
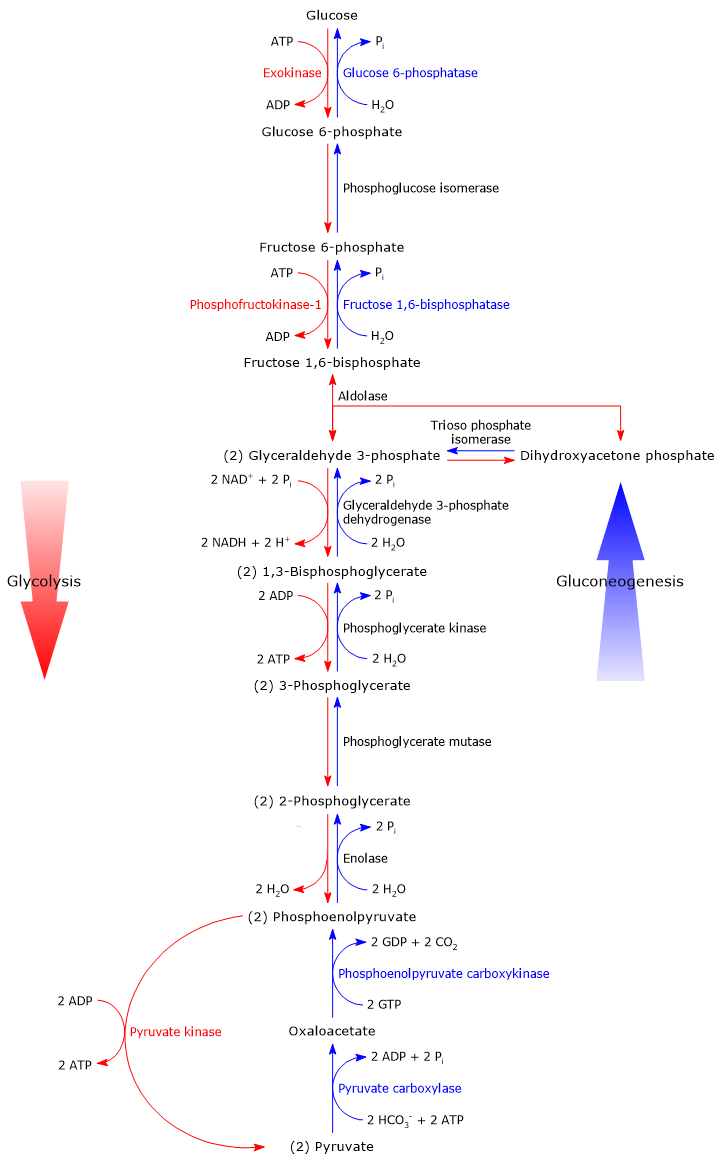
Irreversible steps of gluconeogenesis
- The phosphorylation of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate, catalyzed by hexokinase (EC 2.7.1.1) or glucokinase (EC 2.7.1.2).
- The phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, catalyzed by phosphofructokinase-1 or PFK-1...
- The conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate or PEP to pyruvate, catalyzed by pyruvate kinase (EC 2.
- Steps 1 and 2: pyruvate. Glycolysis to phosphoenolpyruvate. ...
- Steps 3–8: phosphoenolpyruvate. ...
- Step 9: dephosphorylation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate. ...
- Step 10: fructose-6-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate via phosphoglucoisomerase.
- Step 11: glucose-6-phosphate to glucose.
What are the three irreversible steps of gluconeogenesis?
- Lactate is a product of anaerobic glycolysis. When oxygen is limited (such as during vigorous exercise or in low perfusion states) cells must perform anaerobic glycolysis to produce ATP. ...
- Glycerol comes from adipose tissue. ...
- Glucogenic amino acids enter gluconeogenesis via the citric acid cycle. ...
When does gluconeogenesis start?
The Gluconeogenesis process mainly occurs during the periods of starvation, fasting, low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise when the glucose level becomes low in blood and other tissues. All animals, plants, and microorganisms require glucose to perform their metabolic activity.
Does ATP generate in gluconeogenesis?
Glycerol, which is released from adipose tissue through lipolysis, is also a gluconeogenic substrate. Fatty acid β oxidation is unable to produce gluconeogenic substrates, but it does generate ATP which is required for gluconeogenesis.
What happens in the process of gluconeogenesis?
The gluconeogenesis pathway: steps and regulation
- Irreversible steps of gluconeogenesis. As previously said, gluconeogenesis is in essence glycolysis in reverse. ...
- Coordinated regulation of gluconeogenesis and glycolysis. If glycolysis and gluconeogenesis were active simultaneously at a high rate in the same cell, the only products would be ATP consumption and heat ...
- Precursors of gluconeogenesis. ...
How many steps are in the gluconeogenesis pathway?
9 stepsThere are 9 steps in the gluconeogenesis process: Step #1: Pyruvate gets converted into phosphoenolpyruvate.
What is the first step of gluconeogenesis?
The first step of gluconeogenesis that bypasses an irreversible step of glycolysis, namely the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate kinase, is the conversion of pyruvate to phosphoenolpyruvate. Phosphoenolpyruvate is synthesized through two reactions catalyzed, in order, by the enzymes: pyruvate carboxylase (EC 6.4. 1.1);
Where does each step of gluconeogenesis occur?
The pathway of gluconeogenesis (Figure 1) occurs mainly in the liver and kidney cortex and to a lesser extent in the small intestine. The major substrates for gluconeogenesis include lactate, pyruvate, propionate, glycerol, and 18 of the 20 amino acids (the exceptions are leucine and lysine).
What are the 3 bypass steps of gluconeogenesis?
