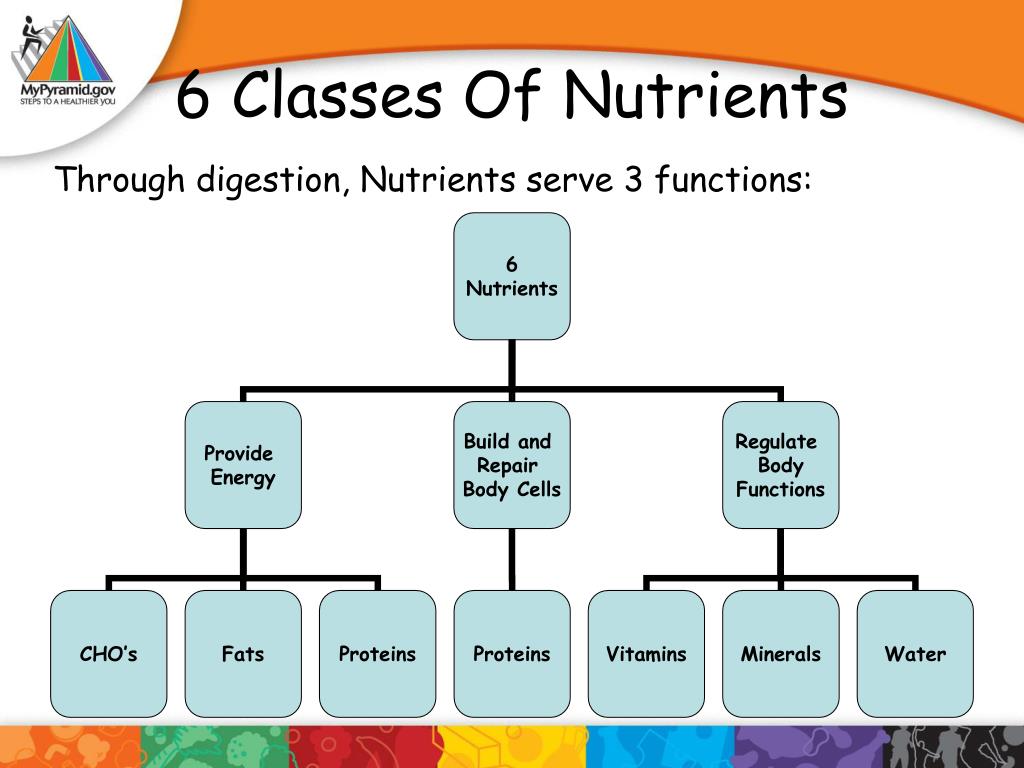
There are six classes of nutrients required for the body to function and maintain overall health. These are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, water, vitamins, and minerals. Foods also contain non-nutrient that may be harmful such as natural toxins common in plant foods and additives like some dyes and preservatives or beneficial like antioxidants.
What are the six classes of nutrients and their functions?
What are the 6 nutrients and their functions?
- Water. Water makes up 45-75% of our bodies and is important for good health.
- Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates (carbs for short) are the main sources of energy in our body.
- Protein. Protein is made of amino acids, which are the building blocks of our tissues.
- Fat.
- Vitamins.
- Minerals.
What are the six major nutrients?
The six major nutrients are:
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
- Proteins
- Vitamins
- Minerals and
- Water
What are the 6 nutrients groups?
What Are The 6 Essential Nutrient Groups?
- Carbohydrates
- Protein (there are 8 essential amino acids)
- Fats or lipids (there are 2 essential fatty acids)
- Water
- Minerals (there are 5 essential minerals and 16 essential trace minerals)
- Vitamins (there are 13 essential vitamins)
How many number of classes of essential nutrients?
Nutrients are used for many body functions such as: growing, moving your muscles, repairing tissues and much more! There are six classes of essential nutrients required for the body to function and maintain overall health. These six classes of essential nutrients are: carbohydrates, lipids (fats), proteins, water, vitamins, and minerals. Foods ...
What are the 6 classes of nutrients and describe their function in the body?
These basic functions allow us to detect and respond to environmental surroundings, move, excrete wastes, breathe, grow, and reproduce. There are six classes of nutrients required for the body to function and maintain overall health. These are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, water, vitamins, and minerals.
