What are the 6 types of seizures?
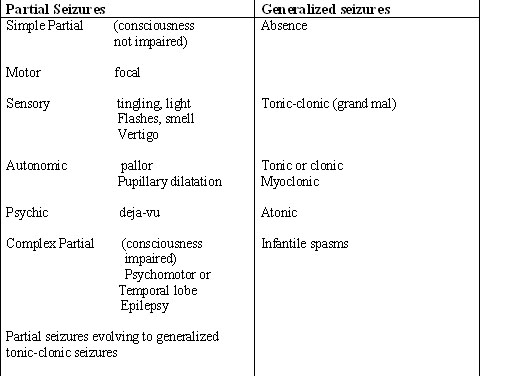
6 Different Types of SeizuresSimple Focal Seizures. Simple focal seizures occur for a short amount of time – typically lasting less than one minute. ... Complex Focal Seizure. ... Absence Seizure. ... Atonic Seizure. ... Tonic-Clonic Seizure. ... Myoclonic Seizure.
What are the 5 most common seizures?
Types of Generalized-Onset SeizuresAbsence Seizures (“Petit Mal Seizures”) ... Myoclonic seizures. ... Tonic and Atonic Seizures (“Drop Attacks”) ... Tonic, Clonic and Tonic-Clonic (Formerly called Grand Mal) Seizures.
What are the 8 types of seizures?
Types of generalized seizuresgeneralized tonic-clonic seizures (GTC)tonic seizures.clonic seizures.absence seizures.myoclonic seizures.atonic seizures.infantile or epileptic spasms.
What is the most common type of generalized seizure?
There are six types of generalized seizures. The most common and dramatic, and therefore the most well known, is the generalized convulsion, also called the grand-mal seizure. In this type of seizure, the patient loses consciousness and usually collapses.
What are the 4 stages of a seizure?
Seizures take on many different forms and have a beginning (prodrome and aura), middle (ictal) and end (post-ictal) stage. These phases are described below....Beginning phaseMood changes.Anxiety.Feeling lightheaded.Difficulty sleeping.Difficulty staying focused.Behaviour changes.
What is the difference between focal and generalized seizures?
Complex focal seizures can make a person with epilepsy confused or dazed. The person will be unable to respond to questions or direction for up to a few minutes. Secondary generalized seizures begin in one part of the brain, but then spread to both sides of the brain.
What are the most common types of seizures?
Focal SeizuresTemporal Lobe Seizures. Temporal lobe seizures, a category of focal seizures, are the most common type of epilepsy. ... Frontal Lobe Seizures. ... Occipital Lobe Seizures. ... Parietal Lobe Seizures. ... Absence Seizures. ... Myoclonic Seizures. ... Generalized Tonic–Clonic Seizures.
What are the three major groups of seizures?
There are 3 major groups of seizures: generalized onset, focal onset, and unknown onset. You may experience just one or more than one kind of seizure. The type of seizure you have and symptoms you show depend on what part of the brain the seizures come from.
What are the classification of seizures?
In this revised classification, epilepsy is classified into three levels: the seizure type, epilepsy, and epilepsy syndrome.
How many types of Generalised seizures are there?
Generalized seizures include absence, atonic, tonic, clonic, tonic-clonic, myoclonic, and febrile seizures.
What is a primary generalized seizure?
Primary generalized, or absence, epilepsy is characterized by repeated lapses of consciousness that generally last less than 15 seconds each and usually occur many times a day. This type of seizure is sometimes referred to by the older term petit mal.
What are the symptoms of generalized seizure?
SymptomsStiff muscles.Loss of consciousness.A cry or groan.Jerking of the arms or legs.Loss of bladder or bowel control.Limited or even stopped breathing.Blue lips.Loss of muscle tone.More items...
What would cause a seizure all of a sudden?
Anything that interrupts the normal connections between nerve cells in the brain can cause a seizure. This includes a high fever, high or low blood sugar, alcohol or drug withdrawal, or a brain concussion. But when a person has 2 or more seizures with no known cause, this is diagnosed as epilepsy.
What can trigger a seizure?
12 most common seizure triggersMissing medication. The most common reason for a seizure is forgetting to take your anti-epileptic drugs (AED) or deliberately not taking it. ... Alcohol. ... Recreational drugs. ... Caffeine. ... Lack of sleep / tiredness. ... Stress / anxiety. ... Boredom. ... Dehydration.More items...•
How long can a seizure last before brain damage?
If convulsive status epilepticus lasts for 30 minutes or longer it can cause permanent brain damage or even death.
What are the warning signs of having a seizure?
Seizure signs and symptoms may include: Temporary confusion. A staring spell. Uncontrollable jerking movements of the arms and legs.
What is a generalized seizure?
A generalized seizure occurs when the abnormal electrical activity causing a seizure begins in both halves (hemispheres) of the brain at the same time.
What is an atonic seizure?
Atonic Seizures (Drop Attacks) A seizure of this type involves a sudden decrease in muscle tone, causing a person’s body to go limp, slump or collapse, possibly causing injury. Atonic seizures characterize certain epilepsy syndromes such as Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
What is the post-seizure period?
