Potential Risks and Complications of NSAIDs
- Heart-Related Risks. Citing research on the heart-related risks of NSAIDs, the U.S. ...
- Risk of Stomach Problems. Individuals with ulcers or sensitive stomachs are advised to avoid NSAIDs because of the risk of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, including the stomach.
- Risks of Kidney Damage. ...
- Allergic Reactions to NSAIDs. ...
- Additional Safety Concerns. ...
What are the side effects of NSAIDs?
NSAIDs can bring relief, especially if you have chronic pain. But like all drugs, the benefits come with some risks. With NSAIDs, stomach problems are the most common side effect. If your side effects are mild, you may be able to take another drug to lessen the effects.
What increases the risk of heart disease from NSAIDs?
The risk increases the higher the dosage and the longer the length of time you remain on an NSAID for. People with pre-existing heart disease are more at risk and certain NSAIDs, such as diclofenac and celecoxib, have been linked to more heart-related side effects than others.
Who should not take NSAIDs?
Individuals with ulcers or sensitive stomachs are advised to avoid NSAIDs because of the risk of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, including the stomach. People older than 65 and those taking blood thinners or corticosteroids are particularly at risk of gastrointestinal problems. These problems include:
Do NSAIDs increase the risk of GI complications?
While the NSAID itself plays a role in the risk that a patient will develop a GI complication, there are other patient-determined factors that can increase the risk.
Why should NSAIDs be avoided?
All NSAIDs have the potential to aggravate hypertension, congestive heart failure, and edema. It is estimated that a person's mean blood pressure will increase by an average of 5 mm Hg while taking nonselective NSAIDs, and some COX-2 inhibitors have also been shown to increase blood pressure.
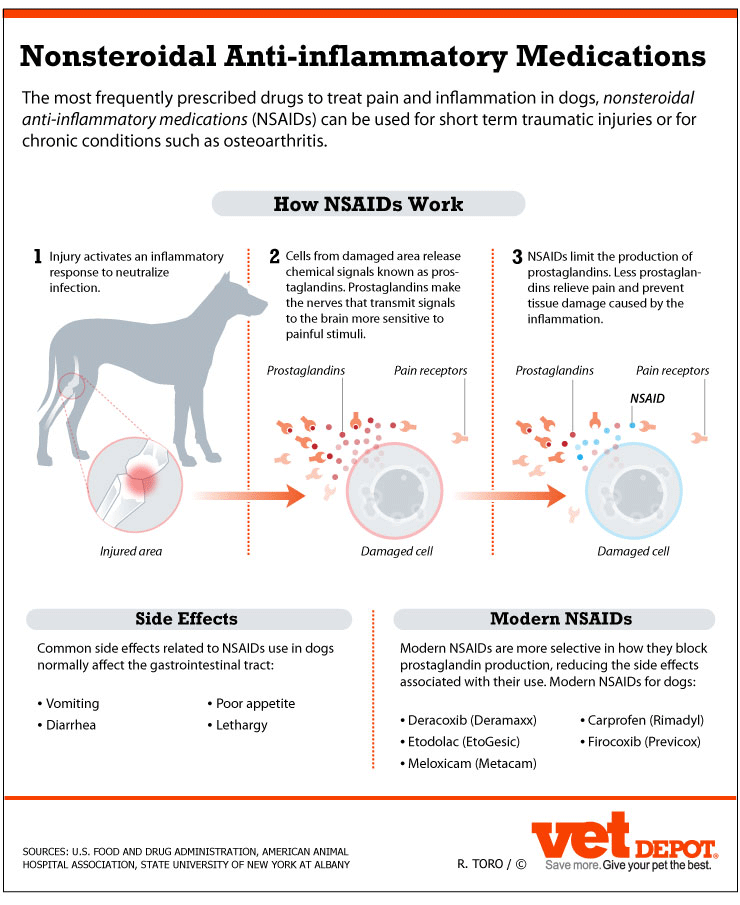
What are the 3 effects of NSAIDs?
Side effects of NSAIDs. While NSAIDs are effective in relieving pain, fever and inflammation, they can cause unwanted side effects. Gastrointestinal side effects such as indigestion, stomach upset (including nausea or feeling sick) or stomach pain are commonly caused by NSAIDs.
