
The symptoms of riboflavin deficiency include:
- swelling and fissuring of the lips (cheilosis)
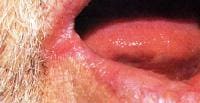
- ulceration and cracking of the angles of the mouth (angular stomatitisis)
- oily, scaly skin rashes on the scrotum, vulva, or area between the nose and lips
- inflammation of the tongue
- red, itchy eyes that are sensitive to light
What are the symptoms of a low riboflavin?
Red, greasy, scaly (seborrheic) patches may appear around the nose, between the nose and the lips, on the ears and eyelids, and in the genital area. Doctors may suspect riboflavin deficiency in people who have typical symptoms and other vitamin B deficiencies.
What are the signs and symptoms of riboflavin deficiency in otitis media (OM)?
Riboflavin deficiency causes various nonspecific skin and mucosal lesions, including maceration of mucosa at the angles of the mouth (angular stomatitis) and surfaces of the lips (cheilosis).
How is riboflavin deficiency diagnosed?
The diagnosis of riboflavin deficiency is based on symptoms and evidence of general undernutrition Symptoms Undernutrition is a deficiency of calories or of one or more essential nutrients. Undernutrition may develop because people cannot obtain or prepare food, have a disorder that makes eating or... read more .
What happens if you don’t take riboflavin?
Poor Iron Absorption And Anemia A riboflavin deficiency may also impair absorption of other B vitamins, further compounding any B vitamin deficiencies. 8 Not having adequate riboflavin in the body can interfere with your body’s ability to handle or use iron. This deficiency affects your bone marrow, resulting in lower red blood cell count.
See more
Which disease is caused by deficiency of riboflavin?
Anemia and cataracts can develop if riboflavin deficiency is severe and prolonged [1].
What food is high in riboflavin?
Riboflavin is found mostly in meat and fortified foods but also in some nuts and green vegetables.Dairy milk.Yogurt.Cheese.Eggs.Lean beef and pork.Organ meats (beef liver)Chicken breast.Salmon.More items...
How do you fix B2 deficiency?
(Vitamin B2 Deficiency) The diagnosis is based on symptoms, urine tests, and response to riboflavin supplements. High doses of riboflavin supplements, usually taken by mouth, can correct the deficiency.
Is B12 A riboflavin?
Vitamin B, unlike other vitamins, is actually a family of eight different vitamins, each of which performs its own distinct functions. B1 (thiamin), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenate), B6 (pyridoxine), B7 (biotin), B9 (folate) and B12 (cobalamin) make up this vitamin family.
What are the side effects of riboflavin?
Riboflavin may cause urine to have a more yellow color than normal, especially if large doses are taken. This is to be expected and is no cause for alarm. Usually, however, riboflavin does not cause any side effects.
What blocks B2 absorption?
Anticholinergic medications: Doctors use anticholinergic drugs to treat a variety of conditions, including gastrointestinal spasms, asthma, depression, and motion sickness. These drugs may make it hard for the body to absorb riboflavin.
How long does it take for riboflavin to work?
For treating low levels of riboflavin (riboflavin deficiency) in adults: 5-30 mg of riboflavin (Vitamin B2) daily in divided doses. For preventing migraine headaches: 400 mg of riboflavin (Vitamin B2) per day. It may take up to three months to get best results.
How can I get more riboflavin in my diet?
You can get recommended amounts of riboflavin by eating a variety of foods, including the following: Eggs, organ meats (such as kidneys and liver), lean meats, and low-fat milk. Some vegetables (such as mushrooms and spinach) Fortified cereals, bread, and grain products.
Which food provides the most riboflavin per serving?
Beef liver is the richest source of riboflavin outside of supplements. A single three-ounce serving of cooked liver contains as much as 2.9 milligrams of riboflavin, or twice your daily requirement. Most breakfast cereals are fortified with riboflavin and other B vitamins.
Can too much riboflavin be harmful?
The primary risk of excess B-2 is damage to the liver. However, excess riboflavin, or riboflavin toxicity, is rare. You'd have to eat almost impossibly large quantities of food to overdose on riboflavin naturally.
What's riboflavin good for?
It's required for the proper development of the skin, lining of the digestive tract, blood cells, and brain function. People most commonly use riboflavin to prevent riboflavin deficiency, for migraine, and for high levels of homocysteine in the blood.
How does riboflavin get out of the body?
It is a water-soluble vitamin and moves through your body through the bloodstream. Excess riboflavin passes out of the body through urine.
What is riboflavin supplement?
A riboflavin supplement is mainly helpful to manage and prevent riboflavin deficiency.
How much does riboflavin reduce homocysteine?
Riboflavin supplements can reduce homocysteine levels by 40%.
What happens when your body cannot absorb B2?
Secondary deficiency: When your intestines cannot absorb B2, the body cannot use it, or the vitamin is excreted rapidly.
Where is riboflavin found?
Riboflavin is present in certain foods such as spinach, meat, eggs, almonds, and many others.
