Chitin is a fibrous substance while cellulose is an insoluble substance Chitin is a major component of the exoskeleton of arthropods and fungi cell wall whereas cellulose is a major component of plant cell wall The monomer
Monomer
A monomer (mono-, "one" + -mer, "part") is a molecule that may bind chemically or supramolecularly to other molecules to form a (supramolecular) polymer. The process by which monomers combine end to end to form a polymer is called polymerization. Molecules made of a small number of monomer units (up to a few dozen) are called oligomers.
Full Answer
What is the difference between starch glycogen and cellulose?
Starch, glycogen, and cellulose all are forms of glucose stored inside the living cells. The hydroxyl groups in all three polysaccharides are held together by hydrogen bonds with adjacent chains. All three of these polysaccharides have 1-4 glycosidic bonds in monomers. The starch vs. cellulose vs. glycogen differences are listed here:
What is the difference between cellulose and chitin?
Chitin and cellulose are almost similar polysaccharide compounds, cellulose contains a hydroxyl group, whereas chitin contains an acetamide group. Chitin is a high molecular weight polymer, specifically β (1-4) (N-acetyl-d-glucoamine), as shown in Fig. What is the difference between starch cellulose and chitin?
What type of glycosidic bonds are in cellulose?
The glucose units in cellulose are linked by β glycosidic bonds, different than the α glycosidic bonds found in glycogen and starch. Cellulose has more hydrogen bonds between adjacent glucose units, both within a chain and between adjacent chains, making it a tougher fiber than glycogen or starch.
Does starch have glucose residues?
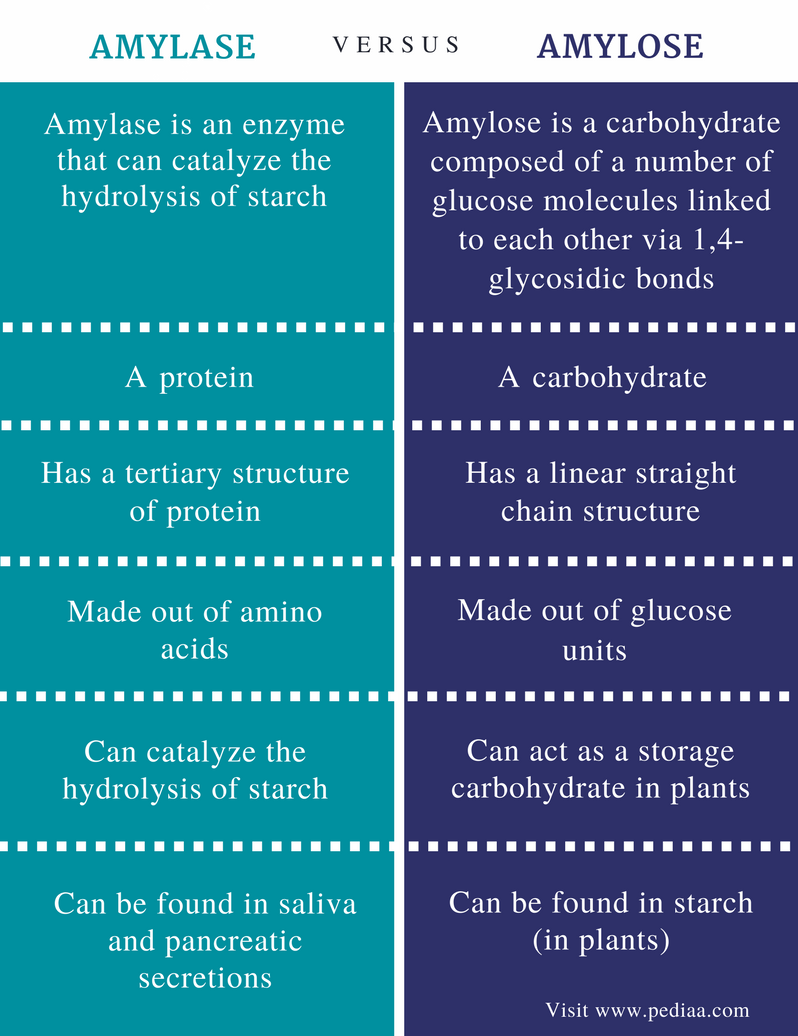
Starch contains glucose residues as α (1-4) glycosidic bonds in amylose, while in amylopectin α (1-6) glycosidic linkages at branching points, otherwise α (1-4) linkages. Glycogen also contains α (1-4) and α (1-6) (at branching points) glycosidic bonds between their monomers. The molar mass of starch varies.
