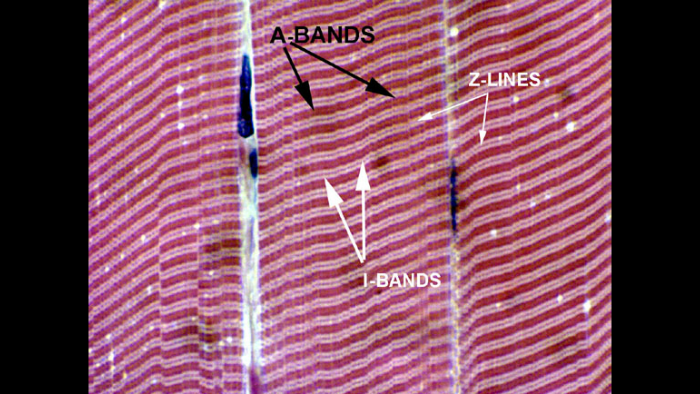
What are the 4 steps of muscle contraction?
What are the factors that affect the stages of muscle contraction?
- age. -lose fast twitch as you age because of muscle atrophy from less activity and less testosterone.
- sex. -women are 70% as strong as men. ...
- fiber type. fast = greater force, speed, fatigue. ...
- speed of movement. max strength and power. ...
- relative strength. ...
- cross-sectional muscle area. ...
- joint angle.
What is the correct order of steps in muscle contraction?
What are the 8 steps of muscle contraction?
- an action potential travels along a neuron to a synapse at a muscle fiber.
- acetylcholine (neurotransmitter) is released from a neuron.
- acetylcholine (neurotransmitter) binds to muscle cell membrane.
- sodium ions diffuse into the muscle fiber starting an action potential.
What are the steps of the contraction cycle?
Tags related to this set
- Contraction Cycle Begins Begins with the arrival of calcium ions within the zone of overlap
- Active-Site Exposure Calcium ions bind to troponin, weakening the bond between actin and the troponin-tropomyosin complex. ...
- Cross-Bridge Formation Once the active sites are exposed, the energized myosin heads bind to them, forming cross bridges.
What causes constant muscle contraction?
Types include:
- Action: Moving or just thinking about moving brings on muscle twitches. ...
- Epileptic: People with epilepsy are more prone to muscle twitches and jerks.
- Essential: Healthcare providers don’t know what causes essential myoclonus. ...
- Sleep: Muscle twitches happen as you’re falling asleep. ...
What is the correct sequence of events for muscle contractions quizlet?
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events for muscle contraction? Motor neuron action potential, neurotransmitter release, muscle cell action potential, release of calcium ions from SR, ATP-driven power stroke, sliding of myofilaments.
What are the 5 steps of muscle contraction?
Terms in this set (5)exposure of active sites - Ca2+ binds to troponin receptors.Formation of cross-bridges - myosin interacts with actin.pivoting of myosin heads.detachment of cross-bridges.reactivation of myosin.
What are the 6 steps of muscle contraction?
Terms in this set (6)Ca2+ release from SR terminal Cisterinae binding site exposure.Myosin head binding to actin binding sites.Release of ADP & Pi Causes power stoke.ATP causes Myosin head to be released.ATP is hydrolyzed, re-energizes the Myosin head.Ca2+ pumped back into SR terminal cisterine.
Which is the sequence of events in muscle contraction use of ATP?
ATP binds to the myosin cross-bridge, breaking the actin- myosin bond and allowing the cross-bridge to dissociate from actin.
What are the 12 steps of muscle contractions?
Terms in this set (12)Motor neurons release ACh into synapse.ACh travels across the synapse and binds to ACh receptors on the sarcolemma.Binding of ACh causes an action potential to spread across the sarcolemma and into the T-tubules.Action potential causes the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.More items...
What are the 9 steps of muscle contraction?
