
Other answers from study sets
- 1. Occurs in the matrix
- 2. Reactants = 2 acetyl CoA, 2 ADP, 2 Pi, 6 NAD+, 2 FAD
- 3. Products = 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 4 CO2
- 4. For every acetyl-CoA that enters the Krebs cycle, the cycle turns once. For every glucose molecule that starts cell respiration, 2 pyruvates are formed, forming 2 acetyl CoAs, thus turning the Krebs cycle twice
What is needed for the Krebs cycle to occur?
Krebs Cycle Steps. It is an eight-step process. Krebs cycle or TCA cycle takes place in the matrix of mitochondria under aerobic condition. Step 1: The first step is the condensation of acetyl CoA with 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate to form 6C citrate, coenzyme A is released. The reaction is catalysed by citrate synthase.
What is the function of Krebs cycle?
The main function of the Krebs cycle is to produce energy, stored and transported as ATP or GTP. The cycle is also central to other biosynthetic reactions where the intermediates produced are required to make other molecules, such as amino acids, nucleotide bases and cholesterol.
Which molecules can enter the Krebs cycle?
- pyruvate. This pyruvate then undergoes a reaction to form Acetyl CoA. ...
- acetyl CoA formed then enters the Kreb's cycle to combine with oxaloacetate
- to form citrate or citric acid. ...
- and a single glycerol molecule are termed monoglycerides. ...
- linked to glycerol via an ester bond. ...
- triglycerides. ...
- oxidation of fatty acids. ...
- fatty acids. ...
What are the enzymes involved in Krebs cycle?
The citrate synthase is an enzyme widely used as a biomarker for the presence of intact mitochondria in cell cultures or organelle preparations. Despite being a mitochondrial enzyme it is encoded by nuclear DNA and synthesized in the cytosol. This enzyme is the first regulatory enzyme in the Krebs cycle.
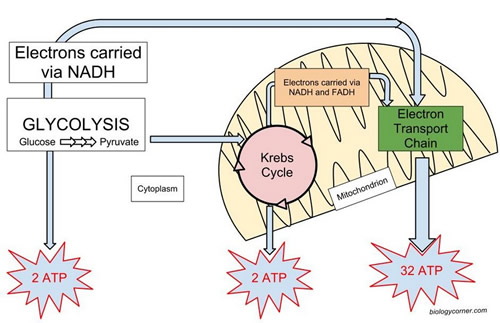
What are reactants and products of Krebs cycle?
During the first step of Krebs cycle, oxalo acetic acid reacts with acetyl CoA to form citric acid. As Krebs cycle is a cyclic pathway, the initial reactant oxalo acetic acid also acts as final product of the cycle.
What are the 4 reactants of the Krebs cycle?
It is also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle. It is a series of chemical reactions required for cellular respiration; it involves redox, dehydration, hydration, and decarboxylation reactions that produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), a coenzyme energy carrier for cells.
What are two reactants of the Krebs cycle?
It is the respiratory cycle that is responsible for production of large quantities of ATP and consumption of oxygen. In addition, the respiratory cycle converts NADH and FADH2 into reactants that the Krebs cycle requires to function.
What are the reactions in Krebs cycle?
There are only 4 types of reactions in the Krebs Cycle: Condensation, Hydration/Dehydration, Redox, and Substrate level phosphorylation. All enzymes/coenzymes can be found in the mitochrondia of eukaryotes and the cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochrondia.
Is NADH a reactant or product?
Glucose is the reactant; while ATP and NADH are the products of the Glycolysis reaction.
What are the products of the Kreb cycle quizlet?
What are the Krebs Cycle products? Electron Carriers (NADH and FADH2), ATP, and Carbon Dioxide.
What reactants are required for the citric acid cycle?
The Citric Acid Cycle reactants include pyruvic acid, oxaloacetic acid, succinic acid, fumarate and malate. In the first stage, pyruvic acid is oxidized into a molecule called acetyl-coenzyme A.
1. What is the Krebs Cycle?
Also known as the citric acidity cycle, Kreb’s cycle is a chain of reactions occurring in the mitochondria, through which almost all living cells p...
2. How Many ATP are Produced in Krebs Cycle?
2 ATPs are produced in one Krebs Cycle. For complete oxidation of a glucose molecule, the Krebs cycle yields \[4 CO_{2}\], 6NADH, \[2 FADH_{2}\], a...
3. Where Does Krebs Cycle Occur?
Mitochondrial matrix. In all eukaryotes, mitochondria are the site where the Krebs cycle takes place. The cycle takes place in a mitochondrial matr...
4. How does the Krebs Cycle Works?
It is an Eight-Step ProcessCondensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate (4C) forming citrate (6C), coenzyme A is released.Conversion of Citrate to...
