
- 1. Chemical level
- 2. Cellular level
- 3. Tissue level
- 4. Organ level
- 5. Organ system level
- 6. Organismal level
What are the 6 levels of structural organization in the body?
Chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, system, and organism are the six structural levels. What is the most basic level of structural organization in the human body? From the most basic to the most complex, the body is organized into atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and the human organism.
What is the highest level of organization in the body?
The highest level of organization in the body is the organism level. This is the entirety of a living thing, such as the entire human body. An organ system is a collection of organs in the body that works together to perform a function. There are eleven examples of organ systems in the human body including:
What is an example of level of organization in anatomy?
The levels of organization in anatomy and levels of organization examples include the following: The levels of organization from cell to organism in a mouse. The highest level of organization in the body is the organism level. This is the entirety of a living thing, such as the entire human body.
What is tissue level of organization in the body?
There are four main types of tissue level of organization in the body: Epithelial tissue forms the covering of the body and organs. Its main function is to offer protection and separation from the environment. Connective tissue binds, connects, and cushions the body. Muscle tissue is for contraction and movement.
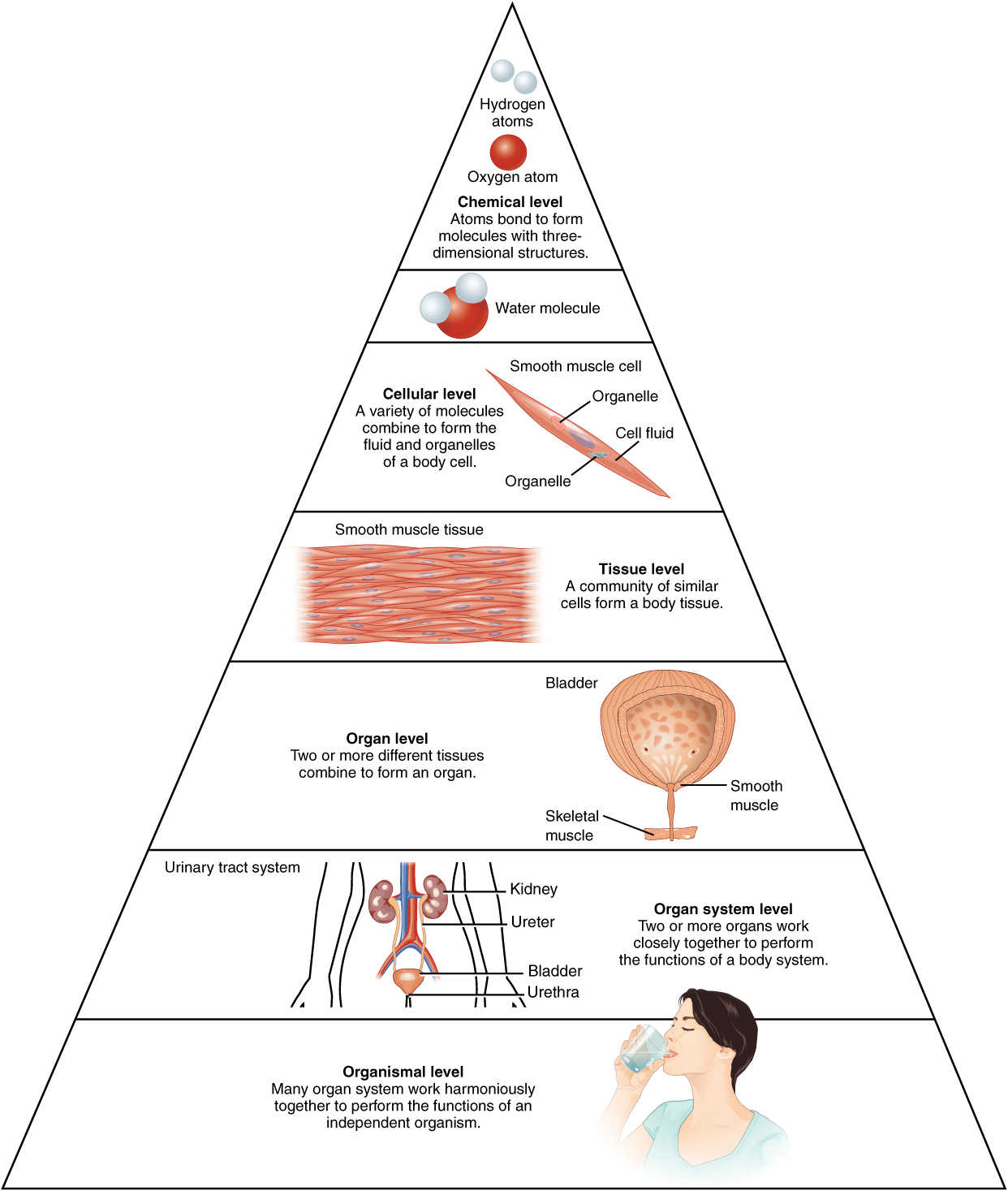
What are the 6 levels of organization of the body?
Life processes of the human body are maintained at several levels of structural organization. These include the chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism level.
What is the level of organization from simplest to most complex?
The biological levels of organization of living things arranged from the simplest to most complex are: organelle, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystem, and biosphere.
What level of organization is most complex?
The most complex level of organization is the organismal level, where all eleven organ systems function in the human organism, the whole living person.
What are the levels of organization of the human body from smallest to largest?
Body organization:Six general levels of the organization listed from smallest to largest are chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and organism levels.Chemicals are regarded to be the smallest and lowest unit of organization in a living system, ranging from the smallest atoms to the largest macromolecules.More items...
Which sequence of terms is in the correct order from most complex to simplest?
The correct answer is (a) organ systems, organs, tissues, cells.
What is the order from least complex to most complex?