What organs are damaged mostly by taking NSAIDs?
The action of NSAIDs on major organs including stomach, small intestine, heart, liver, kidney, respiratory tract and brain is mainly mediated through PGHS-dependent prostanoid modulation and alteration of mitochondrial functional integrity leading to mitochondrial oxidative stress (MOS) generation, depolarization of ...
Who should avoid NSAIDs?
NSAIDs are generally not recommended for people with kidney disease, heart failure, or cirrhosis, or for people who take diuretics. Some patients who are allergic to aspirin may be able to take selective NSAIDs safely, although this should be discussed in advance with a health care provider.
What are the 3 most common NSAIDs?
Most Common Types of NSAIDsAspirin (Bayer, Bufferin, and Ecotrin, St. Joseph). ... Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin). Ibuprofen can treat a range of conditions including post-surgical pain and pain from inflammatory diseases, such as ankylosing spondylitis. ... Naproxen (Aleve, Anaprox DS, Naprosyn). ... Celecoxib (Celebrex).
Which of the following are potential side effects of NSAIDs in older adults?
NSAIDs, like other drugs, have the risk of side effects. Older people and those with some chronic illnesses may have increased risk for side effects from NSAIDs....These include:irritation or pain.heartburn.gas.diarrhea or constipation.bleeding and ulcers.nausea.vomiting.
Do NSAIDs affect the liver?
NSAIDs exhibit a broad spectrum of liver damage ranging from asymptomatic, transient, hyper-transaminasemia to fulminant hepatic failure.
What are the side effects of ibuprofen?
Ibuprofen may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:constipation.diarrhea.gas or bloating.dizziness.nervousness.ringing in the ears.
What are the risks of taking NSAIDs?
Research into NSAIDs’ risks includes an analysis of multiple studies. There were several important findings from the analysis: 1 The risk of heart attack or stroke was raised by one-third when high doses of the NSAID diclofenac were taken. 3 2 The risk was similar with celecoxib (Celebrex) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin). 3 3 Naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn) did not show an increase in heart attacks or stroke. 3 4 he risk of heart failure doubled with all four NSAIDs studied—diclofenac, ibuprofen, celecoxib, and naproxen.
Which NSAIDs double the risk of heart failure?
he risk of heart failure doubled with all four NSAIDs studied—diclofenac, ibuprofen, celecoxib, and naproxen.
How long can you take NSAIDs for back pain?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends people taking an over-the-counter NSAID for more than 10 days see a doctor, and that NSAIDs be used in ...
How much does diclofenac raise the risk of heart attack?
The risk of heart attack or stroke was raised by one-third when high doses of the NSAID diclofenac were taken. 3
Can you take NSAIDs without a doctor?
Individuals whose kidney function is impaired should not take NSAIDs without consulting a doctor.
Can NSAIDs cause kidney failure?
Water and salt retention, high blood pressure, and electrolyte imbalances have been linked to NSAIDs’ effect on the kidneys. In rare cases, kidney failure can result.
Do you have to consult a doctor about NSAIDs?
This is not a comprehensive list of potential risks and complications associated with NSAIDs. Anyone taking NSAIDs should consult their treating physician and/or pharmacist regarding their individual situation.
What are the dangers of NSAIDs?
These dangers of NSAIDs include risks for your heart, gastrointestinal tract and kidneys, among others. 1. Increased Risk of Heart Failure.
What Are NSAIDs?
( 11 ) NSAIDs are also the most commonly prescribed anti-inflammatory medicine for management of inflammatory conditions like arthritis. ( 12)
How long have NSAIDs been around?
The whole principle of NSAIDs is said to go back over 5,000 years to the use of willow bark for musculoskeletal pain.
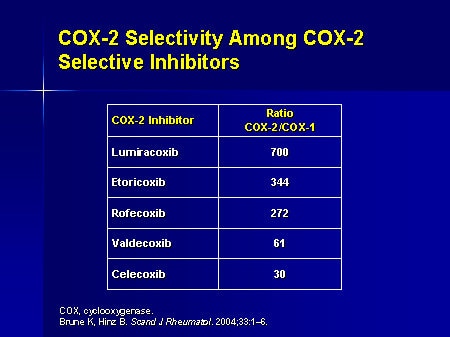
What are the two COX-2 inhibitors?
