at extremely low levels. This table contains the elements that have no stable isotopes. Each element is followed by the most stable known isotope and its half-life . Note increasing atomic number doesn't necessarily make an atom more unstable.
What is radioactive element?
A radioactive element is one with an unstable nucleus, which radiates alpha, beta or gamma radiation and gets converted to a stable element. This article has a comprehensive list of radioactive elements and their properties. Home / Uncategorized / List of Radioactive Elements. Like it?
Why is radioactivity called radioactivity?
The name ‘radioactivity’ is a misnomer because these elements have nothing to do with radio waves! The reason is that energy and frequency of a gamma ray which is emitted by a radioactive element, is far beyond that of the radio band of electromagnetic spectrum! So, we are just stuck up with the name!
How many protons does Uranium have?
In a nucleus like Uranium, which has almost 92 protons, coulomb repulsive force becomes too much for the nuclear force to contain. Subsequently, the nucleus is very unstable and radioactive decay occurs and Uranium decays into a more stable element.
What are radioactive isotopes used for?
These radioactive isotopes have a lot of applications today, ranging from medicine to atomic energy. Since these radioactive elements are harmful, burning up radioactive waste or disposing it, is difficult. Every development in science and technology brings in new problems. Now, it’s for us to decide, how we intend to use the power of technology placed in our hands.
What is the difference between electron and positron?
Electron emission causes an increase in the atomic number by 1, while positron emission causes a decrease in the atomic number by 1. In some cases, double beta decay may occur, involving the emission of two beta particles.
How long have radioactive isotopes been around?
15.6 million years. These radioactive isotopes have a lot of applications today, ranging from medicine to atomic energy. Since these radioactive elements are harmful, burning up radioactive waste or disposing it, is difficult. Every development in science and technology brings in new problems.
How to understand radioactivity?
To understand radioactivity, we need to explore the structure of an atomic nucleus. Every nucleus contains neutrons as well as protons. Neutrons are neither positively charged, nor negatively charged, they are neutral particles. Protons are positively charged.
What is the radioactive element that can be found in soil, air, water, rocks, plants, and food?
Uranium. Uranium is a radioactive element that can be found in soil, air, water, rocks, plants and food. Uranium decays or breaks down very slowly into other elements including radium and radon. Learn more about uranium in drinking water.
What are the elements that give off energy called?
Radioactive Elements Found in the Environment. Radioactive Elements Found in the Environment. Radioactive materials give off a form of energy called ionizing radiation. When a person comes in contact with radiation, the energy may be absorbed by the body.
What is alpha radiation?
Alpha radiation is a type of energy released when certain radioactive elements decay or break down. For example, uranium and thorium are two radioactive elements found naturally in the Earth’s crust. Over billions of years, these two elements slowly change form and produce decay products such as radium and radon.
Where does radon come from?
Radon is a radioactive gas that has no color, smell or taste. Radon comes from the decay of uranium, which is a radioactive element found naturally in the Earth’s crust. Over billions of years, uranium decays into radium, and eventually into radon.
Where is polonium produced?
It can be produced in university or government nuclear reactors, but it requires expertise to do so.
Is Po-210 a radiation hazard?
Po-210 only becomes a radiation hazard if it gets inside the body through breathing, eating or by entering through a wound. This internal contamination can cause irradiation of organs, which can result in serious medical symptoms or death. Po-210 and its radiation do not get through intact skin or membranes. It is not an external hazard to the body . Most traces can be removed through careful washing.
What is radioactivity in science?
radioactivity, property exhibited by certain types of matter of emitting energy and subatomic particles spontaneously. It is, in essence, an attribute of individual atomic nuclei. An unstable nucleus will decompose spontaneously, or decay, into a more stable configuration but will do so only in a few specific ways by emitting certain particles ...
What are the two types of radioactivity associated with uranium and thorium?
The early work on natural radioactivity associated with uranium and thorium ores identified two distinct types of radioactivity: alpha and beta decay.
What are the particles that are responsible for radioactive decay?
The emissions of the most common forms of spontaneous radioactive decay are the alpha (α) particle, the beta (β) particle, the gamma (γ) ray, and the neutrino. The alpha particle is actually the nucleus of a helium-4 atom, with two positive charges 4/2 He. Such charged atoms are called ions.
What is radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay is a property of several naturally occurring elements as well as of artificially produced isotopes of the elements. The rate at which a radioactive element decays is expressed in terms of its half-life; i.e., the time required for one-half of any given quantity of the isotope to decay.
What is the antiparticle of the electron?
The beta plus particle, also called the positron, is the antiparticle of the electron; when brought together, two such particles will mutually annihilate each other. Gamma rays are electromagnetic radiations such as radio waves, light, and X-rays.
What is the term for the element that emits ionizing radiation?