Does riboflavin affect hemoglobin?
Riboflavin alters iron absorption, which is an important component of your hemoglobin.
Does riboflavin cause cataracts?
Riboflavin plays an essential role in maintaining eye health, and deficiency may increase the risk of cataracts.
How do you know if you have riboflavin deficiency?
Symptoms of riboflavin deficiency may vary. Most commonly, people appear pale and have painful cracks in the corners of the mouth and on the lips. The mouth and tongue are sore, and the tongue may turn magenta.
What is the best way to correct a deficiency in riboflavin?
High doses of riboflavin supplements, usually taken by mouth, can correct the deficiency. The vitamin riboflavin (vitamin B2) is essential for the processing (metabolism) of carbohydrates (to produce energy) and amino acids (the building blocks for proteins). It also helps keep mucous membranes (such as those lining the mouth) healthy.
What are the conditions that affect the absorption of food?
Chronic disorders (such as recurrent diarrhea, liver disorders, and chronic alcoholism) Impaired absorption of food ( malabsorption disorders) Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis—procedures that filter the blood. Use of barbiturates for a long time.
Can you take riboflavin with hemodialysis?
Sometimes riboflavin given by injection. As a preventive measure, people who are undergoing hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis or who have a malabsorption disorder should take riboflavin supplements or a daily multivitamin. People who have riboflavin deficiency are given high doses of riboflavin, taken by mouth, until symptoms resolve.
Is riboflavin toxic?
Riboflavin is not toxic, so consuming excess amounts of riboflavin is not a concern. Good sources of riboflavin include milk, cheese, liver, meat, fish, eggs, and enriched cereals.
Can riboflavin be taken with vitamin B?
Relief of symptoms when riboflavin supplements are taken. Doctors may suspect riboflavin deficiency in people who have typical symptoms and other vitamin B deficiencies. The diagnosis of riboflavin deficiency is based on symptoms and evidence of general undernutrition. The diagnosis is confirmed by measuring riboflavin excreted in urine ...
What are the symptoms of riboflavin deficiency?
Symptoms and signs include sore throat, lesions of the lips and mucosa of the mouth, glossitis, conjunctivitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and normochromic-normocytic anemia. Diagnosis is usually clinical. Treatment consists of oral or, if needed, intramuscular riboflavin.
Is riboflavin deficiency nonspecific?
The lesions characteristic of riboflavin deficiency are nonspecific. Riboflavin deficiency should be suspected if characteristic signs develop in a patient with other B vitamin deficiencies.
What are the symptoms of riboflavin deficiency?
The signs and symptoms of riboflavin deficiency (also known as ariboflavinosis) include skin disorders, hyperemia (excess blood) and edema of the mouth and throat, angular stomatitis (lesions at the corners of the mouth), cheilosis (swollen, cracked lips), hair loss, reproductive problems, sore throat, itchy and red eyes, and degeneration of the liver and nervous system [ 1-3, 8 ]. People with riboflavin deficiency typically have deficiencies of other nutrients, so some of these signs and symptoms might reflect these other deficiencies. Severe riboflavin deficiency can impair the metabolism of other nutrients, especially other B vitamins, through diminished levels of flavin coenzymes [ 3 ]. Anemia and cataracts can develop if riboflavin deficiency is severe and prolonged [ 1 ].
What happens when you eat too much riboflavin?
When excess amounts are consumed, they are either not absorbed or the small amount that is absorbed is excreted in urine [ 3 ]. Bacteria in the large intestine produce free riboflavin that can be absorbed by the large intestine in amounts that depend on the diet.
How much riboflavin is in breast milk?
In well-nourished women, riboflavin concentrations in breast milk range from 180 to 800 mcg/L and concentrations of riboflavin in breast milk increase over time [ 27, 28 ]. In developing countries, in contrast, riboflavin levels in breast milk range from 160 to 220 mcg/L [ 27 ].
Where is riboflavin absorbed?
Most riboflavin is absorbed in the proximal small intestine [ 4 ].
Does the FDA require riboflavin?
FDA does not require food labels to list riboflavin content unless riboflavin has been added to the food. Foods providing 20% or more of the DV are considered to be high sources of a nutrient, but foods providing lower percentages of the DV also contribute to a healthful diet.
Is riboflavin deficiency a measure of FAD?
Riboflavin status is not routinely measured in healthy people. A stable and sensitive measure of riboflavin deficiency is the erythrocyte glutathione reductase activity coefficient (EGRAC), which is based on the ratio between this enzyme’s in vitro activity in the presence of FAD to that without added FAD [ 1, 6, 7 ].
Does riboflavin produce more riboflavin?
More riboflavin is produced after ingestion of vegetable-based than meat-based foods [ 2 ]. Riboflavin is yellow and naturally fluorescent when exposed to ultraviolet light [ 1 ]. Moreover, ultraviolet and visible light can rapidly inactivate riboflavin and its derivatives.
What is riboflavin deficiency?