See more

What do starch glycogen cellulose and chitin have in common?
They include starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin. They generally either store energy or form structures, such as cell walls, in living things.
What are the similarities and differences between starch cellulose and glycogen?
Starch, cellulose and glycogen are all polysaccharides made up of glucose subunits. Starch and glycogen are made up of 𝜶-glucose subunits, whereas cellulose is made up of 𝛃-glucose subunits. Cellulose is unbranched and a straight-chain polymer of glucose, whereas starch and glycogen are branched.
What are the similarities and differences between cellulose and chitin?
Chitin is the structural component of the fungal cell wall and the exoskeleton of arthropods. Cellulose is the structural component of the plant and algal cell wall. The strength of chitin is higher than that of cellulose. The main difference between chitin and cellulose is the occurrence and strength of the molecules.
What are the similarities between cellulose starch and glycogen?
Glycogen Similarities Explained. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose all are forms of glucose stored inside the living cells. The hydroxyl groups in all three polysaccharides are held together by hydrogen bonds with adjacent chains. All three of these polysaccharides have 1-4 glycosidic bonds in monomers.
What is the major difference between cellulose and glycogen?
Glycogen is a storage form of energy in animals. It is a branched polymer composed of glucose units. It is more highly branched than amylopectin. Cellulose is a structural polymer of glucose units found in plants.
What is difference between starch and cellulose?
There is one major difference between Starch and Cellulose. For starch, glucose repeat units are located in the same direction, and each successive glucose unit is rotated 180 degrees in cellulose.
Why is chitin similar to cellulose?
Chitin occurs in the structural components of arthropod exoskeletons or in the cell walls of fungi and yeast [42]. Chitin and cellulose are almost similar polysaccharide compounds; cellulose contains a hydroxyl group, whereas chitin contains an acetamide group.
Are chitin and cellulose the same?
Chitin is formed by a series of glycosidic bonds between substituted glucose molecules. Chitin is different from cellulose because of the substitution that occurs on the glucose molecule. Instead of a hydroxyl group (OH), the glucose molecules in chitin have an amyl group attached that consists of carbon and nitrogen.
What is the major structural difference between starch and glycogen?
So the main structural difference between the starch and glycogen is that the starch is a complex molecule or it is a linear or discharge, has a linear or coil structure. Okay, linear or coil structure. And our glycogen is brand retrain structure. Okay, Glycogen forms a brand and chain structure.
What are two similarities between starch and glycogen?
Both are made of the monosaccharide alpha glucose. Both are used as energy storage. Amylopectin in starch and glycogen both have 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds. Both form glycosidic bonds between monosaccharide molecules in condensation reactions.
What do starch and cellulose have in common?
Starch and cellulose are two very similar polymers. In fact, they are both made from the same monomer, glucose, and have the same glucose-based repeat units.
What are the common features of starch and glycogen?
Both starches and glycogen are polymers formed from sugar molecules called glucose. Each independent molecule of glucose has the formula C6H12O, and joining these subunits together in a certain way forms the long chains that make up glycogen and starch. There are two types of starch: amylose and amylopectin.
Which of these describe some of the similarities and differences between glycogen and starch?
Glycogen is made up of only one molecule while starch is made up of two. 2. While both are polymers of glucose, glycogen is produced by animals and is known as animal starch while starch is produced by plants.
What are the structural and functional differences between starch glycogen and cellulose?
The main difference between starch, cellulose and glycogen is that starch is the main storage carbohydrate source in plants whereas cellulose is the main structural component of the cell wall of plants and glycogen is the main storage carbohydrate energy source of fungi and animals.