Elements that emit ionizing radiation are called radionuclides. When it decays, a radionuclide transforms into a different atom - a decay product. The atoms keep transforming to new decay products until they reach a stable state and are no longer radioactive.
What is radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay is the emission of energy in the form of ionizing radiation ionizing radiation Radiation with so much energy it can knock electrons out of atoms. Ionizing radiation can affect the atoms in living things, so it poses a health risk by damaging tissue and DNA in genes.. The ionizing radiation that is emitted can include alpha particles alpha particle A form of particulate ionizing radiation made up of two neutrons and two protons. Alpha particles pose no direct or external radiation threat; however, they can pose a serious health threat if ingested or inhaled., beta particles beta particle A form of particulate ionizing radiation made up of small, fast-moving particles. Some beta particles are capable of penetrating the skin and causing damage such as skin burns. Beta-emitters are most hazardous when they are inhaled or swallowed. and/or gamma rays gamma rays A form of ionizing radiation that is made up of weightless packets of energy called photons. Gamma rays can pass completely through the human body; as they pass through, they can cause damage to tissue and DNA.. Radioactive decay occurs in unbalanced atoms called radionuclides.
What is gamma radiation?
gamma rays A form of ionizing radiation that is made up of weightless packets of energy called photons. Gamma rays can pass completely through the human body; as they pass through, they can cause damage to tissue and DNA. . Radioactive decay occurs in unbalanced atoms called radionuclides.
How long does a radionuclide decay?
Every radionuclide has a specific decay rate, which is measured in terms of ". half-life. half-life The time required for half of the radioactive atoms present to decay or transform. Some radionuclides have half-lives of mere seconds, but others have half-lives of hundreds or millions of years. .".
What are alpha particles?
alpha particles A form of particulate ionizing radiation made up of two neutrons and two protons. Alpha particles pose no direct or external radiation threat; however, they can pose a serious health threat if ingested or inhaled. ,
Is each series of radionuclides radioactive?
Each series has its own unique decay chain. The decay products within the chain are always radioactive. Only the final, stable atom in the chain is not radioactive. Some decay products are a different chemical element. Every radionuclide has a specific decay rate, which is measured in terms of ".
Is an element stable or unstable?
Some of these forms are stable; other forms are unstable. Typically, the most stable form of an element is the most common in nature. However, all elements have an unstable form. Unstable forms emit ionizing radiation and are radioactive.
What are radioactive forms of elements called?
Radioactive forms of elements are called radionuclide radionuclide Radioactive forms of elements are called radionuclides . Radium-226, Cesium-137, and Strontium-90 are examples of radionuclides. s. Some occur naturally in the environment, while others are man-made, either deliberately or as byproducts of nuclear reactions. Learn the Radiation Basics.
What is the half life of a radioactive atom?
Radioactive half-life is the time required for half of the radioactive atoms present to decay. Radioactive decay is when a radioisotope transforms into another radioisotope; this process emits radiation in some form. Some radionuclides have half-lives of mere seconds, but others have half-lives of millions of years.
How long do radionuclides have?
Some radionuclides have half-lives of mere seconds, but others have half-lives of millions of years. Learn more about radioactive decay. Below you will find links to basic information about twelve radionuclides encountered in medical, commercial, and military activities.
What is the unit of decay of radioactive material?
Activity (radioactivity): the rate of decay of radioactive material expressed as the number of atoms breaking down per second measured in units called becquerels or curies.
What is the atomic number of an atom?
Atomic number: the total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Atomic mass unit (amu): 1 amu is equal to one twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. Atomic mass number: the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Atomic weight: the mass of an atom, expressed in atomic mass units.
How long does it take to die from a dose of radiation?
Hair loss, bleeding, swelling of the mouth and throat, and general loss of energy may follow. If the exposure has been approximately 1,000 rads or more, death may occur within 2 – 4 weeks. For more information, see CDC’s fact sheet “Acute Radiation Syndrome” at emergency.cdc.gov/radiation/ars.htm.
How does a fission chain reaction work?
A fission chain reaction is self-sustaining when the number of neutrons released in a given time equals or exceeds the number of neutrons lost by absorption in non-fissile material or by escape from the system.
What are beta particles?
Beta particles: electrons ejected from the nucleus of a decaying atom. Although they can be stopped by a thin sheet of aluminum, beta particles can penetrate the dead skin layer, potentially causing burns. They can pose a serious direct or external radiation threat and can be lethal depending on the amount received.
Is iodine a solid or a nonmetallic element?
Iodine: a nonmetallic solid element. There are both radioactive and non-radioactive isotopes of iodine. Radioactive isotopes of iodine are widely used in medical applications. Radioactive iodine is a fission product and is the largest contributor to people’s radiation dose after an accident at a nuclear reactor.
Which atom has fewer or more electrons than it has protons?
Ion: an atom that has fewer or more electrons than it has protons causing it to have an electrical charge and, therefore, be chemically reactive.