Riboflavin, vitamin B2, is a water-soluble and heat-stable vitamin that the body uses to metabolize fats, protein, and carbohydrates into glucose for energy. In addition to boosting energy, riboflavin functions as an antioxidant for the proper function of the immune system, healthy skin, and hair.
How does riboflavin affect the body?
Riboflavin is excreted from the body while only 15% of it is absorbed . Carbohydrates received from food convert to ATP, which is then used to produce energy in the body. It is essential to consume riboflavin every day either by food or with supplement. Most of the riboflavin is absorbed in the small intestine, and excess passes out of the body as urine. Urinary excretion can also decrease with age and stress. Hydrolysis of FAD and FMN to riboflavin done by pyrophosphates and phosphatase must occur in the upper intestine for dietary riboflavin absorption. Individuals who eat nutritional diets may not need supplements; therefore, it is necessary that they consume foods rich in B vitamins along with others. Also, foods provide better absorption of riboflavin when compared to supplements.
Why is riboflavin important?
Riboflavin is necessary for normal development, lactation, physical performance, and reproduction. This activity illustrates the evaluation and management of riboflavin deficiency and reviews the role of the interprofessional team in improving care for patients with this condition. Objectives:
What are the two coenzymes that make up the riboflavin?
These effects occur with the help of two coenzymes, flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FA D). Without an adequate amount of riboflavin, macronutrients like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins cannot be digested and maintain the body.
What is riboflavin vitamin B2?
Riboflavin, vitamin B2, is a water-soluble and heat-stable vitamin that the body uses to metabolize fats, protein, and carbohydrates into glucose for energy. In addition to boosting energy, riboflavin functions as an antioxidant for the proper function of the immune system, ...
What is riboflavin used for?
Riboflavin is necessary for normal development, lactation, physical performance, and reproduction. [1][2] Riboflavin, vitamin B2, is a water-soluble and heat-stable vitamin that the body uses to metabolize fats, protein, and carbohydrates into glucose for energy. In addition to boosting energy, riboflavin functions as an antioxidant for ...
Where is riboflavin absorbed?
Most of the riboflavin is absorbed in the small intestine, and excess passes out of the body as urine. Urinary excretion can also decrease with age and stress. Hydrolysis of FAD and FMN to riboflavin done by pyrophosphates and phosphatase must occur in the upper intestine for dietary riboflavin absorption.
Why is riboflavin in the body?
Riboflavin is continuously excreted through the urine, thus increasing the risk of a deficiency when dietary intake is insufficient. A deficiency of Vitamin B2 in the body can be primarily due to poor vitamin sources in one's daily diet or as a result of conditions that affect its absorption in the intestine.
How do you know if you have a vitamin B2 deficiency?
Poor intake of Vitamin B2 may cause the following symptoms1. Weakness or fatigue . 2. Change in mood. 3. Soreness of throat. 4.
Can B2 cause birth defects?
Moreover, a deficiency of Vitamin B2 during pregnancy can result in birth defects including congenital heart defects and limb deformities.There is no side effect seen for Vitamin B2 toxicity produced by excessive intake because it has a lower water solubility than other B vitamins.
Why is my riboflavin yellow?
It is also a sign your body is excreting unneeded vitamin B2, and do not have a problem with riboflavin deficiency.
Why is riboflavin important?
Riboflavin is needed in high amounts to allow other B vitamins to work properly. Together, B vitamins are responsible for heart and blood health, eye and skin health, nerve health, digestion, metabolism, hormonal function, and reducing inflammation.
Does riboflavin help with migraines?
It also helps reduce homocysteine levels for protection against heart disease. Riboflavin can also improve muscle function, prevent cramping, and reduce the frequency of migraine headaches.
Is riboflavin deficiency common in the Western diet?
Vitamin B2 is needed for the functioning of every single cell in the body, and a lack of riboflavin in the diet can create various adverse effects. Riboflavin or vitamin B2 deficiency is not very common in the Western diet because many refined carbohydrates contain fortified vitamin B2.
What is the name of the condition where a person's B6 levels are low?
Deficiency of B6 can cause nerve damage called peripheral neuropathy.
What to do if you have a B6 deficiency?
Correcting B6 deficiency with foods rich in the vitamin or a supplement may clear up these symptoms.
Why does B6 cause rash?
One reason B6 deficiency may result in skin rashes is that the vitamin helps synthesize collagen, which is needed for healthy skin. In these cases, consuming B6 may clear up the rash quickly ( 10, 11 ).
What are the effects of B6?
Shortfalls of B6 may affect your mood, sometimes contributing to depression, anxiety, irritability and increased feelings of pain ( 16 ).
What does it mean when your tongue is red?
If you have a B6 deficiency, your tongue may become swollen, sore, smooth, inflamed or reddened. This is called glossitis.
Does B6 help with glossitis?
Replenishing B6 treats glossitis, provided that a deficiency is the only cause.
Does B6 deficiency affect T cells?
A B6 deficiency may also reduce your body’s production of white blood cells, including T cells. These cells regulate immune function, helping it respond appropriately.
