What are 5 examples of powers reserved to the States?
Which powers are reserved for state governments?
- ownership of property.
- education of inhabitants.
- implementation of welfare and other benefits programs and distribution of aid.
- protecting people from local threats.
- maintaining a justice system.
- setting up local governments such as counties and municipalities.
What gives states reserved powers?
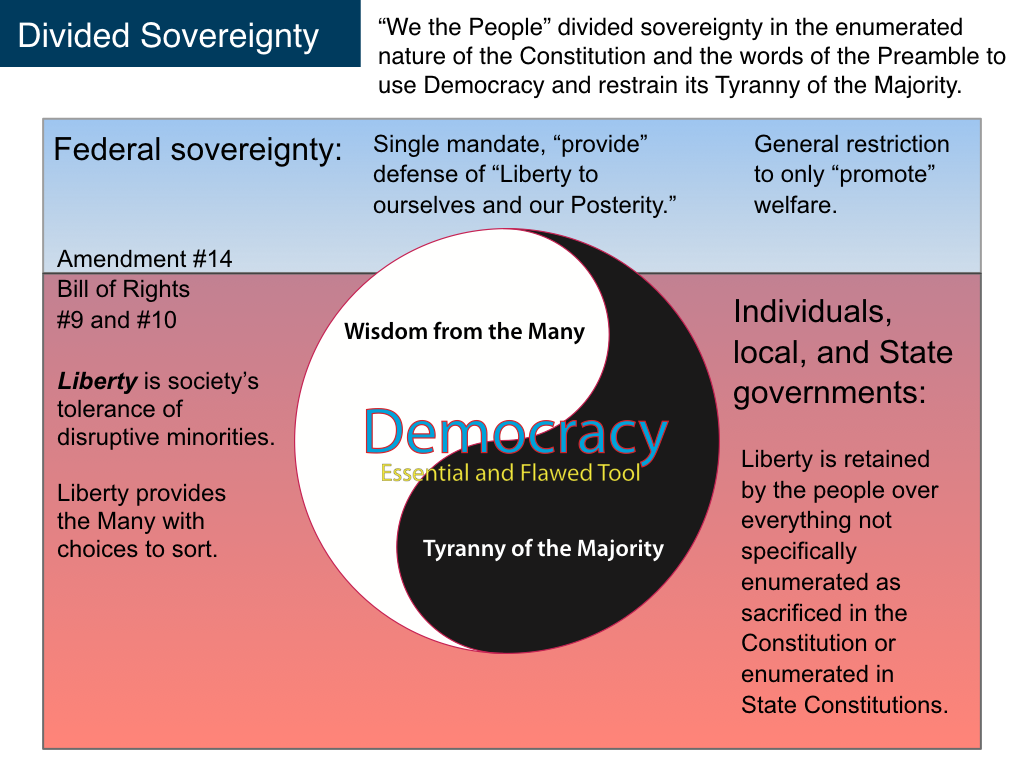
“The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people.” This final version of the 10th Amendment was ratified and added to the U.S. Constitution on December 15, 1791.
What is an example of a reserved power?
The powers and rights protected by the 10th Amendment are called reserved powers, because they are not specifically assigned to the federal government. For example, the Constitution doesn't give the federal government power over driver's licenses. This is a reserved power for each state.
Who are reserved powers granted to?
The reserved powers of government are the powers that are reserved to the states by the Tenth Amendment in the Bill of Rights. Any powers not given to the national government are reserved to the states. What do reserved powers mean?

What are examples of reserved powers?
Reserved powers include running elections, creating marriage laws, and regulating schools.
What are 5 examples of reserved powers?
Powers Reserved to the Statesownership of property.education of inhabitants.implementation of welfare and other benefits programs and distribution of aid.protecting people from local threats.maintaining a justice system.setting up local governments such as counties and municipalities.More items...
What are reserved powers called?
Reserved powers, residual powers, or residuary powers are the powers that are neither prohibited nor explicitly given by law to any organ of government.
What are reserved powers quizlet?
Reserved Powers-To reserve means to save. All powers not specifically delegated by the Federal government are to be reserved or saved for the state governments. The 10th amendment declares states are governments of reserved powers.
What does reserved powers mean in government?