What is a difference between starch and glycogen quizlet?
Glycogen is very similar in structure to starch but has shorter chains and is more highly branched. It is the major carbohydrate storage product of animals. In animals it is stored as many small granules mainly in the muscles and the liver.
What is the main structural difference between glycogen and starch?
Main Differences Between Glycogen and Starch Glycogen is made up of the single-molecule whereas starch is made up of two molecules namely amylose and amylopectin. Glycogen forms the branched-chain structure whereas Starch forms linear, coiled, and branch structure.
What is the difference between cellulose, starch and glycogen?
Starting from the cellulose which is the monomer of beta glucose and is found in plant cell wall only. While Starch and Glycogen act as the carbohydrate reserve in plants and animals respectively .
What is starch made of?
Another type of polysaccharide, acting as the chief carbohydrate reserve for the plants, and the principal dietary source for the animals and humans. Starch occurs in two types of polymer amylose and amylopectin. Both the polymers are composed of the D-glucose, with the alpha glycosidic bonds known as glucan or glucosan.
What is glycogen in plants?
Definition of Glycogen. Glycogen, often termed as animal starch, though found in plants that do not contain chlorophyll like yeast, fungi, etc. It is also the homopolysaccharide having the glycogen bonds or linkages similar to that of the amylopectin, with the more branches.
Where is glycogen found?
Glycogen is also homopolysaccharide and found in animals as their carbohydrate reserve; it is also found in fungi and plants that do not contain chlorophyll. Cellulose is found only in plants (cell wall). Starch is found in plants. Present in animals and the plants that do not contain chlorophyll like fungi.
How many D-glucose units are in a chain?
The linking of the glucose unit or the glycosidic bond is of β (1-4). The chain is unbranched, linear containing 10,000 to 15,000 D-glucose units.
What are the three main categories of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are further classified as the monosaccharide, disaccharide, and polysaccharide. This classification is on the number of glucose or sugar units linked to each other. With this, we will be discussing the difference between the three main polysaccharides, which marks their presence adequately wherever needed or required.
Is glycogen a monomer?
Similar to starch (amylopectin), Glycogen also contains α (1-4) and α (1-6) (at branching points) glycosidic bonds between their monomers. Though the molar mass of the starch varies but the glycogen has 666.5777 g/mol. Cellulose constitutes long, straight, unbranched chains forming H-bonds with the adjacent chains and are insoluble in water.
What is the difference between glucose and starch?from askanydifference.com
Main Differences Between Glycogen and Starch 1 Glycogen is the energy storage carbohydrate that is found mainly in animals and fungi whereas Starch is the energy storage carbohydrate that is found predominantly in plants. 2 Glycogen is made up of the single-molecule whereas starch is made up of two molecules namely amylose and amylopectin. 3 Glycogen forms the branched-chain structure whereas Starch forms linear, coiled, and branch structure. 4 Starch is used for commercial purposes such as paper and textile industry whereas glycogen is not used for commercial purposes. 5 Glycogen is stored in liver cells and the muscle cells whereas starch are stored in the amyloplasts of the plant cells.
What is Starch?from askanydifference.com
Starch is the essential energy storage component in plants. It is the polymer that is of extreme importance to plants in energy storage and production. Some of the plants that contain starch in the ample amounts are potatoes, rice, corn, etc.
What is the name of the polymer that forms the short branched chains?from askanydifference.com
Glycogen is the polymer where the monomer units form the short branched chains. It comprises of the monomer unit known as alpha glucose held by glycosidic bonds. Starch is made up of two further polymers- amylose and amylopectin where former forms the linear and coiled chains and latter forms the branched chains.
What is the main component of glucose?from askanydifference.com
Glycogen is the polymeric carbohydrate of glucose that is the major component for animals and fungi. Starch is the complex sugar of glucose that is the major storage carbohydrate for plants. Glycogen is the polymer where the monomer units form the short branched chains.
What is the function of glucose in polymers?from askanydifference.com
Glucose forms polymers to further produce complex sugars or carbohydrates glycogen and starch. During the formation of these polymers, the monomer unit of glucose is held together by glycosidic bonds.
