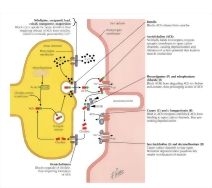
The steps of neuromuscular transmission are as follows:
- (1) An action potential is conducted down the motor axon to the prejunctional axon terminal.
- (2) Depolarization of the terminal buttons opens up voltage-gated Ca 2+ channels in its membranes. Ca 2+ moves into the...
- (3) Elevated Ca 2+ concentration in the terminal button causes exocytosis of the ACh-containing...
What is the mechanism of neuromuscular transmission?
Neuromuscular transmission is dependent on a coordinated mechanism involving (1) synthesis, storage, and release of acetylcholine from the presynaptic motor nerve endings at the neuromuscular junction; (2) binding of acetylcholine to nicotinic receptors on the postsynaptic region of the muscle membrane, with consequent generation of the action ...
What are the neuromuscular junction steps?
Neuromuscular Junction Steps STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by Jorge_Velazquez Terms in this set (9) Step 1 Nerve impulse arrives at axon terminal of motor neuron and triggers release of acetylcholine (ACh) Step 2 ACh diffuses, binds to its receptors, and triggers muscle action potential.
What happens at the neuromuscular junction of a nerve?
Nerve impulses cause the release of a neurotransmitter, acetylcholine (ACh), into the junction between the nerve cell and the muscle cell. Diseases involving the neuromuscular junction are called NMT disorders because they are caused by a dysfunction in the transmission of ACh at the nerve–muscle synapse.
What triggers the action potential at the neuromuscular junction?
When the nerve impulse from the peripheral or central nervous system reaches the presynaptic membrane (nerve terminal) of the neuromuscular junction in the form of the action potential, it triggers voltage-gated Ca2+ channels at the active zones of the nerve terminal to open, and Ca2+ ions enter the nerve terminal from the extracellular space.
What is the steps of neuromuscular junction?
Steps of Signalling at Neuromuscular Junctions Firstly, the signal from the axon terminal of the previous neuron travels down the motor neuron to the presynaptic axon terminal. This causes the activation and opening of calcium channels in the membrane, allowing calcium ions to enter the neuron.
What is the first step in the neuromuscular junction transmission of an action potential?
Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-gated calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron.
What are the 3 main phases in neuromuscular action potential?
An action potential has three phases: depolarization, overshoot, repolarization.
What are the types of neuromuscular transmission?
Neuromuscular TransmissionMyasthenia gravis.Electromyography.Acetylcholine.Antibody.Protein.Stimulation.Cholinergic Receptor.Eaton Lambert Syndrome.
What are the 7 steps of the neuromuscular junction?
Terms in this set (7) An AP travels down the axon. to the axon terminal. Electrical gated calcium channels open. ... Calcium causes the vesicles to. ... ACH diffuses across the synaptic cleft. ... ACH binding opens ion channels. ... If the muscle reaches the threshold (-55mv) at the motor end plate. ... ACH is broken down by.
What are the 4 basic steps in the sliding filament theory?
In the sliding filament theory, myosin heads attach to an actin filament, bend to pull the actin filaments closer together, then release, reattach, and pull again.
What are the 6 steps of action potential?
Six Steps of an Action PotentialFlashcards. Review terms and definitions.Learn. Focus your studying with a path.Test. Take a practice test.Match. Get faster at matching terms.
What are the 3 phases of a muscle twitch?
A muscle twitch has a latent period, a contraction phase, and a relaxation phase. A graded muscle response allows variation in muscle tension.
What is the correct order of a signal being transmitted across a neuromuscular junction?
The signal moves down the neuron and then allows the chemical junction to occur between the neuron and the muscle. The signal jumps over the synapse and hits the muscle head on, causing the muscles to move accordingly!
What are the steps that occur at the neuromuscular junction to allow acetylcholine to be released as a response to an action potential?
Upon stimulation by a nerve impulse, the terminal releases the chemical neurotransmitter acetylcholine from synaptic vesicles. Acetylcholine then binds to the receptors, the channels open, and sodium ions flow into the end plate.
What are the four parts of a neuromuscular junction?
The neuromuscular junction comprises four cell types: the motor neuron, terminal Schwann cell, skeletal muscle fibre and kranocyte, with the motor neuron and muscle fibre separated by a gap called the synaptic cleft.
What are the events at the neuromuscular junction?
0:081:562-Minute Neuroscience: Neuromuscular Junction - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt.MoreIt.
What are the steps of action potential?
The action potential can be divided into five phases: the resting potential, threshold, the rising phase, the falling phase, and the recovery phase.
What are the steps that take place at a neuromuscular junction that lead to muscle contraction?
When the nervous system signal reaches the neuromuscular junction a chemical message is released by the motor neuron. The chemical message, a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, binds to receptors on the outside of the muscle fiber. That starts a chemical reaction within the muscle.
What are the events at the neuromuscular junction?
0:081:562-Minute Neuroscience: Neuromuscular Junction - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt.MoreIt.
What initiates action potential on a muscle cell?
(A) Neurotransmitter (acetylcholine, ACh) released from nerve endings binds to receptors (AChRs) on the muscle surface. The ensuing depolarization causes sodium channels to open, which elicits an action potential that propagates along the cell.
What is neuromuscular transmission?
Neuromuscular transmission is a complex and dynamic process in which the effects of drugs are composites of actions that vary with drug, dose, activity at the junction and muscle, presence of other drugs, age and concomitant disease. The neuromuscular junction undergo constant structural remodeling influenced by multiple factors including ...
