
What are the 3 steps of signal transduction?
- Reception: A cell detects a signaling molecule from the outside of the cell.
- Transduction: When the signaling molecule binds the receptor it changes the receptor protein in some way.
- Response: Finally, the signal triggers a specific cellular response.
- First, reception, whereby the signal molecule binds the receptor.
- Then, signal transduction, which is where the chemical signal results in a series of enzyme activations.
- Finally, the response, which is the resulting cellular responses.
What happens during the three phases of signal transduction?
What happens during the three phases of signal transduction?
- Reception-a protein at the cell surface detects chemical signals.
- Transduction-a change in protein stimulates other changes including signal-transduction pathways.
- Response-almost any cellular activity.
What are the four steps of cell signaling?
Some of the other types of cell signaling pathways include:
- AMPK signaling pathway
- mTOR signaling pathway
- VEGF signaling pathway
- Insulin signal transduction pathway
- Eph/ephrin signaling pathway
How are signal transduction pathways turned off?
Signal transducing receptors are of four general classes:
- Receptors that penetrate the plasma membrane and have intrinsic enzymatic activity or are enzyme associated ( Enzyme-linked Receptors)
- Receptors that are coupled, inside the cell, to G proteins ( 7-TM Receptors)
- Receptors that are found intracellularly and upon ligand binding directly alter gene transcription ( Nuclear Receptors)
Which of these is responsible for initiating a signal transduction pathway?
A transcription factor is a protein that binds to DNA and regulates the expression of a gene. A signal transduction pathway, on the other hand, is an electrical or chemical signaling route in cells. It starts with an extracellular stimulus like a hormone or neurotransmitter binding to its receptor on the cell surface.
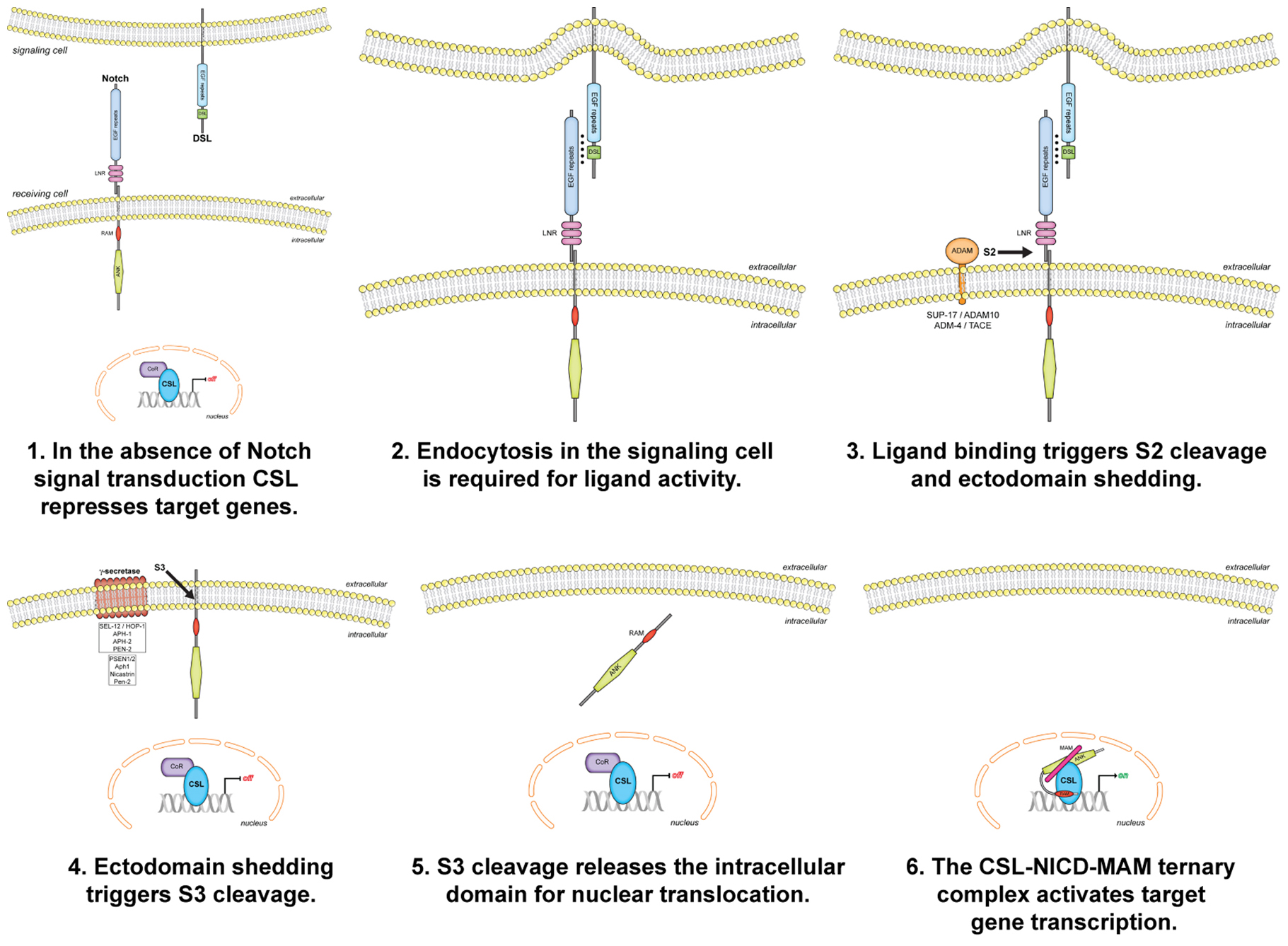
What are the 4 steps in the signal transduction pathway?