What is the process of breaking down glycogen into glucose?from askanydifference.com
When the body requires energy, glycogen is instantly broken down into glucose to provide the body energy that it requires. This process is known as glycogenolysis. This process is stimulated with the help of hormone glucagon.
Why is glycogen stored in muscle cells?from askanydifference.com
The storage of glycogen by the muscle cells helps to keep the body ready for strenuous exercises and actions when required.
What is the difference between starch and glycogen?
The query “What is the difference between starch and glycogen?” often takes us to the structural differences between the two. Starch has a linear, branched, and coiled structure while glycogen displays a branched-chain structure.
Which is better, glycogen or starch?
Glycogen is better than starch when comparing the glycogen vs. starch energy-releasing capacity. Glycogen doesn’t get crystallized like starch and thus, is readily available for release in case of an energy slump.
What is Cellulose?
Cellulose is the stored form of glucose in plants. It is present in the cell wall and the woody areas of the plants but are absent in vertebrates. It has β glycosidic bonds and has a fixed molecular mass.
What is Starch?
Starch is the stored form of glucose in plants. It is present in chlorophyll-rich areas of plants and some vertebrates. It has α glycosidic bonds and has a variable molecular mass.
How does cellulose become more stable?
Every alternate glucose molecule in cellulose is flipped over the other after a 180 degrees rotation. This firms up the cellulose fiber like corrugated sheets and thus, makes it more stable than starch.
What are the forms of glucose stored inside the cells?
Starch, glycogen, and cellulose all are forms of glucose stored inside the living cells.
Where is glycogen stored?
Glycogen is the stored form of glucose in animals. It is present in non-chlorophyll plants like fungi and all the vertebrates’ liver, skeletal muscles, and brain. It has α glycosidic bonds and has a fixed molecular mass.
Difference between Starch, Cellulose and Glycogen
The table below shows the main differences between starch, cellulose and glycogen.
Structure of Starch
Starch is the main storage carbohydrate of plants. It is made up of 𝜶-glucose subunits. It contains two types of polymers, amylose and amylopectin.
Structure of Cellulose
Cellulose is the main structural component of the plant cell wall. It is exclusively present in plants. Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound of the plant kingdom. It is made up of 𝛃-glucose subunits that are joined by 1–4 glycosidic bonds. It is a straight and unbranched polymer of glucose.
Structure of Glycogen
It is the main storage carbohydrate in animals and fungi. It is highly branched and the structure is similar to that of amylopectin. It is a polymer of 𝜶-glucose subunits joined together by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds. It has branching after around every 10 subunits.

What Is starch?
What Is glycogen?
What Is cellulose?
- Cellulose is the stored form of glucose in plants. It is present in the cell wall and the woody areas of the plants but are absent in vertebrates. It has β glycosidic bonds and has a fixed molecular mass.
Starch vs. Cellulose vs. Glycogen Similarities Explained
- Starch, glycogen, and cellulose all are forms of glucose stored inside the living cells.
- The hydroxyl groups in all three polysaccharides are held together by hydrogen bonds with adjacent chains.
- All three of these polysaccharides have 1-4 glycosidic bonds in monomers.
FAQ
- Why do Starch Glycogen and Cellulose have Different Properties?
Starch, glycogen, and cellulose have different types of glucose bonds. Where starch and glycogen have α glycosidic bonds, cellulose has β glycosidic bonds. Also, starch and glycogen have fewer hydrogen bonds and cellulose has more hydrogen bonds. All this makes them display different p… - What is the Main Structural Difference between Starch and Glycogen?
The query “What is the difference between starch and glycogen?” often takes us to the structural differences between the two. Starch has a linear, branched, and coiled structure while glycogen displays a branched-chain structure.
The Final Words
- Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are different forms of glucose but differ in their properties. Starch is present in chlorophyll-rich areas of plants whereas glycogen is found in non-chlorophyll plants like fungi. On the other hand, cellulose is found in the woody areas of the plants. While starch has a variable molecular mass, cellulose and glycoge...
References