What is the mechanism of neuromuscular transmission in skeletal muscle?
Neuromuscular transmission in skeletal muscle occurs when acetylcholine released from the nerve ending binds to the endplate nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) on the postjunctional muscle membrane. These AChRs respond by opening channels for the influx of sodium ions into the muscle leading to endplate depolarization and muscle contraction. Activation is terminated when acetylcholine is hydrolyzed by acetylcholinesterase.
What is the safety factor of neuromuscular transmission?
Neuromuscular transmission relies on the generation of a junctional muscle membrane depolarization of sufficient amplitude to sustain the formation of a propagated action potential; the difference between the magnitude of the first parameter and the threshold of the action potential is called the safety factor of neuromuscular transmission. Inexorably, impulse transmission must proceed across multiple conformational changes in the molecules that underlie NMJ excitability. An inherently stochastic (as opposed to a deterministic all-or-nothing) process, normal transmission necessitates a large safety factor in order to operate with fidelity. Among the processes that are non-deterministic, that is, best described by probability distribution laws rather than individually, are the opening of voltage-gated Ca 2+ channels, the number of ACh vesicles released, the diffusion of ACh in the cleft, the binding of two ACh molecules to the AChR, the onset of desensitization and closing of the AChR and the encounter of the neurotransmitter with AChE, to name but a few events for which probability distributions are known. The origin of this stochastic behavior is intrinsic to all molecules that change conformation or move, but it is accentuated by the limited dimensions of the NMJ, which includes a relatively small number of molecules. In contrast, an enzymatic reaction taking place, for example, in solution carried out by an ensemble of many more molecules behaves, as a whole, predictably. The limitation to the size of the NMJ may be due to the large energetic expense associated with its maintenance, particularly when it is subject to frequent use (think, for example, of a flying hummingbird) and, thus, energy may be safely spared by reducing synaptic size as long as the safety factor of transmission remains large. In line with the importance of neuromuscular transmission for the survival of the organism, all key molecular elements of the NMJ are encoded by highly conserved genes whose absence or severe dysfunction is incompatible with life. Instead, diseases of the NMJ tend to shift the probability distribution laws for the different conformations of its key molecules, and may be thus viewed as processes that decrease the safety factor of transmission. This is a fundamental principle in molecular neuromuscular pathology.
What is the function of the neuromuscular junction?
Neuromuscular transmission (NMT) is a process that permits the central nervous system to control the movement of muscles in the body. Nerve impulses cause the release of a neurotransmitter, acetylcholine (ACh), into the junction between the nerve cell and the muscle cell. Diseases involving the neuromuscular junction are called NMT disorders because they are caused by a dysfunction in the transmission of ACh at the nerve–muscle synapse. Depending on the site of dysfunction, NMT disorders are classified into three distinct groups: postsynaptic disorders, presynaptic disorders, and combined presynaptic and postsynaptic disorders.
Which type of fiber is more susceptible to neuromuscular transmission failure?
Accordingly, type IIx and/or IIb fibers are more susceptible to neuromuscular transmission failure. Across muscles, whether of mixed or homogeneous fiber type composition, the total number of vesicles in the readily releasable pool is greater at type IIx and/or IIb fibers compared to type I and IIa fibers.
Which neuromuscular transmission is dependent on a coordinated mechanism?
Neuromuscular transmission is dependent on a coordinated mechanism involving (1) synthesis, storage, and release of acetylcholine from the presynaptic motor nerve endings at the neuromuscular junction; (2) binding of acetylcholine to nicotinic receptors on the postsynaptic region of the muscle membrane, with consequent generation of the action potential; and (3) rapid hydrolysis of acetylcholine by acetylcholine sterase enzyme present in the synaptic cleft.
Which myasthenic disorder affects only the motor system?
Myasthenic disorders affect the motor system only. Sensory and autonomic functions are not impaired. The exception is Lambert-Eaton syndrome , a myasthenic syndrome in which a significant minority of patients have autonomic dysfunction.
What is the function of the neuromuscular junction?
The neuromuscular junction then, is a key component in the body’s ability to produce and control movement. Amazingly, processes at the neuromuscular junction take place at speeds that allow movements to occur with no appreciable delay or lag. This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the neuromuscular junction.
What is the chemical that moves the electrical signal across the synaptic cleft?
The chemical in this case is acetylcholine (ACh), an example of a neurotransmitter that allows neurons to communicate with other cells.
What is the space between the synaptic end bulbs of the neuron and the cell membrane of the muscle fiber?
Between the synaptic end bulbs of the neuron and the cell membrane of the muscle fiber (the sarcolemma) lies a space known as the synaptic cleft, which is the final component of the neuromuscular junction.
What is the axon terminal?
At this point, each axon of the motor neuron will divide into branches called axon terminals. Towards the end of the axon terminal, closest to the muscle fiber, the tip of the axon terminal enlarges and becomes known as the synaptic end bulb. It is the synaptic end bulb of the motor neuron that comprises the nervous system component ...
What is the toxin that blocks the release of ACh from the synaptic vesicles?
Botulinum toxin. A number of the events that occur at the neuromuscular junction can be affected by either plant products or drugs. For example, the botulinum toxin, which is produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum, blocks the release of ACh from the synaptic vesicles contained within the synaptic end bulb.
Does curare cause muscle paralysis?
Curare, a plant based poison, can also cause muscle paralysis by binding to and blocking ACh receptors within the motor end plate of the muscle fiber. In this case, ACh is present, but it cannot activate and open the ion channels that allow the influx of Na+ which initiates the action potential in the muscle fiber.