Answer and Explanation: The order of structures from least complex to most complex: cell, tissue, organ, organ system.
What is the most complex level of body organization quizlet?
Starting with cells, the levels of organization in an organism become more and more complex. A tissue is more complex than a cell, an organ is more complex than a tissue, an organ system is more complex than an organ, and us, as organisms, are the final and most complex level of organization.
Which level of organization is the least complex?
The body's level of organisation, from least complex to most complex are cells, tissues, organs and organ systems.
What is the order from least complex to most complex?
Answer and Explanation: The order of structures from least complex to most complex: cell, tissue, organ, organ system.
What are the levels of organization from most complex to least complex?
Solution. The body's level of organisation, from least complex to most complex are cells, tissues, organs and organ systems.
Which level of organization is the most simple?
Level 1: Cells The first and most basic level of organization is the cellular level. A cell is the basic unit of life and the smallest unit capable of reproduction. While cells vary greatly in their structure and function based on the type of organism, all cells have a few things in common.
What are the 12 levels of organization?
Typical levels of organization that one finds in the literature include the atomic, molecular, cellular, tissue, organ, organismal, group, population, community, ecosystem, landscape, and biosphere levels.
What are some examples of organs?
Consist of organs which are two or more tissue types performing specific functions. And example is the small intestine composed of all four types working to process and absorb digested nutrients.
What is the smallest unit of matter?
Involves Atoms and molecules. "Atoms" are the smallest unit of matter and example is carbon and oxygen. "Molecules" are described as one or more combined atoms an example of sugar and vitamins. The more complex molecules are called "macromolecules"such as proteins in DNA. "Organelles" are made from microscopic subunits in cells composed of macromolecules
What Are The Six Levels Of Organization Of The Body?
Life processes of the human body are maintained at several levels of structural organization. These include the chemical cellular tissue organ organ system and the organism level.
What are the six levels of organization of the human body?
The major levels of organization in the body from the simplest to the most complex are: atoms molecules organelles cells tissues organs organ systems and the human organism.
What are the six levels of organization of the body quizlet?
The six levels of structural organization are: chemical cellular tissue organ system and organism.
What are the 6 levels of organization from smallest to largest?
The levels from smallest to largest are: molecule cell tissue organ organ system organism population community ecosystem biosphere.
What are the different levels of organization of the human body?
It is convenient to consider the structures of the body in terms of fundamental levels of organization that increase in complexity: subatomic particles atoms molecules organelles cells tissues organs organ systems organisms and biosphere (Figure 1.3).
What are the 6 levels of structural organization of the human body in order of increasing complexity?
It is convenient to consider the structures of the body in terms of fundamental levels of organization that increase in complexity: subatomic particles atoms molecules organelles cells tissues organs organ systems organisms and biosphere (Figure 1).
What are the 6 levels of organization that ecologists study?
Levels of ecological organization from smallest to largest: individual population species community ecosystem biosphere.
What Are The Six Levels Of Structural Organization Of The Body?
Life processes of the human body are maintained at several levels of structural organization. These include the chemical cellular tissue organ organ system and the organism level.
What are the 6 levels of organization from smallest to largest?
The levels from smallest to largest are: molecule cell tissue organ organ system organism population community ecosystem biosphere.
What are the six levels of biological organization?
The biological levels of organization of living things arranged from the simplest to most complex are: organelle cells tissues organs organ systems organisms populations communities ecosystem and biosphere.
How many levels of organization are in the body?
Name the six levels of organization of the human body. Chemical cellular tissue organ organ system organism.
What are the levels of organization and define each?
These parts are divided into levels of organization. There are five levels: cells tissue organs organ systems and organisms. … The cells involved are specialized to cooperate with each other to accomplish one common goal. There are many different types of tissue in both plants and animals.
What are the levels of body organization from smallest to largest?
It is convenient to consider the structures of the body in terms of fundamental levels of organization that increase in complexity such as (from smallest to largest): chemicals cells tissues organs organ systems and an organism. Figure 1.2.
What are the organizational levels in ecology?
Levels of organization in ecology include the population community ecosystem and biosphere. An ecosystem is all the living things in an area interacting with all of the abiotic parts of the environment.
What are the levels of organization from simple to complex?
The biological levels of organization of living things arranged from the simplest to most complex are: organelle, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystem, and biosphere.
What are the 5 levels of organizations from smallest to largest?
There are five levels: cells, tissue, organs, organ systems, and organisms.
Which is the most complex level of organization?
An ecosystem is the most complex level of organization in nature. It is made up of a community and its abiotic (nonliving or physical) environment, including climate, soil, water, air, nutrients, and energy.
What are the levels of organization in life?
In this order thirteen levels of organization are considered: atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, biomes and biosphere. The atom is the basic unit that makes up all matter. This includes living things and also inorganic matter.
What are the levels of organization?
Answer: In terms of six level organization, there are: 1. Chemical Level: Atoms bond to form molecules with three dimensional structures. 2. Cellular Level: A variety of molecules combine to form the fluid organelles of a body cell. 3.
What are the nine body regions?
The nine body regions of human body are: Right hypochondrium, Right lumbar, Right iliac region, Hypogastrium, Left iliac, Left lumbar, Left hypochondrium, Epigastric region, Umbilical region. Importance: 1. To rule out the cause of abdominal pain. 2. To localize any diseased organ. 3. Surgical landmarks to avoid injury to viscera, nerves and blood vessels. 4. More precise and accurate diagnosis of diseases.
What is the study of anatomical structure of large body parts?
More precise and accurate diagnosis of diseases. Define the following terms: gross anatomy: It is the study of anatomical structure of large body parts (which includes external and internal organs) microscopic anatomy: It is the study of anatomical structure of small body parts of cells and tissues.
