
Special VFR Requirements:
- Special VFR must be specifically requested by the pilot but differ based on if an aircraft is fixed wing, or rotary wing
- Fixed Wing Requirements: Day Considerations: Operations performed under Part 91 ATC Clearance (before entering...
- Day Considerations: Operations performed under Part 91 ATC Clearance (before entering controlled...
- VFR during the day
- IFR at night
What are the basic VFR minimums?
the basic VFR weather minimums for operating an aircraft within class D airspace are VFR flight in controlled airspace above 1200 feet AGL and below 10,000 feet MSL requires a minimum visibility and vertical cloud clearance of 3 miles, and 500 feet below or 1000 feet above the clouds in controlled airspace.
What are VFR fuel requirements?
VFR Fuel requirements (airplanes and helicopters): Day: You need enough fuel to fly to your first landing point and then still have 30 minutes of fuel remaining at a normal cruise speed. Night: Same as above, but you need 45 minutes after reaching your first point. Helicopters: Same as above but you need 20 minutes regardless of day or night ...
What is the minimum ceiling for VfR?
Ceiling Minimums Basic VFR flight is limited to flight with a ceiling of 1,000 ft. within the lateral boundaries of controlled airspace. In other words, you cannot takeoff from an airport that has controlled airspace to the surface, when the ceiling at that airport is less than 1,000 ft.
When is VFR flight not allowed?
VFR flight is not allowed in airspace known as class A, regardless of the meteorological conditions except after failure of two way radio communications or during declared emergencies such as VFR traffic attempting to avoid severe weather formations.

What does a Special VFR clearance allow?
Special VFR clearances allow VFR pilots to land at surface E, class D, and some C and B airports when the field is IFR, but only if the pilot can maintain clear of clouds and the visibility is at least 1 SM.
Does Special VFR require instrument rating?
While the clearance issued by ATC is similar to an instrument clearance and must be read back by the pilot, an instrument rating is not required for special VFR. However, if the request is made between sunset and sunrise, the pilot requesting the clearance needs to be a current instrument pilot.
What is the minimum visibility required for Special VFR flight?
14 CFR Section 91.157 prohibits VFR aircraft (other than helicopters) from landing at any airport within a surface area when ground visibility is less than 1 mile. A pilot could inadvertently encounter conditions that are below SVFR minimums after entering a surface area due to rapidly changing weather.
What are the minimum requirements for airline operations under Special VFR in D?
What are the minimum requirements for airplane operations under special VFR in Class D airspace at night? The pilot must be instrument rated, and the airplane must be IFR equipped.
Where is Special VFR not allowed?
You can get SVFR into larger airports as well, like Class D, C, and even some B airports. However, many Class C and B airports don't allow SVFR - they're listed in FAR 91, Appendix D, Section 3.
What does Special VFR mean?
Definition. Special VFR is a sub category of Visual Flight Rules (VFR) flight. Permission to operate under Special VFR within a Control Zone, in meteorological conditions not meeting Visual Meteorological Conditions (VMC) minima, is given to a flight by means of an Air Traffic Control clearance.
Can a student pilot fly Special VFR?
Student, Sport and Recreational Pilots may not request Special VFR clearances. Note that typically only one aircraft may operate under a Special VFR clearance at a time in the class B airspace, and ATC reserves the right to deny Special VFR depending upon workload or other operational considerations.
What is the minimum VFR ceiling?
IFR means a ceiling less than 1,000 feet AGL and/or visibility less than three miles. Low IFR (LIFR) is a sub-category of IFR. VFR means a ceiling greater than 3,000 feet AGL and visibility greater than five miles.
What is the minimum flight visibility required?
What minimum visibility and clearance from clouds are required for VFR operations in Class G airspace at 700 feet AGL or below during daylight hours? 1 mile visibility and clear of clouds.
At which airports is fixed wing Special VFR not authorized?
Two-way radio communications equipment, a 4096-code transponder, and an encoding altimeter. (Fig 25) At which airports is fixed-wing Special VFR not authorized? Dallas-Fort Worth International and Dallas Love Field.
Can a student pilot request special VFR in less than VFR conditions?
Student, Sport and Recreational Pilots may not request Special VFR clearances. Note that typically only one aircraft may operate under a Special VFR clearance at a time in the class B airspace, and ATC reserves the right to deny Special VFR depending upon workload or other operational considerations.
Which instrument is not required for a day VFR flight?
Actually, no. VFR flight does not require a radio unless the pilot is operating in controlled airspace. If so, then the FAA requires him/her to have an appropriate radio in the airplane. This is so the pilot can communicate with and get the appropriate clearances from Air Traffic Control (ATC).
At which airport is fixed wing Special VFR not authorized?
Two-way radio communications equipment, a 4096-code transponder, and an encoding altimeter. (Fig 25) At which airports is fixed-wing Special VFR not authorized? Dallas-Fort Worth International and Dallas Love Field.
Does a Cessna 172 have a Mel?