5. Why is Krebs Cycle Called an Amphibolic Pathway?
It is called amphibolic as in the Krebs cycle both catabolism and anabolism take place. The amphibolic pathway indicates the one involving both cat...
6. What is the Krebs cycle?
The Krebs cycle is a process that occurs in one of the most significant reaction sequences in biochemistry is the Krebs cycle, commonly known as th...
7. What is the biochemistry of muscle mitochondria?
The hydrogen atoms (or the electrons derived from them) do not react directly with oxygen in the Krebs cycle oxidation processes; instead, they tra...
8. What is the biochemistry of muscle mitochondria?
The steps in the Krebs cycle are:The TCA cycle starts with an enzymatic aldol addition reaction of acetyl CoA to oxaloacetate, which results in the...
9. What is the efficiency of the Krebs cycle?
The theoretical maximal yield of ATP from glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation is 38. Glycolysis, which occurs in the c...
10. What is the role of the Krebs cycle in the metabolism of carbohydrates?
The role of mitochondria in oxidative phosphorylation has already been discussed, as has their role in carbohydrate metabolism due to the presence...
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process responsible for converting chemical energy, and the reactants/products involved in cellular respiration are oxygen, glucose (sugar), carbon dioxide, and water. While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration.
What is released during the citric acid cycle?
Carbon dioxide is released during the citric acid cycle, and ATP, FADH2, and NADH are produced here. The electrons within FADH2 and NADH are then sent to the next portion of the cellular respiration process, the electron transport chain.
How do plants release carbon dioxide?
Carbon dioxide is released by many different microorganisms during not only the process of cellular respiration but also the process of fermentation. Plants use carbon dioxide to create their own energy, much as heterotrophic organisms use glucose and oxygen to create energy. The carbon dioxide will enter the cells of the plant through small holes in the leaves referred to as stomata. After the carbon dioxide has entered the cells of the plant, the chloroplasts within the cell will begin the process of photosynthesis and create carbohydrates as a result.
What is the chemical formula for glucose?
Glucose, or sugar, has the chemical formula C6H12O6. While this formula can potentially be applied to a variety of different molecules, depending on how the atoms within the molecule are arranged, most molecules with this chemical formula are sugars of one form or another. The most notable formation of C6H12O6 is glucose, which is sometimes referred to as blood sugar or dextrose. The cells of animals convert glucose into a substance known as pyruvate through a process called glycolysis. The glycolysis process takes glucose and generates two molecules of ATP, or energy, with it.
How does glucose convert into pyruvate?
The cells of animals convert glucose into a substance known as pyruvate through a process called glycolysis. The glycolysis process takes glucose and generates two molecules of ATP, or energy, with it. Dioxygen, frequently just called oxygen, it made up of two oxygen atoms and it is what vertebrates used to breathe.
What is the relationship between oxygen and glucose?
In plain English, this can be read as: Glucose + oxygen –> carbon dioxide + water + energy. During the course of cellular respiration, oxygen and glucose are utilized to create carbon dioxide, water, and energy. The oxygen that an organism breathes in is used to break down the sugars found in food.
How does oxygen break down sugar?
The oxygen that an organism breathes in is used to break down the sugars found in food. This produces heat energy, similar to how burning a piece of wood releases heat. With cellular respiration, after oxygen breaks down the sugar and its energy is released, carbon dioxide is released as a byproduct.
Why is the acetyl-coa cycle called a cycle?
It is a cycle because the 4 carbon molecule produced in the last step is the same molecule that accepts the Acetyl-CoA in the first step.
What happens to the carbons in Pyruvic Acid?
So 1 carbon atom from Pyruvic Acid becomes part of a molecule of carbon dioxide, which gets released to the air. Then the other 2 carbon atoms from Pyruvic Acid, are going to rearrange and form Acetic Acid. The Acetic Acid is joined to a compound called Coenzyme A. The resulting molecule is called Acetyl-CoA then enters the Krebs Cycle. 2 high-energy electrons are passed to NAD+ to produce NADH. Then, the 2 carbons from Acetyl-CoA are added to a 4 carbon molecule that is already present in the cycle, producing a 6 carbon molecule called Citric Acid.
How many carbons are in a molecule of citric acid?
Citric Acid is broken down into a 4 carbon molecule, more carbon dioxide is released, and electrons are transferred to energy carriers. So 1 carbon atom is removed from the 6 carbon atoms in Citric Acid, and then another is released, releasing 2 molecules of carbon dioxide and leaving a 4 carbon molecule.
What is pyruvic acid broken down into?
Pyruvic Acid is broken down into Carbon Dioxide, in a series of energy extracting reactions.