Terms in this set (9)Electrical current goes through neuron releasing ACH. ... ACH released into synapse. ... Electric current spreads to sarcolema. ... Current goes down to T tubules. ... Action potential travels to sarcoplasmic reticulum releasing calcium. ... Calcium binds to troponin, changing shape of tropomysium. ... Myosin binds with actin.More items...
What are the steps of muscle contraction quizlet?
Terms in this set (6)Calcium ions rush into muscle fibers.Calcium binds to troponin.Troponin changes shape and exposes actin binding site.Myosin heads bind to actin binding site making a cross bridge.Myosin heads do a powerstroke (using ADP and P) which slides actin and decreases length of sarcomere (Z line to Z line)More items...
What are the steps of muscle contraction quizlet?
Terms in this set (7)Action potential generated, which stimulates muscle. ... Ca2+ released. ... Ca2+ binds to troponin, shifting the actin filaments, which exposes binding sites. ... Myosin cross bridges attach & detach, pulling actin filaments toward center (requires ATP) ... Muscle contracts.More items...
What is the first step of muscle contraction?
The first step in the process of contraction is for Ca++ to bind to troponin so that tropomyosin can slide away from the binding sites on the actin strands. This allows the myosin heads to bind to these exposed binding sites and form cross-bridges.
How does acetylcholine work?
A multistep molecular process within the muscle fiber begins when acetylcholine binds to receptors on the muscle fiber membrane. The proteins inside muscle fibers are organized into long chains that can interact with each other, reorganizing to shorten and relax. When acetylcholine reaches receptors on the membranes of muscle fibers, membrane channels open and the process that contracts a relaxed muscle fibers begins: 1 Open channels allow an influx of sodium ions into the cytoplasm of the muscle fiber. 2 The sodium influx also sends a message within the muscle fiber to trigger the release of stored calcium ions. 3 The calcium ions diffuse into the muscle fiber. 4 The relationship between the chains of proteins within the muscle cells changes, leading to the contraction.
What is the process of muscle contraction?
Messages from the nervous system cause these muscle contractions. The whole process is called the mechanism of muscle contraction and it can be summarized in three steps: (1) A message travels from the nervous system to the muscular system, triggering chemical reactions. (2) The chemical reactions lead to the muscle fibers reorganizing themselves ...
What is the process of acetylcholine binding?
A multistep molecular process within the muscle fiber begins when acetylcholine binds to receptors on the muscle fiber membrane. The proteins inside muscle fibers are organized into long chains that can interact with each other, reorganizing to shorten and relax. When acetylcholine reaches receptors on the membranes of muscle fibers, membrane channels open and the process that contracts a relaxed muscle fibers begins:
How does muscle contraction begin?
Muscle contraction begins when the nervous system generates a signal. The signal, an impulse called an action potential, travels through a type of nerve cell called a motor neuron. The neuromuscular junction is the name of the place where the motor neuron reaches a muscle cell. Skeletal muscle tissue is composed of cells called muscle fibers. When the nervous system signal reaches the neuromuscular junction a chemical message is released by the motor neuron. The chemical message, a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, binds to receptors on the outside of the muscle fiber. That starts a chemical reaction within the muscle.
What is the chemical signal released by the motor neuron?
When the nervous system signal reaches the neuromuscular junction a chemical message is released by the motor neuron. The chemical message, a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, binds to receptors on the outside of the muscle fiber. That starts a chemical reaction within the muscle. 2.
What is the purpose of open channels in muscle fibers?
Open channels allow an influx of sodium ions into the cytoplasm of the muscle fiber. The sodium influx also sends a message within the muscle fiber to trigger the release of stored calcium ions. The calcium ions diffuse into the muscle fiber.
When do muscle fibers relax?
Muscle Fibers Relax When the Nervous System Signal Is No Longer Present. When the stimulation of the motor neuron providing the impulse to the muscle fibers stops, the chemical reaction that causes the rearrangement of the muscle fibers' proteins is stopped.