Study Tips. An equipment list is a list of items that must be operational for a particular flight. For example, the landing lights in the Cessna 172 do not have to be operational for flights during the day but must be operational for flights at night.
What is special VFR?
Special VFR is a tool available to any private pilot. Additionally, it is a great tool to avoid inadvertent IMC. ATC will never solicit a Special VFR clearance unless specifically requested by the pilot. At the end of the day however, just because you can do something doesn't mean you should.
How many NM does SVFR apply?
Remember that SVFR only applies within the terminal area (approximately 5 NM around the airfield) and therefore operations outside of this area (usually class E airspace) require VFR minimums be maintained. Use Special VFR with caution, especially at night.
What is SVFR in aviation?
Special VFR, or SVFR, therefore exists as a tool for pilots to continue operating under Visual Flight Rules (VFR) in Instrument Meteorological Conditions (IMC) Said another way, VFR requirements will match those of Class G basic VFR minimums if you are within 1200' of the ground, only requiring 1 mile visibility and clear of clouds, ...
What class of aircraft must remain clear of clouds?
Helicopters must remain clear of clouds and may operate in Class B, Class C, Class D, and Class E surface areas with less than 1 statute mile visibility
Who has the prerogative of permitting completion of a SVFR operation already in progress?
The controller has the prerogative of permitting completion of a SVFR operation already in progress when an IFR aircraft becomes a factor if better overall efficiency will result
Is visibility determined by pilots?
The determination of visibility by a pilot is not an official weather report or an official ground visibility report
Do you need a flight plan to get clearance?
It is not necessary to file a complete flight plan with the request for clearance, but pilots should state their intentions in sufficient detail to permit ATC to fit their flight into the traffic flow
Who Can Get A Special VFR Clearance?
If you're a non-instrument rated private pilot, you can use a Special VFR clearance from sunrise to sunset. But what happens when the sun goes down?
Who Actually Uses Special VFR?
Now that we've covered all of this, who actually uses Special VFR? The Coast Guard, for one. Coastal airports (especially West Coast) often have ceilings under 1,000', but Coast Guard helicopters typically operate lower than 1,000' anyway.
When to transmit SVFR clearance?
Transmit SVFR clearances only for operations within surface areas on the basis of weather conditions. If weather conditions are not reported, transmit an SVFR clearance whenever a pilot advises unable to maintain VFR and requests an SVFR clearance, provided the pilot reports having at least 1-mile flight visibility.
What to do if no agreement exists for SVFR?
If no agreement exists, request clearance from the control facility. State the aircraft's location and route of flight.
What to do if pilot is operating inside surface area and requests SVFR clearance?
If the pilot is operating inside the surface area and requests an SVFR clearance, advise the pilot to maintain VFR and standby for clearance.
What is 14 CFR Part 91?
14 CFR Part 91 prescribes use of officially reported ground visibility as the governing ground visibility for VFR and SV FR operations at airports where it is provided and landing or takeoff flight visibility where it is not.
What to do if the weather is below VFR?
At airports without a commissioned automated weather, or, if the pilot is unable to receive the automated weather broadcast, issue the most current weather report available. Advise the pilot that the weather is below VFR minima, and request the pilot's intentions.
When an aircraft requests a SVFR clearance to enter surface area during periods of SVFR activity, what is?
When an aircraft requests a SVFR clearance to enter surface area during periods of SVFR activity, instruct the pilot to maintain VFR conditions outside surface area pending arrival/recall/departure of SVFR operations.
How far can you see on a plane when transmitting a clearance?
Transmit a clearance to scheduled air carrier aircraft to conduct operations if ground visibility is not less than 1/2 mile.
What is special VFR?
Special VFR was conceived to address certain situations where weather is below VFR minimums, but flights can still be conducted safely. For Special VFR, the minimums are essentially the same as Class G weather minimums, those being at least 1 statue mile visibility and clear of clouds.
Why do pilots need special VFR clearance?
Receiving a Special VFR clearance can give a pilot more flexibility in getting where they need to go if the weather is bad.
How far below clouds do you need to be to fly under VFR?
Generally, most airspace requires aircraft flying under VFR conditions to remain 500’ below clouds.
What does FSS stand for in airports?
If the airport is non-towered, calling up the local Flight Service Station (FSS) will allow the pilot to request this type of clearance.
What is the term for flying lower than normally allowed?
This gives pilots more flexibility, and allows them to fly lower than normally allowed, also known as “Scud running.”
Does Air Traffic Control give VFR clearance?
Image: Wikimedia.org. One caveat to this type of clearance is that Air Traffic Control cannot freely give it. It must be specifically requested by the pilot.
Can IFR clearance be requested at night?
This type of clearance can be requested at night, but only if the aircraft and pilot are both rated to operate under Instrument Flight Rules (IFR).
When to consider special VFR?
Only consider it when you are flying from or to an area of excellent weather. Here are some specific examples for appropriate times to consider Special VFR (helicopter pilots have way more leeway): Half the airport is fogged in, but not the runway you are using.