This is the post-seizure or post-ictal period, and during this phase the person’s brain is extremely active as it tries to contain the abnormal electrical impulses and bring the seizure under control. People regaining consciousness after a seizure are likely to be sore, confused or frightened and very tired.
What is the cause of a seizure?
When the brain experiences abnormal electrical discharge from cortical neurons, this causes seizures occur. There are six different types of generalized seizures. Absences, also known as petit mal seizures, typically occur in children ages 4 to 14, and cause a short incident of “blanking out” where the person appears to be staring into space. ...
How do clonic seizures get their name?
Clonic seizures get their name from the word “clonus”, meaning quick alternation between muscles contracting and relaxing. When one of these seizures occur, the person experiences rapid, rhythmic jerking movements in both the arms and legs, which can occur on one or both sides of the body. When the seizure ends, the person normally does not suffer ...
How to tell if a child has an atonic seizure?
Because these seizures are difficult to identify, the first sign is when a child starts struggling in school. Atonic seizures are characterized by sudden loss in muscle strength, and can occur in both adults and children, often beginning in childhood.
How long does an atonic seizure last?
These seizures can occur just one at a time or many times in a row. The seizure normally lasts less than 15 seconds, however, atonic seizures can cause significant injury.
What happens when a seizure ends?
For the sufferer, they become unaware of their surroundings and become unresponsive to communication. When the seizure ends, they go about their day as usual, as if nothing had occurred. These seizures can occur simultaneously with other types of seizures. There are two main types of absences, simple and complex.
Why is neurofeedback important for epilepsy?
A highly important part of treatment for epilepsy, it is often considered first choice because it can lead to overall improved function, improvement of the effects of medication, and/or a reduction or complete elimination of medication.
Can neurofeedback help with seizures?
Both adults and children have been known to suffer tonic-clonic seizures. How Neurofeedback Can Help. Once diagnosed, epilepsy is commonly controlled by anti-seizure medication. Epilepsy can also be treated using neurofeedback in conjunction with medication, or when medication is unable to produce the desired results.
What are the two main types of seizures?
There are two major classes or groups of seizures: focal onset and generalized onset . Focal onset seizures start in one area and can spread across the brain and cause mild or severe symptoms, depending on how the electrical discharges spread. Generalized seizures can start as focal seizures that spread to both sides of the brain.
What are the symptoms of a seizure?
Seizures symptoms vary and can include a sudden change in awareness or full loss of consciousness, unusual sensations or thoughts, involuntary twitching or stiffness in the body or severe stiffening and limb shaking with loss of consciousness (a convulsion.) There are two major classes or groups of seizures: focal onset and generalized onset.
What is the term for seizures that occur in the morning?
Myoclonic seizures. Myoclonic seizures consist of sudden body or limb jerks that can involve the arms, head and neck. The spasms occur on both sides of the body in clusters, especially in the morning. When these seizures develop in adolescence along with tonic-clonic seizures, they are part of a syndrome called juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.
Why is it important to get a seizure diagnosis?
It is important for the doctor to get an accurate seizure diagnosis in order to implement the most appropriate kind of treatment. Focal and generalized onset seizures usually have different causes and accurately diagnosing seizure types often helps identify the cause for the seizures.
What is focal seizure?
Focal seizures are also called partial seizures since they begin in one area of the brain. They can be caused by any type of focal injury that leaves scar tangles. Medical history or MRI will identify a cause (such as trauma, stroke or meningitis) in about half of the people who have focal seizures.
Why are focal seizures important?
These seizures are important to treat and prevent since they can cause respiratory problems and injuries.
What is generalized onset?
Generalized seizures can start as focal seizures that spread to both sides of the brain. They also can occur as “generalized onset” seizures in which seiz ure activity starts simultaneously over both sides of the brain. Generalized onset seizures usually start during childhood and are similar to a thermostat surge or a light flash — abnormal ...
What are the two types of seizures?
There are two major types of seizures: Focal seizures: These start in a particular part of your brain, and their names are based on the part where they happen. They can cause physical and emotional effects and make you feel, see, or hear things that aren’t there. About 60% of people with epilepsy have this type of seizure, ...
What is a partial seizure?
About 60% of people with epilepsy have this type of seizure, which is sometimes called a partial seizure. Sometimes, the symptoms of a focal seizure can be mistaken for signs of mental illness or another kind of nerve disorder. Generalized seizures: These happen when nerve cells on both sides of your brain misfire.
Why do people have atonic seizures?
Because of the risk of falling, people who tend to have atonic seizures may need to wear something like a helmet to protect their heads. People who have Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and another kind of epilepsy called Dravet syndrome are more likely to have this kind of seizure.
What is the difference between a clonic and a tonic seizure?
That can lead to breathing problems or make you bite your tongue or cheek. Clonic seizures: Your muscles have spasms, which often make your face, neck, and arm muscles jerk rhythmically. They may last several minutes. Tonic seizures: The muscles in your arms, legs, or trunk tense up.
How common are focal seizures in children?
They’re most common in children under 14. Simple focal seizures: They change how your senses read the world around you: They can make you smell or taste something strange, and may make your fingers, arms, or legs twitch. You also might see flashes of light or feel dizzy.