Step 1: Reception. Signal reception is the first step of cell signaling and involves the detection of signaling molecules originating from the extracellular environment. ... Step 2: Induction. ... Step 3: Response. ... Step 4: Resetting.
What are the signal transduction pathways?
Signal transduction pathway involves the binding of extracellular signaling molecules and ligands to receptors located on the cell surface or inside the cell that trigger events inside the cell, to invoke a response. The response can then alter the cell's metabolism, shape, and gene expression (Krauss, 2006).
What is the correct order of signal transduction?
What are the four steps of signal transduction? (1) signal molecule binds to receptor that (2) activates a protein that (3) creates second messengers that (4) creates a response. What happens during amplification?
What are the 3 stages of cell signaling?
The three stages of cell communication (reception, transduction, and response) and how changes couls alter cellular responses. How a receptor protein recognizes signal molecules and starts transduction.
What are signal transduction pathways quizlet?
The conversion of the signal to a form that can bring about a specific cellular response. Response. The specific cellular response to the signal molecule.
What is a signal transduction pathway AP biology?
AP Biology The signal transduction pathway is when a small collection of signal molecules produce a large response across the cell. The large response across the cell is called the cascade effect. The response of a cascade can be cell growth, gene expression, or secretion of molecules.
What are the steps in the signal transduction process for the ligand epinephrine in order?
Terms in this set (11)Reception (1) Ligand (Epinephrine) attaches to G-protein (receptor) within the plasma membrane of the target liver cell.Reception (2) ... Reception (3) ... Transduction (4) ... Transduction (5) ... Transduction (6) ... Transduction (7) ... Transduction (8)More items...
What are the three parts of signal transduction pathway quizlet?
Signal transduction is the process by which a signal on a cell's surface is converted to a specific cellular response. The three phases of signal transduction are reception, transduction, and response.
What are the three stages of cell signaling quizlet?
List and briefly define the three stages of cell signaling. Reception, transduction, and response.
Why do most transduction pathways have multiple steps?
Why do transduction pathways have multiple steps? multiple steps provide for greater amplification of a signal. Hypothesize as to how signal transduction could be explored in research to treat cancer.
How many signal transduction pathways are there?
threeThe three main pathways that lead to its activation are GPCR pathways, RTK pathways, and gated ion channels; it regulates proteins either directly or by binding to an enzyme.
What are the 4 types of cell signaling?
There are four basic categories of chemical signaling found in multicellular organisms: paracrine signaling, autocrine signaling, endocrine signaling, and signaling by direct contact.
What is a signal transduction pathway give an example?
What is a signal transduction pathway? Process by which a signal on a cell's surface is converted to a specific cellular response in a series of steps. How does a yeast mating serve as an example of a signal transduction pathway? Alpha yeast sends alpha signals that A yeast receives.
How many Signalling pathways are there?
There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein-coupled receptors: cAMP signal pathway and phosphatidylinositol signal pathway.
What is the meaning of signal transduction?
The meaning of signal transduction is a process that cells use to sense changes in the environment and communicate with other cells. Signal transdu...
What happens during signal transduction?
During signal transduction cells receive a signal from the external environment. This is translated into protein activation or deactivation in the...