The two COX-2 inhibitors are etoricoxib and rofecoxib, which are both currently not approved for use in the United States. When diclofenac, indomethacin, piroxicam, etoricoxib and rofecoxib were taken at “very high doses” (meaning two or more daily doses), the risk for heart failure doubled. 2.
Is ibuprofen an NSAID?
NSAIDs have become well-known for their link to stomach bleeding, but now even the FDA has made its overall NSAID warning stronger. It wants consumers to be aware that NSAIDs cause an increased risk of heart attack and stroke, especially in higher doses. ( 3) I’ve talked before about ibuprofen overdose, and now I want to tell you all about NSAIDs in general, including how exactly they’re effective, why the dangers of NSAIDs really can’t be taken lightly and what are some safer, natural alternatives.
Can NSAIDs be used with heart disease?
When it comes to dangers of NSAIDS, more specifically heart health concerns, the American Heart Association recommends that all NSAIDs should be used at their lowest effective doses. In addition, it’s recommended that NSAIDs should be avoided when possible by patients with cardiovascular risk factors, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, angina, edema, recent bypass surgery, and a history of myocardial infarction or other cardiovascular events. ( 16)
Do NSAIDs work?
Even though NSAIDs might work to temporarily calm the pain and inflammation associated with these issues, these man-made painkillers are not without their significantly concerning side effects, as we’ve learned, and the serious dangers of NSAIDs make them concerning. Luckily, there are safer alternatives out there.
How do NSAIDs work?
They work by blocking specific proteins, called COX enzymes. This results in the reduction of prostaglandins, which play a key role in pain and inflammation. There are two types of NSAIDs: nonselective NSAIDs and COX-2 selective NSAIDs (these are sometimes referred to as “coxibs”). There is a growing body of evidence that NSAIDs may increase ...
What is the most common medication used to treat pain and inflammation?
By: Christian Ruff, MD, MPH , Contributor. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, commonly referred to as NSAIDs, are one of the most common medications used to treat pain and inflammation. Ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin, and other NSAIDs are effective across a variety of common conditions, from acute musculoskeletal pain to chronic arthritis.
Does NSAIDs matter for cardiovascular disease?
For patients with no history of cardiovascular disease the choice of NSAIDs probably does not matter very much. For patients with a history of cardiovascular disease we generally recommend I generally recommend the naproxen or celecoxib,
Can NSAIDs cause heart failure?
There is a growing body of evidence that NSAIDs may increase the risk of harmful cardiovascular events including heart attack, stroke, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation. Given the widespread use of NSAIDs, these findings have generated significant concern among patients and healthcare providers.
Does aspirin cause heart attacks?
Basically preventing platelets from clumping together to form blood clots. While there is some overlap between the platelet effects of NSAIDs and aspirin, NSAIDs have have other effects on the lining of blood vessels which may actually predispose to clots to forming clots which can result in heart attacks or strokes. NSAIDs can also cause the kidneys to retain salt and water which may cause or exacerbate heart failure.
What are the risks of taking NSAIDs?
The use of NSAIDs increases the risk of GI toxicity, such as the development of peptic ulcer disease (PUD), upper GI hemorrhage, or GI perforation. The risk of GI complications may vary among NSAIDs. About 25% of patients who use NSAIDs chronically will develop PUD. 15 A meta-analysis by Castellsague et al pooled relative risks (RRs) of upper GI complications associated with individual NSAID use. 16 Agents such as celecoxib and ibuprofen were shown to have a low RR (1.5 and 1.8, respectively), while piroxicam and ketorolac have a higher RR (7.4 and 11.5, respectively). 16
How many people use NSAIDs?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are one of the most commonly used drug classes in the world. 1 It is estimated that more than 30 million people use these medications on a daily basis, and they account for 60% of the analgesic market in the United States. 2 There are approximately 20 different OTC and prescription NSAIDs available in the U.S. ( TABLE 1 ). 1,3 NSAIDs are used for the treatment of fever, acute or chronic pain, and inflammation caused by a variety of conditions.