What are the six classes of nutrients and examples?
The Six Basic NutrientsWater. Water makes up 45-75% of our bodies and is important for good health. ... Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates (carbs for short) are the main sources of energy in our body. ... Protein. Protein is made of amino acids, which are the building blocks of our tissues. ... Fat. ... Vitamins. ... Minerals.
Why are the 6 essential nutrients important?
Essential nutrients are compounds that the body can't make or can't make in sufficient quantity. According to the World Health Organization , these nutrients must come from food, and they're vital for disease prevention, growth, and good health.
What is the 6 classes of food?
The Six Classes of Food In other words, nutrients are things that humans need to consume in order to survive and to thrive. The six classes include: fat, carbohydrates, protein, vitamins, minerals and water. Yes, even water! These are elements of a diet that you cannot live without ingesting.
What is the most essential nutrient?
waterThat's because water is the most important essential nutrient. It is involved in many of your body's vital functions, and it distributes other essential nutrients to your cells. Get more: The Institute of Medicine recommends that men consume about 125 ounces of water a day and women 91 ounces per day.
What are the types of nutrients?
How many types of nutrients are there?Carbohydrates.Proteins.Fats.Vitamins.Minerals.Dietary fibre.Water.
What are the sources of essential nutrients?
Foods that naturally are nutrient-rich include fruits and vegetables. Lean meats, fish, whole grains, dairy, legumes, nuts, and seeds also are high in nutrients.
What is meant by an essential nutrient?
An essential nutrient is a nutrient required for normal body function that either cannot be made by the body or cannot be made in amounts adequate for good health and therefore must be provided by the diet.
What are nutrients give examples?
Nutrient. Nutrients are chemical compounds in food that are used by the body to function properly and maintain health. Examples include proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
What are the classes of food and examples?
What are the classes of food and their sources?Carbohydrates - These are energy-giving nutrients found in potatoes, rice, wheat, maize, and other starches.Proteins - These are bodybuilding nutrients found in meat, legumes and dairy products.Fats - These are found in nuts and fruits like avocados.More items...
What are the examples of fat and oil food?
Butter, ghee, lard, suet, goose fat, hard margarines, coconut oil and palm oil. Oils made from vegetables and seeds such as olive, rapeseed, sunflower and soya oil, and fat spreads made from these. Fatty meat and processed meat products such as sausages, bacon, salami and canned meat.
What are the examples of vitamins?
Vitamins are substances that our bodies need to develop and function normally. They include vitamins A, C, D, E, and K, choline, and the B vitamins (thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, and folate/folic acid).
What are the six essential nutrients?
The six essential nutrients are vitamins, minerals, protein, fats, water, and carbohydrates .
What are the two categories of essential nutrients?
The WHO divide these essential nutrients into two categories: micronutrients and macronutrients. Micronutrients are nutrients that a person needs in small doses. Micronutrients consist of vitamins and minerals.
What are micronutrients and macronutrients?
Micronutrients are nutrients that a person needs in small doses. Micronutrients consist of vitamins and minerals. Although the body only needs small amounts of them, a deficiency can cause ill health. Macronutrients are nutrients that a person needs in larger amounts.
How many vitamins are there in the body?
There are 13 essential vitamins that nutritionists divide into two groups: fat soluble and water soluble. Fat soluble vitamins are: Water soluble vitamins are: Typically, a person who eats a diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins can get all the vitamins they need in their food.
How many types of nutrients are needed for a healthy body?
A person needs to consume all six types of essential nutrients to ensure the best possible health. These nutrients support vital functions, including growth, the immune, the central nervous system, and preventing disease.
How many nutrients do we need to maintain optimal health?
A person’s body cannot produce everything that it needs to function. There are six essential nutrients that people need to consume through dietary sources to maintain optimal health.
What are the two types of carbohydrates?
They are sugars or starches that provide energy for all the cells and tissues in the body. There are two different types of carbohydrates: simple and complex . People should limit their intake of simple carbohydrates, such as white bread, pasta, and rice.
How many nutrients are in the Merck Manual?
The Merck Manual estimates that only some of the 300 nutrients in the typical diet are essential, meaning your body cannot produce them and must obtain them from your diet. They belong to seven classes: water, carbohydrates, ...