What are the steps in the signal transduction pathway?
There are three main steps in the signal transduction pathway: Reception - The cell senses a change in the environment Transduction - The signal...
What are the functions of signal transduction pathways?
Signal transduction pathways regulate all aspects of cell function, including metabolism, cell division, death, differentiation, and movement. Multiple extracellular and intracellular signals for proliferation or quiescence must be integrated by the cell, and it is this integration of signals from multiple pathways that determines the response of a cell to competing and complementary signals. Extracellular signals include growth factors, cytokines, and hormones; the presence or absence of adequate nutrients and oxygen; and contact with other cells or an extracellular matrix. Signaling mediators often bind to membrane-bound receptors on the outside of the cell, but they may also diffuse into the cell and bind receptors in the cytoplasm or on the nuclear membrane. Binding of a ligand to a receptor stimulates the activities of small-molecule second messengers—proteins necessary to continue the transmission of the signal. Signaling pathways ultimately effect the activation of nuclear transcription factors that are responsible for the expression or silencing of genes encoding proteins involved in all aspects of cellular physiology.
What is signal transduction?
Signal transduction pathways are used to convey messages of ligands into changes of biological activity of target cells. Aberrant signaling through communication pathways may result in diseases, and signal transduction pathways are increasingly the target for drug development. Furthermore, interactions with cell signaling pathways may be involved ...
What is the signal transduction pathway of MTLR?
The signal transduction pathway of MTLR is unknown. However, the molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in motilin- induced MTLR desensitization have been observed. After motilin-induced stimulation, the MTLR becomes phosphorylated, probably via GPCR kinases. This leads to recruitment of β-arrestin-2, which targets the receptor to clathrin-coated pits. Upon internalization, the β-arrestin dissociates from the receptor, and the motilin–receptor complex is subsequently sorted to the recycling endosomes that transport the MTLR back to the plasma membrane [8].
What are the diseases that arise from defects in signal transduction pathways?
Many disease processes, such as diabetes, heart disease, autoimmunity and cancer, arise from defects in signal transduction pathways, further highlighting the critical importance of signal transduction to biology, as well as the development of medicine ( Huang et al., 2010 ). Unicellular organisms may also respond to environmental stimuli ...
What is the WNT pathway?
In the Wnt pathway, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor–related protein 5 (LRP5) interacts with Frizzled receptor to transduce signals from Wnt ligands.
What is signal transduction?
Signal Transduction Definition. Signal transduction is the process of transferring a signal throughout an organism, especially across or through a cell. Signal transduction relies on proteins known as receptors, which wait for a chemical, physical, or electrical signal. Chemical signals are called ligands, and can be produced by organisms ...
What happens to the signal during transduction?
Then, the receptor protein embedded in the cellular membrane must accept the signal. Upon receiving the signal, this protein goes through a conformational change. This changes its shape and thus, how it interacts with the molecules around it.
What happens when the action potential reaches the end of the first cell?
Upon reaching the end of the first cell, the signal must cross a synapse to another nerve cell. To do this, another signal transduction pathway is used. As the action potential reaches the end of the first cell, specialized receptor proteins receive the signal, and trigger the release of neurotransmitters.
How does touch and vision work?
Touch and Vision. The signal transduction pathway of touch and vision works in the same way that many nerve signals do. Instead of creating a second messenger or processing a signal internally, the stimulation of the receptor protein causes an influx of ions into the cell. This causes the cell membrane to depolarize.
How does a signal get received?
A signal is received by a receptor protein, and the protein transfers the signal through the cell membrane and into the cell. The kinds of receptors and the second messengers they create can be very different. This is based on the action which the signal must stimulate.
What are the signals that your body creates to regulate itself?
Hormones . Unlike touch and vision, hormones are signals that your body creates to regulate itself. Hormones can cause the body to do many different things, and they themselves are often triggered by a separate signal transduction pathway.
What is the action potential of a nerve?
This event triggers an action potential, which is how the signal travels down a nerve . This is caused by a series of other receptor proteins which are sensitive to the change in voltage. Upon feeling the voltage change, they too allow the ions to even out, which sends the signal down the cell.
What is Signal Transduction?
Signal transduction is a process where cells translate signals from the extracellular environment into changes inside the cell.
Signal Transduction Response
Signal transduction allows cells to communicate through a three step process. The main three steps include:
Signal Transduction Pathway
Signal transduction depends on multi-step processes, called signal transduction pathways. During transduction, signals can be amplified by increasing the number of proteins being activated. This allows for a more widespread and quicker response.