How do you request Special VFR?
Does the airport have a tower and is the tower is open? Also, is the airport in Class G airspace? Because if it is, there is no requirement for a Special VFR clearance.
What is a Special VFR clearance?
Special VFR clearances allow VFR pilots to land at surface E, class D, and some C and B airports when the field is IFR, but only if the pilot can maintain clear of clouds and the visibility is at least 1 SM.
How many statute miles do you need for VFR?
Basic requirements for Special VFR: Before you ask for a clearance you need to know the basics. First, the visibility must be at least 1 statute miles for airplanes and less for helicopters. So, if the METAR says 1/2 mile visibility, you will need to file an IFR flight plan or stay at home as a VFR pilot.
What is the VFR clearance for Class E?
Remember, though, if you end up staying in Class E airspace outside of the airport’s airspace (Class E starts at 700′ or 1200′ AGL), you have to maintain VFR cloud clearances (500′ below, 1000′ above and 2000′ horizontal).
How do you know if a field is IFR?
You will know a field is IFR because the rotating beacon will come on during the day.
How many statute miles do you have to maintain for a flight?
You have to maintain 1 statute miles or 1-mile flight visibility at all times once you receive the clearance.
When flying VFR, do you need to stay in VMC?
When flying VFR, you need to stay in VMC…Visual Meteorological Conditions, and stay out of IMC…Instrument Meteorological Conditions. Let’s start by looking at the cloud clearance and visibility minimums based on which airspace you are flying into and out of.
How far can you fly in VFR?
Basic VFR flight is limited to flight with a ceiling of 1,000 ft. within the lateral boundaries of controlled airspace. In other words, you cannot takeoff from an airport that has controlled airspace to the surface, when the ceiling at that airport is less than 1,000 ft. This would include Class B, Class C, Class D, and some Class E airports.
What Is Marginal VFR (MVFR)?
Another term you’ll sometimes hear in aviation is Marginal VFR (MVFR). This is a term used on meteorological reports and charts. The Weather Depiction Chart is an example of a meteorological chart where the term is used. It is not a term used for establishing VFR weather minimums.
What makes a ceiling for VFR flight?
There you have it. If an airport is reporting the clouds to be broken or overcast, that makes a ceiling for VFR flight.
What to do if ground visibility is not reported?
If ground visibility is not reported, use the flight visibility (visibility from cockpit of aircraft in takeoff position if the airport is a satellite airport that does not have weather reporting capabilities)
What is the Class G night exception?
Under 1,200 ft AGL, if the visibility is less than 3 statute miles but not less than 1 statute mile, during night hours, you may operate within an airport traffic pattern, ½ mile of the runway, and stay clear of clouds.
Where to make VFR clearance?
Requests for Special VFR clearances should be made to the tower of the primary airport inside the airspace by radio or telephone. If at a Class E airport surface area, the request can be made to a Flight Service Station or center facility.
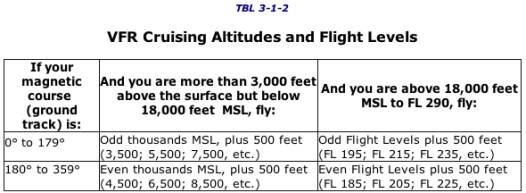
What Is Special VFR?
Why Would I Want to Ask For A Special VFR Clearance?
- Let’s say you’re on the way to the airport for a pleasure flight. Checking the weather, it is cloudy with somewhat limited visibility, but is still within VFR minimums, 1000’ ceiling with 3SM visibility. However, by the time you arrive at the airport, the green and white beacon is spinning, indicating that the airport is now below VFR minimums. According to radar, the cloud bank ends after a fe…
How Do I Request A Special VFR Clearance?
- One caveat to this type of clearance is that Air Traffic Control cannot freely give it. It must be specifically requested by the pilot. If the airport has an operating control tower, Special VFR can be requested through them. If the airport is non-towered, calling up the local Flight Service Station (FSS) will allow the pilot to request this type of clearance. Often times, the control tower will hin…
Frequently Asked Questions
- 4. Can I request this type of clearance at night?
Yes, a pilot can request Special VFR clearance at night. However, the pilot must be IFR rated and current, and the aircraft must be IFR certified. Although it is possible to request this type of clearance at night, it is generally unadvisable. This is because the darkness makes it almost imp… - 5. Can I request a Special VFR clearance in Class Bravo airspace?
Yes, but there are certain Class Bravo airports that do not allow this type of clearance under any circumstances. A pilot can find the list of airports that prohibit Special VFR operations in 14 CFR, Part 91, Appendix D.
Conclusion
- Receiving a Special VFR clearance can give a pilot more flexibility in getting where they need to go if the weather is bad. Requesting this type of clearance can be done via the control tower, of the local Flight Service Station. Special VFR clearance must be specifically requested by the pilot, however. The tower/FSS cannot freely offer it. From sunrise to sunset, this type of clearance ca…