Reserved powers are laws that are not specifically given to the national government and are reserved for the states. The state governments hold these powers under the Tenth Amendment, the last amendment in the Bill of Rights.
Why are reserved powers important?
“The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people.” In simple terms, the reserved powers amendment solidifies that the new government is limited to the specific powers outlined in the Constitution.
What is reserved power in simple words?
Definition of reserved power : a political power reserved by a constitution to the exclusive jurisdiction of a specified political authority.
What enumerated powers?
1. Delegated (sometimes called enumerated or expressed) powers are specifically granted to the federal government in Article I, Section 8 of the Constitution. This includes the power to coin money, to regulate commerce, to declare war, to raise and maintain armed forces, and to establish a Post Office.
What are delegated powers?
These are also sometimes called "enumerated" or "expressed" powers. The delegated powers include the power to coin money, to regulate commerce, to declare war, to raise and maintain armed forces, and to establish a Post Office.
What are reserved and concurrent powers?
Concurrent Powers – are those powers that both the National and State Government possess and exercise. Reserved Powers are those powers that the Constitution does not grant to the National Government and does not, at the same time deny to the States.
What are reserved powers of government?
The reserved powers of government are the powers that are reserved to the states by the Tenth Amendment in the Bill of Rights. Any powers not given...
What do reserved powers mean?
Reserved powers are those that are not specifically granted to the national government in the Constitution and are therefore reserved to the states...
What are the five examples of reserved powers?
Reserved powers are laws that are not specifically given to the national government and are reserved to the states. Five examples of reserved power...
What is the purpose of Section 8?
The Congress shall have Power To lay and collect Taxes, Duties, Imposts and Excises, to pay the Debts and provide for the common Defence and general Welfare of the United States; but all Duties, Imposts and Excises shall be uniform throughout the United States;
How often are the House of Representatives elected?
The House of Representatives shall be composed of Members chosen every second Year by the People of the several States, and the Electors in each State shall have the Qualifications requisite for Electors of the most numerous Branch of the State Legislature.
How long is the executive term?
The executive Power shall be vested in a President of the United States of America. He shall hold his Office during the Term of four Years, and, together with the Vice President, chosen for the same Term, be elected, as follows:
Which amendment states that the United States has the right to deny or disparage others retained by the people?
Amendment IX. The enumeration in the Constitution, of certain rights, shall not be construed to deny or disparage others retained by the people. Amendment X. The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people.
When is section 2 inoperative?
This article shall be inoperative unless it shall have been ratified as an amendment to the Constitution by the legislatures of three-fourths of the several States within seven years from the date of its submission to the States by the Congress. Amendment XXIII. Section 1.
What is the purpose of the Rule of Naturalization?
To borrow Money on the credit of the United States; To regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and among the several States, and with the Indian Tribes; To establish an uniform Rule of Naturalization, and uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies throughout the United States;
Why was the Interpretative Rule important?
That interpretative rule was vital because some of the provisions of the Bill of Rights purport to limit federal powers that are not actually granted by the original Constitution and thus might give rise to a (faulty) inference that the Bill of Rights implied the existence of such powers.
What does "reserved powers" mean?
Meaning of Reserved Powers. Any powers outlined as reserved for Congress, the President, or any other part of the federal government are reserved, or saved, only for those people. Anything that is reserved is defined as being saved for a specific person or a specific purpose. Reserving any unnamed powers for states in the Tenth Amendment ensures ...
Why are reserved powers difficult to find?
Examples of reserved powers are difficult to find, because the nature of the Tenth Amendment is vague. Without a concrete list of powers assigned to the states and the people, these reserved powers are open to interpretation.
Why did Roland Dagenhart argue against the Keating-Owen Act?
Textile worker Roland Dagenhart took his case to the Supreme Court arguing against the Keating-Owen Act of 1916 which prohibited shipment of goods manufactured by children across state lines. Dagenhart argued this was unconstitutional as it was a reserved right of the states to make their own child labor laws.
What are some examples of reserved powers?
Ratified in 1791, the 10th Amendment outlines all the reserved powers of individual states or the people. American flag and Declaration of Independence.
Which amendment lists reserved powers?
List of Reserved Powers in Amendment X. The Tenth Amendment is titled “Rights Reserved to States or People.”. It does not include a list of reserved powers. It includes only one sentence that reads: “The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, ...