What are the minerals in the body?
Minerals are inorganic or carbon-lacking substances that assist with life-sustaining processes in your body. Your body needs macro-minerals in relatively large amounts, while trace minerals are required in small amounts. Macro-minerals include sodium, chloride, potassium, calcium, phosphorus and magnesium.
What percentage of calories are fats?
The USDA recommends obtaining 20 to 35 percent of your daily calories from fats, primarily from the unsaturated type.
How many calories are in a gram of protein?
Each gram yields 4 calories of energy, and the USDA recommends a daily intake of 10 to 35 percent of calories from protein. Of the 20 amino acids that constitute the building blocks of protein, nine are essential. Animal sources, soy and quinoa contain all the essential amino acids you need, while most other plants do not.
What is the most important macronutrient for energy?
Carbohydrates. With a recommended daily intake of 45 to 65 percent of calories, carbohydrates are the macronutrients the USDA considers the most important for energy. They're your body's main fuel source, especially for your brain, kidneys and muscles. Your body breaks carbs down to glucose, deriving 4 calories of energy from each gram.
What is the body's most important macronutrient?
Water. By definition, your body needs macronutrients in large quantities. Water accounts for as much as 60 percent of the human body, according to physiologist Linda Costanzo. All nutrients transit through your blood, which mostly consists of water . Urine also primarily consists of water, which helps eliminate waste from your body.
Which vitamins are water soluble?
As Champe, remarks, many vitamins assist the enzymes that drive your metabolism. Vitamin C and the eight vitamins of the B-complex are all water-soluble, meaning that they dissolve in water. The vitamin B complex specifically includes biotin, folic acid, niacin, pantothenic acid, B-2, B-1, B-6 and B-12.
Do you know the 6 classes of nutrients?
The food we eat contains nutrients, which are basically the substances the body needs for its basic functions. Since our bodies don’t synthesize nutrients, we must take them in form of diet. The body uses nutrients to produce energy, move, grow, breathe, detect and respond to the environment, excrete wastes, and reproduce.
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the nutrients that the body needs in large quantities. They are the nutrients that give the body energy and help the body maintain its systems and structures. As part of a healthy diet, all four macronutrients should be consumed.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are the essential nutrients that the body requires in lesser quantities to carry out bodily functions. They include all the essential vitamins and minerals. As opposed to macronutrients which are directly used to make energy, micronutrients aid in the process as being part of enzymes (i.e., they act as coenzymes).
What are the nutrients that are needed for proper body function?
In general, the nutrients that are necessary for proper body functions include 6 groups: proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals, vitamins and water . The daily requirements for each group vary, depending on age, sex, and physical activity. By including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, dairy products and healthy fats in your diet, you can get a good amount of these nutrients naturally. If you are not sure whether you are having a balanced diet, consult a dietitian.
What are the two main sources of nutrients?
Nutrients and Their Sources. 1. Proteins . Protein is a necessary nutrient to ensure the normal growth of skin, bone and muscle. It can be mostly found in animal sources such as poultry, meat and fish. Consuming enough protein is not a problem in industrialized countries such as the U.S.
What are the sources of energy for the body?
Carbohydrates are fuel for the body. The sources of carbohydrates include vegetables, fruits, grains, legumes, flour, sugar and dairy products. They provide the energy for physical activity and other involuntary body functions such as the heartbeat, digestive process and breathing. They should account for about 40% to 60% ...
What are some foods that are good for you?
By including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, dairy products and healthy fats in your diet, you can get a good amount of these nutrients naturally. If you are not sure whether you are having a balanced diet, consult a dietitian.
What are the six classes of nutrients that are needed for the body to function?
There are six classes of nutrients required for the body to function and maintain overall health. These are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, water, vitamins, and minerals.
What are the nutrients?
The foods we eat contain nutrients. Nutrients are substances required by the body to perform its basic functions. Nutrients must be obtained from our diet since the human body can not make them. Nutrients have one or more of three basic functions: they provide energy, contribute to body structure, and/or regulate chemical processes in the body. These basic functions allow us to detect and respond to environmental surroundings, move, excrete wastes, breathe, grow, and reproduce. There are six classes of nutrients required for the body to function and maintain overall health. These are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, water, vitamins, and minerals. Foods also contain non-nutrient that may be harmful such as natural toxins common in plant foods and additives like some dyes and preservatives or beneficial like antioxidants.
