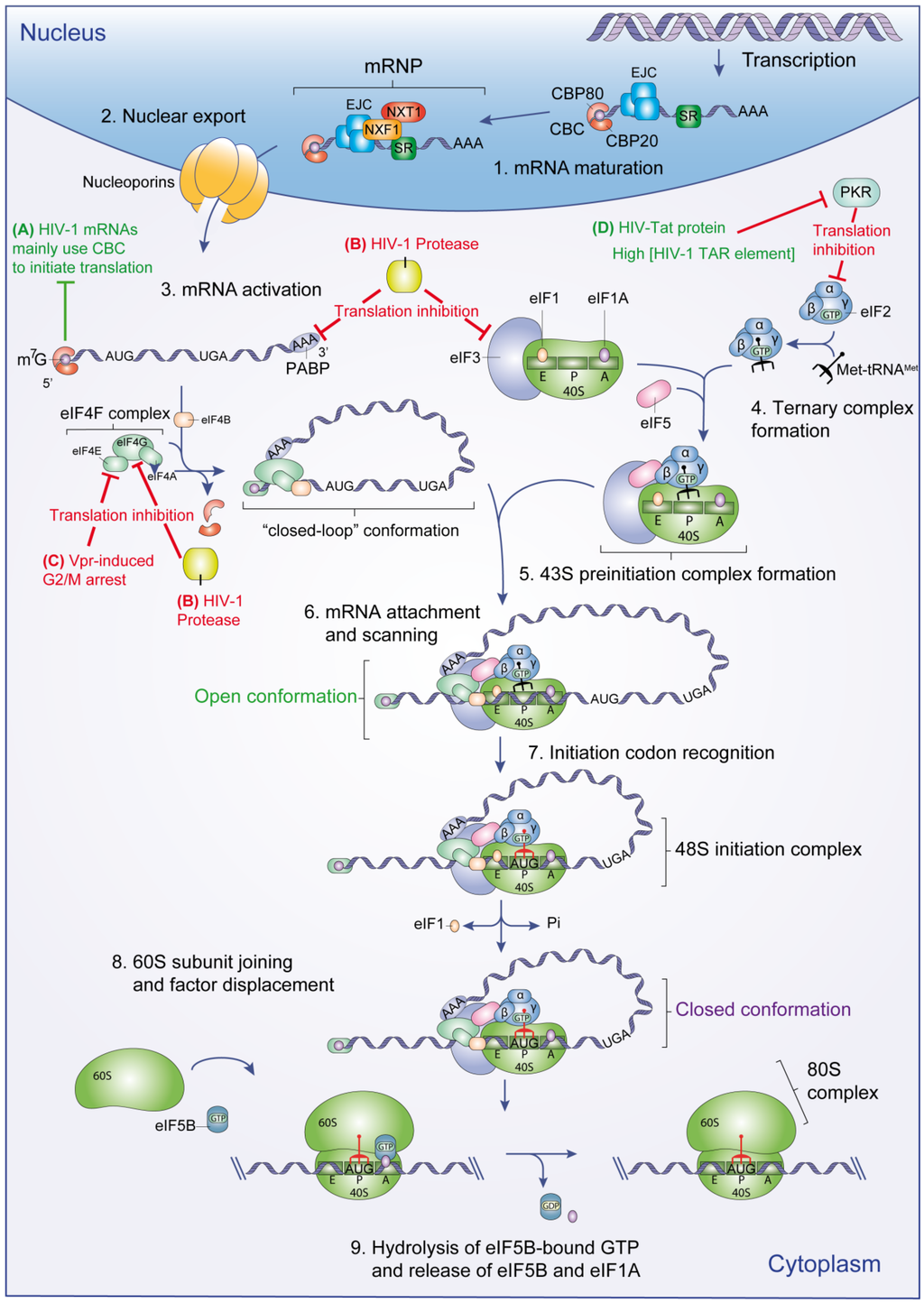
Steps of Translation
- Initiation of Translation. Protein synthesis begins with the formation of an initiation complex. In E. coli, this...
- Elongation of Translation. The 50S ribosomal subunit of E. coli consists of three compartments: the A (aminoacyl) site...
- Termination of Translation. Termination of translation occurs when a stop codon, or nonsense codon (UAA, UAG, or...
What are the 7 steps of translation?
Jan 28, 2020 · Three steps of translation • Initiation: mRNA, ribosome and tRNA are brought together. Elongation: amino acids are added (via tRNA-mRNA interaction) to lengthen the peptide chain. Termination: releasing the completed polypeptide and …
What is the first step in translation?
Translation can be subdivided into several steps: initiation, elongation, termination and recycling. Of these, initiation is the most complex and the most divergent among the different kingdoms of …
What are the stages of translation?
Translation begins when an initiator tRNA anticodon recognizes a codon on mRNA. The large ribosomal subunit joins the small subunit, and a second tRNA is recruited. As the mRNA moves relative to the ribosome, the polypeptide chain is formed. Entry of a release factor into the A site terminates translation and the components dissociate.
What are the steps of translation?
The four steps of translation are: Activation or charging of tRNA Initiation – recognition of start codon, binding of ribosomal subunits to mRNA and formation of initiation complex with Met-tRNA at the P site Elongation – peptide bond formation and growing of polypeptide chain

What are the 3 steps of the initiation of translation?
Translation of an mRNA molecule occurs in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination.Jun 22, 2020
What are the 5 steps of translation in order?
The multi-step translation process professional translators useStep 1: Scope out the text to be translated.Step 2: Initial translation.Step 3: Review the accuracy of the translation.Step 4: Take a break.Step 5: Refine translation wording.