What was the reason for Schechter v. United States?
v. United States (1935) The National Industrial Recovery Act (NIRA) of 1933 was deemed unconstitutional and the Supreme Court ruled that it violated the Tenth Amendment. This is because the issues raised were about intrastate sale of poultry.
What are delegated powers?
Delegated powers are listed and explained in the Constitution. They define what each branch of the government can do . Implied powers are the things you assume a specific branch of government can do, because they are similar to the delegated powers for that branch.
Why is the federal government a concurrent power?
Since the Constitution also empowers the federal government to 'promote the general welfare,' many Americans interpret education as part of that obligation. The powers shared by both levels of government are called concurrent powers, and they include things like the levying of taxes, since both state and federal authorities can do that, and defining crimes and punishments, since you could, theoretically, be charged with a crime in both a state and federal court. The elegance of the reserved powers clause is that it is a mechanism of government, not a list of powers that could never be complete or detailed enough for the real world.
What is reserved powers?
In the United States Constitution, the reserved powers clause states that states have control over things not explicitly covered by the federal government. Learn more about the definition of reserved powers, and see how they act as a safety valve of the U.S. Constitution. Also, learn about what was involved in writing a Constitution, the 10th Amendment, overlapping powers, and disputes between state and federal, in this lesson. Updated: 10/10/2021
What was the most important thing that the Framers of the Constitution agreed on?
Probably the most important of these was the fact that we were going to have a federal republic.
Why did the Framers want to create a safety valve?
The Framers knew that state governments were closer to the 'people' than the central government could ever be (even today, with cell phones and the Internet), and therefore they wanted to create a sort of safety valve, which would keep the central government from growing too large.
Why does the Supreme Court exist?
Generally, the U.S. Supreme Court exists for one overall reason--to determine whether or not acts of government are 'constitutional.' A major element of that is the issue of reserved powers; when has the federal government overreached and infringed on the rights of states?
How can federal arguments get settled?
Of course, in one spectacularly awful example of how federal arguments can get settled, a group of states once thought the federal government was infringing on their right to own, buy, and sell other human beings. They tried to leave the Union as a result; and the Civil War was the solution to that argument over reserved powers. But mostly, such questions regarding acts of government are settled peacefully.
What is a community government?
Any community, at its most basic level, is a government--a shared agreement by the members of that community (whether it's a family, or a group of friends, or an entire nation), to live according to a certain set of rules. This is helpful to keep in mind, since forming a government isn't really as unusual as it sounds.
What amendment was used to create corporations?
The counsel for the State of Maryland cited fears of opponents of ratification of the Constitution about the possible swallowing up of states’ rights and referred to the Tenth Amendment to allay these apprehensions, all in support of his claim that the power to create corporations was reserved by that amendment to the states. 7 Stressing the fact that the amendment, unlike the cognate section of the Articles of Confederation, omitted the word expressly as a qualification of granted powers, Marshall declared that its effect was to leave the question whether the particular power which may become the subject of contest has been delegated to the one government, or prohibited to the other, to depend upon a fair construction of the whole instrument. 8
What does the Constitution say about the powers not delegated to the United States?
"The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people.".
What is the 10th amendment?
The Tenth Amendment: Reserving Power for the States. Passed by Congress in 1789 and ratified in 1791, the Tenth Amendment is the last in the group of Constitutional Amendments known as the Bill of Rights. Unlike several of the other early amendments, it is quite brief – only one sentence.
Which amendment states that all is retained which has not been surrendered?
2. United States v. Darby, 312 U.S. 100, 124 (1941) . While the Tenth Amendment has been characterized as a ‘truism,’ stating merely that ‘all is retained which has not been surrendered,’ [citing Darby], it is not without significance. The Amendment expressly declares the constitutional policy that Congress may not exercise power in a fashion that impairs the States’ integrity or their ability to function effectively in a federal system. Fry v. United States , 421 U.S. 542, 547 n.7 (1975). This policy was effectuated, at least for a time, in National League of Cities v. Usery , 426 U.S. 833 (1976).
Why are states reserving power?
Reserving powers for state governments helps maintain a balance of power between the states and the federal government. They also allow states the freedom to try out different ideas and programs, which is why states are sometimes called "laboratories of democracy.".