Signal Transduction Cascade
The signal transduction pathway creates a cascade pattern of activation within the cell. The receptor protein activates other proteins that activate other proteins, forming an activation cascade that results in a change in cell behavior.
What is the role of signal transduction?
Signal transduction pathways play a crucial role in a variety of cellular processes including self renewal and differentiation, proliferation, and cell death , and ultimately regulate the balance between regenerative potential and the risk of neoplastic transformation. The major regulatory mechanism controlling signal transduction is reversible phosphorylation, which involves a delicate balance between multiple kinases and phosphatases. Kinases have a classic role in the regulation of numerous signaling pathways and are considered potent therapeutic targets. Recent findings that phosphatases are just as important in the same pathways involving kinases have brought phosphatases to the forefront of biomedical research.
What are the signal transduction pathways in type B photoreceptors?
Signal transduction pathways contributing to the modifications of excitability and synaptic efficacy in type B photoreceptors of conditioned animals involve protein kinase C (PKC), extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK), cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) , and Rho GTPase activity and its downstream target, ROCK.
How do neurotrophins affect the cell?
The signal transduction pathways and the biological effects of neurotrophins differ depending on the location at which a neuron is stimulated. In general, neurons can be stimulated at either their axon endings (target derived) or locally at their cell bodies. In the classic view, the neurotrophin acts as a messenger produced by the target cell that signals survival to the neuron at its axon ending. The neurotrophin binds to its receptor at the axon ending and the neurotrophin/receptor complex is endocytosed into signaling endosomes. This signal is conveyed retrogradely through the axon to the cell body and culminates in changes in gene expression. Recent work, however, demonstrates that target-derived neurotrophins may not necessarily need to be endocytosed to promote survival, providing evidence for parallel signaling pathways for target-derived neurotrophic support. In addition to stimulating retrograde nuclear responses, neurotrophin signaling occurs locally at axonal endings. Local axonal neurotrophin signaling stimulates axon outgrowth rather than survival.
What receptors can IP 3 bind to?
IP 3 can also bind to its receptor (IP 3 R), which triggers Ca 2+ release from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The Ca2+ influx from the rhabdomeric and the IP 3 R-gated storage compartment can cause Ca 2+ release from the ryanodine receptor-gated compartment.
Which receptors release Ca2+?
Numerous signal transduction pathways generate IP3 ( Fig. 26.7 ), which activates IP 3 receptors to release Ca 2+ from the ER in animal cells. Plants and fungi appear to lack IP 3 receptors.
Where is the PPM1D gene located?
The gene encoding Wip1, namely, PPM1D, is located on human chromosome 17q23 (mouse chromosome 11), and its mRNA expression was found to be ubiquitous in many embryonic and adult mouse tissues, with the highest level of expression in the testis.7 The murine Ppm1d gene is spread over six exons spanning over 36 Kb of DNA.
Can ligands be apoptosis?
Several studies have suggested that integrin ligation by soluble, rather than intact, ligands can function as integrin antagonists and promote apoptosis rather than survival or proliferation; such soluble ligands may be created by matrix degradation during tissue remodeling, and thus promote apoptosis.

Signal Transduction Definition
Signal Transduction Pathway
- During signal transduction, a signal may have many components. There is the primary messenger, which may be a chemical signal, electrical pulse, or even physical stimulation. Then, the receptor protein embedded in the cellular membrane must accept the signal. Upon receiving the signal, this protein goes through a conformational change. This changes...
Examples of Signal Transduction
- Touch and Vision
The signal transduction pathway of touch and vision works in the same way that many nerve signals do. Instead of creating a second messenger or processing a signal internally, the stimulation of the receptor protein causes an influx of ions into the cell. This causes the cell me… - Hormones
Unlike touch and vision, hormones are signals that your body creates to regulate itself. Hormones can cause the body to do many different things, and they themselves are often triggered by a separate signal transduction pathway. Typically, a hormone is release from an endocrine gland, …
Quiz
- 1. Which of the following is NOT an example of signal transduction? A. A molecule found in blood binds to a protein in a shark’s olfactory cells. A signal is sent to the brain. B. Cow’s milk contains growth hormones. Upon receiving these hormones, a baby cow’s cells grow and divide. C.A cell uses the energy for a molecule of glucose to drive other reactions. 2. Why is it necessary that dif…