What is initiation translation?
Initiation ("beginning"): in this stage, the ribosome gets together with the mRNA and the first tRNA so translation can begin. Elongation ("middle"): in this stage, amino acids are brought to the ribosome by tRNAs and linked together to form a chain.
What are the 4 steps of translation?
The four steps of translation are:Activation or charging of tRNA.Initiation – recognition of start codon, binding of ribosomal subunits to mRNA and formation of initiation complex with Met-tRNA at the P site.Elongation – peptide bond formation and growing of polypeptide chain.More items...
What are the steps of translation?
Outline the basic steps of translation. As with mRNA synthesis, protein synthesis can be divided into three phases: initiation, elongation, and termination. The process of translation is similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Here we’ll explore how translation occurs in E. coli, a representative prokaryote, and specify any differences between ...
What is the initiator of protein synthesis?
coli, this complex involves the small 30S ribosome, the mRNA template, initiation factors and a special initiator tRNA . The initiator tRNA interacts with the start codon AUG. Guanosine triphosphate (GTP), which is a purine nucleotide triphosphate, acts as an energy source during translation—both at the start of elongation and during the ribosome’s translocation.
How are ribosomes induced?
Ribosomal steps are induced by conformational changes that advance the ribosome by three bases in the 3′ direction. The energy for each step of the ribosome is donated by an elongation factor that hydrolyzes GTP. Peptide bonds form between the amino group of the amino acid attached to the A-site tRNA and the carboxyl group ...
What happens to ribosomes after translation?
After many ribosomes have completed translation, the mRNA is degraded so the nucleotides can be reused in another transcription reaction.
What enzyme is responsible for peptide bond formation?
The formation of each peptide bond is catalyzed by peptidyl transferase, an RNA-based enzyme that is integrated into the 50S ribosomal subunit. The energy for each peptide bond formation is derived from GTP hydrolysis, which is catalyzed by a separate elongation factor.
What is the process of translation?
Translation, the process of mRNA-encoded protein synthesis, requires a complex apparatus, composed of the ribosome, tRNAs and additional protein factors, including aminoacyl tRNA synthetases. The ribosome provides the platform for proper assembly of mRNA, tRNAs and protein factors and carries the peptidyl-transferase activity.
What is the process of mRNA synthesis?
Translation, the process of mRNA-encoded protein synthesis, requires a complex apparatus, composed of the ribosome, tRNAs and additional protein factors, including aminoacyl tRNA synthetases. The ribosome provides the platform for proper assembly of mRNA, tRNAs and protein factors and carries the pe …. Translation, the process of mRNA-encoded ...
What are the steps of translation?
Outline the basic steps of translation. As with mRNA synthesis, protein synthesis can be divided into three phases: initiation, elongation, and termination. The process of translation is similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Here we’ll explore how translation occurs in E. coli, a representative prokaryote, and specify any differences between ...
How does translation begin?
Translation begins when an initiator tRNA anticodon recognizes a codon on mRNA. The large ribosomal subunit joins the small subunit, and a second tRNA is recruited. As the mRNA moves relative to the ribosome, the polypeptide chain is formed.
What happens when a ribosome moves along the mRNA?
As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, each mRNA codon comes into register, and specific binding with the corresponding charged tRNA anticodon is ensured . If mRNA were not present in the elongation complex, the ribosome would bind tRNAs nonspecifically.
What is the initiation factor for protein synthesis?
In E. coli, this complex involves the small 30S ribosome, the mRNA template, three initiation factors (IFs; IF-1, IF-2, and IF-3), and a special initiator tRNA, called tRNAMet f tRNA f M e t. The initiator tRNA interacts with the start codon AUG (or rarely, GUG), links to a formylated methionine called fMet, and can also bind IF-2. Formylated methionine is inserted by fMet−tRNAMet f fMet − tRNA f Met at the beginning of every polypeptide chain synthesized by E. coli, but it is usually clipped off after translation is complete. When an in-frame AUG is encountered during translation elongation, a non-formylated methionine is inserted by a regular Met-tRNA Met.
How are ribosomes induced?
Ribosomal steps are induced by conformational changes that advance the ribosome by three bases in the 3′ direction. The energy for each step of the ribosome is donated by an elongation factor that hydrolyzes GTP. Peptide bonds form between the amino group of the amino acid attached to the A-site tRNA and the carboxyl group ...
What is the energy source for translation?
Guanosine triphosphate (GTP), which is a purine nucleotide triphosphate, acts as an energy source during translation—both at the start of elongation and during the ribosome’s translocation. Binding of the mRNA to the 30S ribosome also requires IF-III. In eukaryotes, a similar initiation complex forms, comprising mRNA, ...
What happens to ribosomes after translation?
After many ribosomes have completed translation, the mRNA is degraded so the nucleotides can be reused in another transcription reaction.

Initiation of Translation
Elongation of Translation
- The 50S ribosomal subunit of E. coli consists of three compartments: the A (aminoacyl) site binds incoming charged aminoacyl tRNAs. The P (peptidyl) site binds charged tRNAs carrying amino acids that have formed peptide bonds with the growing polypeptide chain but have not yet dissociated from their corresponding tRNA. The E (exit) sitereleases dissociated tRNAs so that t…
Termination of Translation
- Termination of translation occurs when a stop codon, or nonsense codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) is encountered. Upon aligning with the A site, these stop codons are recognized by release factors in prokaryotes and eukaryotes that instruct peptidyl transferase to add a water molecule to the carboxyl end of the P-site amino acid. This reaction forces the P-site amino acid to detach from i…