How long does a person with hypertension take NSAIDS?
Hsu et al determined that patients with hypertension who used NSAIDS for ≥90 days (n = 10,589) had a 32% increased risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD). 19 The study also found that hypertensive patients taking higher doses of NSAIDs have a greater risk of developing CKD than patients on lower doses. 19
Should NSAIDs be avoided?
NSAIDs should be avoided in patients with a high risk for both CV and GI events. Patients should be educated that NSAIDs must be used at the lowest possible dose for the shortest duration possible to avoid adverse effects.
Can NSAIDs increase creatinine?
NSAIDs may attenuate the effect of other antihypertensive agents and increase the risk of elevated serum creatinine and potassium levels when combined with other agents, such as aldosterone antagonists.
Can NSAIDs cause kidney failure?
Chronic NSAID use can lead to severe kidney impairment due to its direct and indirect effects on the organ. The use of NSAIDs can increase blood pressure (thus making antihypertensive drugs less effective), cause fluid retention, and decrease kidney function in patients with kidney disease.
Is Naproxen a selective NSAID?
14 COX-2 selective agents have a higher risk of CV toxicity as compared to nonselective agents. Naproxen, a nonselective NSAID, differs slightly from other NSAIDs because ...
What are common side effects of NSAIDs?
You may have side effects if you take large doses of NSAIDs, or if you take them for a long time. Some side effects are mild and go away, while others are more serious and need medical attention. Unless your doctor tells you to do so, don't take an over-the-counter NSAID with a prescription NSAID, multiple over-the-counter NSAIDs or more than the recommended dose of an NSAID. Doing so could increase your risk of side effects.
When are stronger NSAIDs prescribed?
Prescription-strength NSAIDs are often recommended for rheumatologic diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and moderate-to-severe osteoarthritis. These NSAIDs are also prescribed for moderately painful musculoskeletal conditions such as back pain.
What are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)?
When your back hurts, head aches, arthritis acts up or you’re feeling feverish, chances are you’ll be reaching for an NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) for relief.
How do NSAIDs work?
NSAIDs block the production of certain body chemicals that cause inflammation. NSAIDs are good at treating pain caused by slow tissue damage, such as arthritis pain. NSAIDs also work well fighting back pain, menstrual cramps and headaches.
How long should I use an over-the-counter NSAID?
Don’t use an over-the-counter NSAID continuously for more than three days for fever, and 10 days for pain, unless your doctor says it’s okay. Over-the-counter NSAIDs work well in relieving pain, but they’re meant for short-term use.
How long do NSAIDs take to work?
That depends on the NSAID and the condition being treated. Some NSAIDs may work within a few hours, while others may take a week or two.
How are NSAIDs prescribed?
NSAIDs are prescribed in different doses, depending on the condition. These drugs may need to be taken from one to four times a day. Don’t increase the dose without asking your doctor first.
How many NSAIDs are there in the USA?
There are over 40 NSAIDs sold in USA. Most of the NSAIDs need physician prescriptions. NSAIDs of COX-2 inhibitors cause less side effects such as peptic ulcer and dyspepsia than COX-1 inhibitors.
What are NSAIDs prescribed for?
NSAIDs Are Prescribed For Following Symptoms-. Anti-inflammation- NSAIDs are anti-inflammatory and prevents the symptoms like pain and fever caused by inflammation. Analgesics- Acute and chronic pain is treated with NSAIDs. Opioids are alternative to NSAIDs as analgesics. NSAIDs do not cause addiction.
What is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug?
Non Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug ( medication) is abbreviated as NSAIDs. NSAIDs are non-addictive analgesics. Few NSAIDs like Aspirin, Ibuprofen and Naproxen are sold without doctor’s prescription and are available on counter. NSAIDs blocks actions of enzyme COX-1 and 2 at peripheral and central nervous system.
Can NSAIDs cause addiction?
NSAIDs do not cause addiction. NSAIDs blocks prostaglandin. Advertisement. Antipyeretic- NSAIDs are prescribed for fever. NSAIDs are widely used to treat fever. Dosage has to be watched in children and infants.
Does Warfarin cause bleeds?
Warfarin- Increases tendency to bleed by decreasing coagulability.