Can seizures cause muscle spasms?
They can make you have muscle spasms, black out, or fall. Seizures aren’t always an either-or thing: Some people have seizures that start as one kind, then become another. And it’s not easy to classify some of them: These are called unknown-onset seizures, and they can cause sensory and physical symptoms.
Can you lose consciousness when you have a seizure?
You’re not likely to lose consciousness, but you might feel sweaty or nauseated. Complex focal seizures: These usually happen in the part of your brain that controls emotion and memory. You may lose consciousness but still look like you’re awake, or you may do things like gag, smack your lips, laugh, or cry.
What is a generalized seizure?
A generalized seizure starts when all areas of the brain are affected by an abnormal electrical impulse. There are different types of generalized seizures, including: In some cases, the seizure may begin as a partial, or focal, seizure. These seizures may affect only part of the body.
How long does a generalized seizure last?
Symptoms may include: Most generalized seizures typically last between one to three minutes. Tonic-clonic seizures can last up to five minutes and may need emergency medical attention. Many generalized seizures are caused by epilepsy.
What is a clonic seizure?
Clonic seizures. Tonic seizures. Tonic-clonic seizures (grand mal seizures) Atonic seizures (drop attacks) In some cases, the seizure may begin as a partial, or focal, seizure. These seizures may affect only part of the body. Then they may progress to a generalized seizure, which affects the whole body. Patients experiencing a generalized seizure ...
What causes seizures in the brain?
Many generalized seizures are caused by epilepsy. Other conditions may also cause these seizures, such as: Serious head injury. Stroke. Brain tumor. Brain infection ( meningitis or encephalitis) Alzheimer's disease. Loss of oxygen at birth. Hardening of the brain's arteries.
What exam do you need to see for seizures?
The doctor will also perform a neurological exam. These examinations look at the muscles, including reflexes, muscle tone, and strength.
What is the most common type of seizure?
Tonic-clonic seizures/ grand mal seizures: Most common type of seizure. They involve a loss of consciousness, stiffening of the body, and shaking or jerking, and sometimes, followed by loss of bladder or bowel control.
What is a seizure disorder?
A seizure is a sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbance in the brain. Epilepsy is a neurological disorder where brain activities are abnormal, causing more than one or recurrent episodes of seizures. Most cases of seizures can be managed conservatively with medication and supportive treatments.
What are the symptoms of migraines?
Symptoms unique to migraine and migraine auras are water retention, problems sleeping, appetite changes, and talkativeness. Symptoms unique to seizure and seizures auras are depression, a feeling of heaviness, a feeling that a seizure is approaching, and depression.
How are seizures produced?
Generalized seizures are produced by electrical impulses from throughout the brain , while partial seizures are produced by electrical impulses in a small part of the brain. Seizure symptoms include unconsciousness, convulsions, and muscle rigidity.
What is a recurrent seizure called?
Recurrent seizures are called epilepsy. Seizures are usually categorized into three types depending on their onset. They are: Unknown onset: When the beginning of a seizure is not known, it is now called an unknown onset seizure. A seizure could also be called an unknown onset if it is not witnessed or seen by anyone.
What is a sudden change in the brain's electrical activity?
Seizures are usually categorized into three types depending on their onset. A seizure is a sudden change in the brain's normal electrical activity. During a seizure, brain cells fire uncontrollably than their normal rate, temporarily affecting the way a person behaves, moves, thinks or feels. Recurrent seizures are called epilepsy.
How many children have a febrile seizure?
It is estimated that one in every 25 children will have at least one febrile seizure. It is important to know what to do to help your child if he/she has a febrile seizure. Some of the features of a febrile seizure include losing consciousness, shaking, moving limbs on both sides of the body, and lasts 1-2 minutes.
Focal onset seizures
The first main type of seizures—focal seizures — begin on one side of the brain, in one particular area, according to the Epilepsy Foundation. " Focal means there's a focus, a spot from which everything emanates," Vikram Rao, MD, PhD, an associate professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, tells Health .
Generalized onset seizures
Generalized onset seizures are seizures that affect both sides of the brain (or cells in both sides of the brain) at once, according to the Epilepsy Foundation. "That means that there is no epicenter," Dr. Rao says. "We think of that as kind of a network-level imbalance, where the seizure actually starts everywhere simultaneously."
Unknown onset seizures
Sometimes, doctors don't know where a particular seizure began in the brain. In those cases, it's called an unknown onset seizure, the Epilepsy Foundation says. Unknown onset seizures can also be classified as such if they're not witnessed or seen by anyone else, say, if they happen at night or if the person experiencing the seizures lives alone.
Non-epileptic seizures
Something important to know about seizures in general: They aren't all related to epilepsy. Sometimes, a person without epilepsy can experience a seizure. However, the NINDS insists that regardless of what causes a seizure, or the type of seizure, all seizures should be checked out by a doctor.
Why do the types of seizures matter?
The reason it's so important for a doctor to determine the type of seizure a patient has—and specifically where in the brain his or her seizures are beginning—is because that information will help determine the person's treatment plan.