What is the Krebs cycle?
The Krebs cycle – also called the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle – is the first step in the aerobic pathway, and it operates to continually synthesize enough of a substance called oxaloacetate to keep the cycle going, although, as you'll see , this is not really the cycle 's "mission.".
What is the purpose of the Krebs cycle?
Its purpose is to collect high-energy electrons for use in the electron transport chain reactions. The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
How many carbon atoms does Oxaloacetate pick up?
Oxaloacetate picks up two carbon atoms when it combines with acetyl CoA, but these two atoms are lost in the first half of the Krebs cycle as CO2in successive reactions in which NAD+ is also reduced to NADH. (In chemistry, to simplify somewhat, reduction reactions add protons while oxidation reactions remove them.)
How is pyruvate converted to lactic acid?
In prokaryotes as well as in all eukaryotes but yeast, if there is no oxygen available or if the cell's energy needs cannot be fully met through aerobic respiration, pyruvate is converted to lactic acid via fermentation under the influence of the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase, or LDH.
How is glucose phosphorylated?
In the reactions of glycolysis, the six-carbon glucose is initially phosphorylated – that is, it has a phosphate group appended to it . The resulting molecule is a phosphorylated form of fructose (fruit sugar). This molecule is then phosphorylated a second time. Each of these phosphorylations requires a molecule of ATP, both of which are converted to adenosine diphosphate, or ADP. The six-carbon molecule is then converted into two three-carbon molecules, which are quickly converted to pyruvate. Along the way, in the processing of both molecules, 4 ATP are produced with the help of two molecules of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) that are converted to two molecules of NADH. Thus for every glucose molecule that enters glycolysis, a net of two ATP, two pyruvate and two NADH are produced, while two NAD+ are consumed.
Where does pyruvate move?
Pyruvate destined for the Krebs cycle moves from the cytoplasmacross the membrane of cell organelles (functional components in the cytoplasm) called mitochondria . Once in the mitochondrial matrix, which is a sort of cytoplasm for the mitochondria themselves, it is converted under the influence of the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase to a different three-carbon compound called acetyl coenzyme A or acetyl CoA. Many enzymes can be picked out from a chemical line-up because of the "-ase" suffix they share.
What is the name of the trio of carboxyl groups that make up tricarboxylic acid?
Citrate, a symmetrical molecule, includes three carboxyl groups, which have the form (-COOH) in their protonated form and (-COO-) in their unprotonated form. It is this trio of carboxyl groups that lends the name "tricarboxylic acid" to this cycle.
How many pyruvate molecules are in a Krebs cycle?
So, for every 1 pyruvate molecule added, the Krebs cycle will produce: A molecule of glucose contains 2 pyruvate molecules, so 1 glucose molecule will produce double the amount of products listed above as it moves through the Krebs cycle.
Which part of the mitochondria has the required enzymes and environment for the complex reactions of the Krebs cycle to take place?
The mitochondrial matrix has the required enzymes and environment for the complex reactions of the Krebs cycle to take place. Further, the products of the Krebs cycle drive the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation, both of which occur in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Where Does the Krebs Cycle Take Place?
The Krebs cycle happens only within the mitochondrial matrix. Pyruvate is formed in the cytosol of the cell, then imported into the mitochondria. Here, it is converted to acetyl CoA and imported into the mitochondrial matrix. The mitochondrial matrix is the innermost part of the mitochondria. The graphic below shows the different parts of mitochondria.
What is the process of converting pyruvate into acetyl CoA?
Before the first stages of the Krebs cycle, pyruvate is converted into acetyl CoA. During this process, one molecule of CO 2 and one molecule of the electron carrier NADH are produced. The Krebs cycle involves converting this acetyl CoA into carbon dioxide. During the steps of the cycle, two molecules of CO 2 are released, ...
What is pyruvate converted to?
Pyruvate is then converted to acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA is then utilized within the Krebs cycle to produce several major products. In turn, these products then drive the formation of ATP, the cell’s main energy source. Before the first stages of the Krebs cycle, pyruvate is converted into acetyl CoA. During this process, one molecule ...
What is the first step of the Krebs cycle?
Krebs Cycle Products. The first step of utilizing glucose, glycolysis, produces a few ATP as well as the molecules which will be processed with the Krebs cycle. During glycolysis , a single glucose molecule is split into two smaller, three-carbon molecules called pyruvate. Pyruvate is then converted to acetyl CoA.
Why is the Krebs cycle important?
The Krebs cycle is likely the most important part of the process of aerobic respiration because it drives the formation of electron carriers. These carriers are important. They carry the energy used to create a large number of ATP molecules in the final steps of aerobic respiration.