Can NSAIDs cause kidney damage?
Diuretics- Diuretics when prescribed with NSAIDs causes kidney damage as a result of decreased renal blood flow.
How old do you have to be to take NSAIDs?
Most NSAIDs are not suitable for children or adolescents under the age of 18 years. Ibuprofen is the only NSAID approved for children aged three months and older.
What are the side effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents?
NSAIDs can potentially cause a range of side effects, especially when used at higher than recommended dosages for long periods of time.
What are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents used for?
NSAIDs are used to treat mild-to-moderate pain that arises from a wide range of conditions such as headaches, menstruation, migraines, osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, sprains and strains, and toothache.
Why is aspirin given as a single dose?
It may also be given as a single dose at the time of a heart attack to improve outcomes. This is because it irreversibly inhibits the COX-1 enzyme.
What is the name of the medication that helps to reduce inflammation?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents (usually abbreviated to NSAIDs) are a group of medicines that relieve pain and fever and reduce inflammation.
Do NSAIDs have gastrointestinal side effects?
NSAIDs may be grouped according to their preference for COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes. Those that favor COX-1 are more likely to cause gastrointestinal side effects. Those that favor COX-2 have a higher risk of cardiovascular effects but less gastrointestinal effects. Higher dosages of NSAIDs tend to result in more COX-2 enzyme inhibition ...
Can NSAIDs cause heart attacks?
NSAIDs are one of the most widely prescribed group of medicines; however, they are associated with some serious side effects. NSAIDs can increase your risk of a fatal heart attack or stroke. The risk increases the higher the dosage and the longer the length of time you remain on an NSAID for.
Why are NSAIDs important?
Because these adverse effects occur at a much higher rate in patients with specific comorbidities, it is crucial for physicians, nurses, and pharmacists to pay close attention to a patient's history and to educate the patient accordingly on risks and dosing. The treating clinician will initiate therapy, whether for a short or long-term regimen. The pharmacist will need to verify the dosing and administration and check for potential drug-drug interactions. Pharmacists should also offer patient counseling on how to best use their NSAID and minimize adverse events; this is particularly the case when the patient uses NSAIDs as an OTC agent. Nursing must also take a careful medication history and include OTC NSAID use, so the clinician can make an informed choice for prescribing NSAID therapy. MUrses, pharmacists, and clinicians all need to be cognizant of the signs and symptoms of NSAID toxicity or adverse effects to make changes to the patient's regimen as needed.
What are the adverse effects of aspirin?
Other minor adverse effectsinclude anaphylactoid reactions that involve the skin and pulmonary systems, like urticaria and aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. [17][18]
Can ibuprofen be administered parenterally?
Specific NSAIDs can also be administered parenterally; for example, intravenous ibuprofen is available, given as a 30-minute infusion; this can be used as a non-opioid analgesic to manage pain and can also reduce fever. Trials have shown that using intravenous ibuprofen and morphine in postoperative adult patients can lower the total use of morphine. For treating pyrexia, an initial 400mg dose then 400 or 100 to 200 mg every 4 to 6 hours as needed. For the treatment of pain, 400 to 800 mg, every 6 hours as needed, is the recommended dose regimen.[11] Ketorolac is also available for parenteral administration.
Can NSAIDs cause hematocrit?
Hematologic adverse effects are possible, particularly with nonselective NSAIDs due to their antiplatelet activity. This antiplatelet effect typically only poses a problem if the patient has a history of GI ulcers, diseases that impair platelet activity (hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, von Willebrand, etc.), and in some perioperative cases. [16]
Can NSAIDs be taken over the counter?
Most commonly, NSAIDs are available as oral tablets. According to the package insert, the dosage for the most common over-the-counter NSAIDs are as follows:
Can NSAIDs cause allergic reactions?
With NSAID hypersensitivity or salicylate hypersensitivity, as well as in patients who have experienced an allergic reaction (urticaria, asthma, etc.) after taking NSAIDs
Does diclofenac increase cardiovascular risk?
Cardiovascular adverse effects can also be increased with NSAID use; these include MI, thromboembolic events, and atrial fibrillation. Diclofenac seems to be the NSAID with the highest reported increase in adverse cardiovascular events. [14]