How many micronutrients are there?
Micronutrients include all the essential minerals and vitamins. There are sixteen essential minerals and thirteen vitamins. In contrast to carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, micronutrients are not sources of energy (calories), but they assist in the process as cofactors or components of enzymes (i.e., coenzymes).
What are the main sources of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The major food sources of carbohydrates are grains, milk, fruits, and starchy vegetables, like potatoes. Non-starchy vegetables also contain carbohydrates but in lesser quantities.
What is the function of the body system?
Regulate body processes and promote normal body-system functions. Regulate body processes, are necessary for proper cellular function, and comprise body tissue. Transports essential nutrients to all body parts, transports waste products for disposal, and aids with body temperature maintenance.
What are the functions of nutrients?
Nutrients have one or more of three basic functions: they provide energy, contribute to body structure, and/or regulate chemical processes in the body. These basic functions allow us to detect and respond to environmental surroundings, move, excrete wastes, breathe, grow, and reproduce.
What are the nutrients that we need to live in large quantities?
There is one other nutrient that we must have in large quantities: water. Water does not contain carbon but is composed of two hydrogens and one oxygen per molecule of water . More than 60 percent of your total body weight is water. Without it, nothing could be transported in or out of the body, chemical reactions would not occur, organs would not be cushioned, and body temperature would fluctuate widely. On average, an adult consumes just over two liters of water per day from food and drink combined. Since water is so critical for life’s basic processes, the amount of water input and output is significant, a topic we will explore in detail
What are Nutrients?
Nutrients are chemical substances found in food that are required by the body to provide energy, give the body structure, and help regulate chemical processes . There are six classes of nutrients:
What is the most important nutrient in the human body?
Water . There is one other nutrient that we must have in large quantities: water. Water does not contain carbon but is composed of two hydrogens and one oxygen per molecule of water. More than 60 percent of your total body weight is water .
What are organic nutrients?
The organic nutrients include the macronutrients (carbohydrate, protein, and fat) and vitamins. An organic nutrient contains both carbon and hydrogen. Organic nutrients can be made by living organisms and are complex, made up of many elements (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and sometimes nitrogen) bonded together.
What are the main components of proteins?
Proteins are large molecules composed of chains of amino acids, which are simple subunits made of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen. Food sources of proteins include meats, dairy products, seafood, and a variety of plant-based foods, like beans, nuts, and seeds. The word protein comes from a Greek word meaning “of primary importance,” which is an apt description of these macronutrients as they are also known as the “workhorses” of life. Proteins provide structure to bones, muscles, and skin, and they play a role in conducting most of the chemical reactions occurring in the body. Scientists estimate that more than 100,000 different proteins exist within the human body. Proteins can also provide energy, though this is a relatively minor function, as carbohydrates and fat are preferred energy sources.
What are the main sources of carbohydrates?
The major food sources of carbohydrates are grains, dairy products, fruits, legumes, and starchy vegetables, like potatoes. Non-starchy vegetables, like carrots, also contain carbohydrates, but in lesser quantities.
What is the best thing about food?
Food is one of life’s greatest pleasures. It offers amazing flavors, aromas, and textures. Food also provides our body with essential nutrients and non-nutrients like phytochemicals, both of which are vital to health. This section will discuss the six classes of nutrients and how these nutrients can be classified.
Which nutrient provides the most calories per gram?
Carbohydrates and proteins provide 4 calories per gram, and fats provide 9 calories per gram. Fat is the most energy-dense nutrient, because it provides the most calories per gram (more than double carbohydrates and protein).
What are the six classes of essential nutrients?
The six classes of essential nutrients are proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, fats, water, and...
What are the functions of catalysts in the body?
they serve as catalysts for releasing energy from carbohydrates, they help maintain components of the immune, nervous, and skeletal systems, they aid chemical reactions in the body
Is the FDA allowing phytochemicals?
the FDA has not allowed foods containing phy tochemicals to be marketed as disease preventatives