The three reactions of glycolysis that proceed with a large negative free energy change are bypassed during gluconeogenesis by using different enzymes. These three are the pyruvate kinase, phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) and hexokinase/glucokinase catalyzed reactions.
What are the 10 steps of gluconeogenesis?
11 steps:Steps 1 and 2: pyruvate. Glycolysis to phosphoenolpyruvate. ... Steps 3–8: phosphoenolpyruvate. ... Step 9: dephosphorylation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose-6-phosphate. ... Step 10: fructose-6-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate via phosphoglucoisomerase.Step 11: glucose-6-phosphate to glucose.
What is gluconeogenesis describe the process of gluconeogenesis in detail?
Gluconeogenesis is the metabolic process by which organisms produce sugars (namely glucose) for catabolic reactions from non-carbohydrate precursors. Glucose is the only energy source used by the brain (with the exception of ketone bodies during times of fasting), testes, erythrocytes, and kidney medulla.
What are the reactions of gluconeogenesis?
The four unique reactions of gluconeogenesis are pyruvate carboxylase, located in the mitochondrial matrix, phosphoenolpyruate (PEP) carboxykinase located in mitochondrial matrix and cytosol, fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase located in the cytosol and glucose-6-phosphatase located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
What steps in gluconeogenesis require ATP?
Energetics and mechanism of pyruvate carboxylase This tells us that the gluconeogenic conversion of pyruvate to PEP will require the input of a significant amount of energy. In accordance with this expectation, the pyruvate carboxylase reaction, which is the first step in this conversion, requires ATP.
Which steps in glycolysis do not exist in gluconeogenesis?
To summarize: Steps 1 and 3 of glycolysis are bypassed by gluconeogenesis because the glycolytic steps involve transferring a phosphate group from ATP, and gluconeogenesis can't regenerate ATP. Step 10 of glycolysis is bypassed by gluconeogenesis to work around an irreversible reaction and to avoid a futile cycle.
What is Glycogenolysis pathway?
Glycogenolysis is the biochemical pathway in which glycogen breaks down into glucose-1-phosphate and glucose. The reaction takes place in the hepatocytes and the myocytes. The process is under the regulation of two key enzymes: phosphorylase kinase and glycogen phosphorylase.
Definition Gluconeogenesis
Our body needs glucose, which comes from carbohydrates, to survive. The brain can only use energy that has come from glucose, yet the body can only store enough glucose to last for less than two hours.
The Steps of Gluconeogenesis
Glycolysis is the process of converting glucose into energy. The body has two types of reactions: ones that build products, such as muscle or glucose, and ones that break products down. When products are being built, energy is required. When products are being broken down, energy is created.
Gluconeogenesis Definition
Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway through which convert the pyruvate or three- and four-carbon containing compounds into glucose.
Gluconeogenesis Pathway Steps
Gluconeogenesis may occur in the liver or kidney, in the mitochondria or cytoplasm of those cells. In this pathway, pyruvate is converted into Glusoe through a series of reactions catalyzed by different enzymes.
Importance of Gluconeogenesis
Fulfill the energy demands of skeletal muscle, RBCs, neurons, embryonic tissue, medulla of the kidney, testes, etc.
Substrate for Gluconeogenesis
There are present different substrates for Gluconeogenesis such as Glycerol, lactate, and Glucogenic amino acids.
Regulation of Gluconeogenesis
Acetyl CoA regulates the conversation of Pyruvate to Phophoenolpyruvate. It has both positive and negative regulation on Gluconeogenesis such as;
Location of Gluconeogenesis
Liver, kidney, and intestine; not in skeletal muscle. The first reaction (catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase) takes place in the mitochondria, whereas the rest of the reactions occur in the cytosol.
Steps in Gluconeogenesis
Pyruvate carboxylase converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate in the mitochondrion.
Significance of Gluconeogenesis Pathway
Gluconeogenesis meets the needs of the body for glucose when sufficient carbohydrate is not available from the diet or glycogen reserves.
Associated Disease
Deficiency in any of the gluconeogenic enzymes leads to hypoglycemia. Failure of gluconeogenesis may be fatal.
Gluconeogenesis Definition
Gluconeogenesis is the formation of new glucose molecules in the body as opposed to glucose that is broken down from the long storage molecule glycogen. It takes place mostly in the liver, though it can also happen in smaller amounts in the kidney and small intestine.
Function of Gluconeogenesis
Our bodies produce glucose to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Glucose levels in the blood must be maintained because it is used by cells to make the energy molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Gluconeogenesis occurs during times when a person has not eaten in a while, such as during a period of famine or starvation.
Gluconeogenesis Pathway
Gluconeogenesis begins in either the mitochondria or cytoplasm of the liver or kidney. First, two pyruvate molecules are carboxylated to form oxaloacetate. One ATP (energy) molecule is needed for this.
Location
Glycogenesis takes place in the cytoplasm of cells in muscle, liver, and adipose tissue. Substrate is UDP-glucose and Changes glucose to glycogen.
Glycogenesis
The biosynthesis of glycogen from glucose is called Glycogenesis. Glycogenesis takes place when blood glucose levels are sufficiently high to allow excess glucose to be stored. Glycogenesis is stimulated by the hormone insulin.
Gluconeogenesis Steps with Structures
Glucose phosphorylation – In the initial phase, glucose is phosphorylated into glucose-6-phosphate, a usual reaction in glycolysis. It is catalysed by glucokinase (liver) and hexokinase (muscle).
Regulation
The formation of glycogen primarily depends on the level of glucose in the blood as well as the level of glycogen in the liver and muscle tissues. The activities of hormones in the body also affect the level and release of glycogen. These enzymes include the following:
