Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells Organelle Function Nucleus The “brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA. Mitochondria Make energy out of food Ribosomes Make protein Golgi Apparatus Make, process and package proteins.
...
Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells.
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Mitochondria | Make energy out of food |
| Ribosomes | Make protein |
| Golgi Apparatus | Make, process and package proteins |
| Lysosome | Contains digestive enzymes to help break food down |
What are the parts and functions of an eukaryotic cell?
- Cell wall. It is a rigid structure that resides outside the plasma membrane that gives shape, support, and protection to the cell. ...
- Cell nucleus. It is a central organelle bounded by a double-porous membrane that allows the material to be exchanged between the cytoplasm and its interior. ...
- Ribosomes. ...
- Cytoplasm. ...
What are the two major parts of an eukaryotic cell?
Two major parts of a eukaryotic cell are the Nucleus and the Cytoplasm. 2.) Describe the steps in making, packaging and exporting a protein from a cell First, the ribosome makes a protein.
What are the 4 types of eukaryotic cells?
Types of Eukaryotic Cells
- Animal Cells. Animal cells are the basic building blocks that make up all animals, including birds, fish, reptiles, mammals, and amphibians.
- Plant Cells. Plants are made up of plant cells. ...
- Fungi Cells. The fungi kingdom consists of yeasts, mildews, molds, and mushrooms. ...
- Protist Cells. ...
What organisms have eukaryotic cells?
What are 4 examples of eukaryotic cells?
- The Protists. Protists are one-celled eukaryotes.
- The Fungi. Fungi can have one cell or many cells.
- The Plants. All of the roughly 250,000 species of plants -- from simple mosses to complex flowering plants -- belong to the eukaryotes.
- The Animals.
What are the major organelles of eukaryotic cells?
Overview of the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vacuoles, mitochondria, chloroplasts and lysosomes.
What is the structure and function of major organelles?
An organelle is a subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell, much like an organ does in the body. Among the more important cell organelles are the nuclei, which store genetic information; mitochondria, which produce chemical energy; and ribosomes, which assemble proteins.
What is the function of each organelle in a cell?
Organelles and their FunctionsOrganelleCell TypeFunctionMitochondriaEukaryoticMakes energyLysosomeEukaryotic, animal cells onlyRemoves unwanted material and wastePeroxisomeEukaryoticRegulate biochemical pathways that involve oxidationVacuolesEukaryoticStore water and nutrients14 more rows•Dec 7, 2021
What are the five cell organelles and their functions?
What's found inside a cellOrganelleFunctionNucleusDNA StorageMitochondrionEnergy productionSmooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)Lipid production; DetoxificationRough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)Protein production; in particular for export out of the cell3 more rows
What is structure and function of cell?
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions.
What are the 12 organelles in a cell?
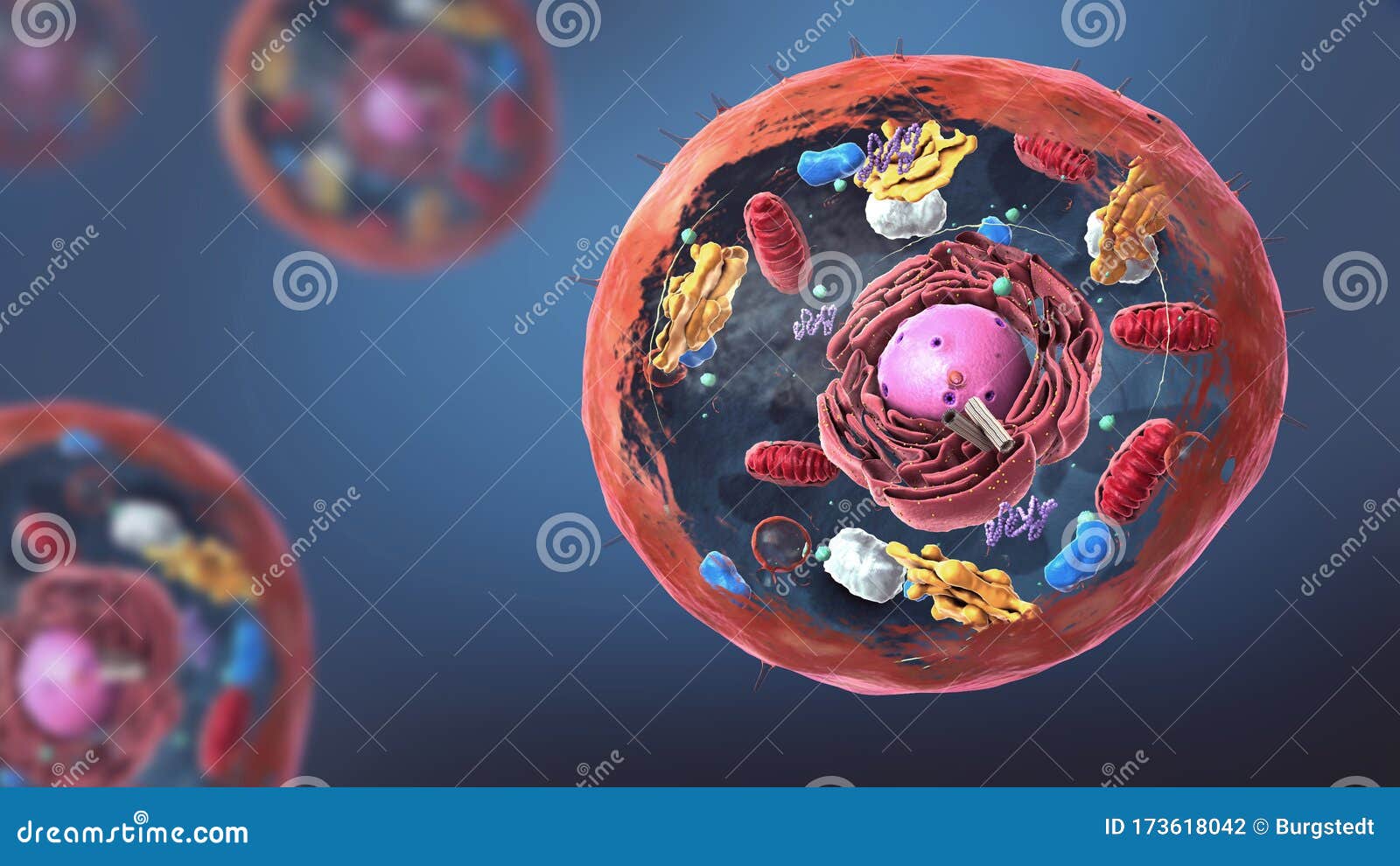
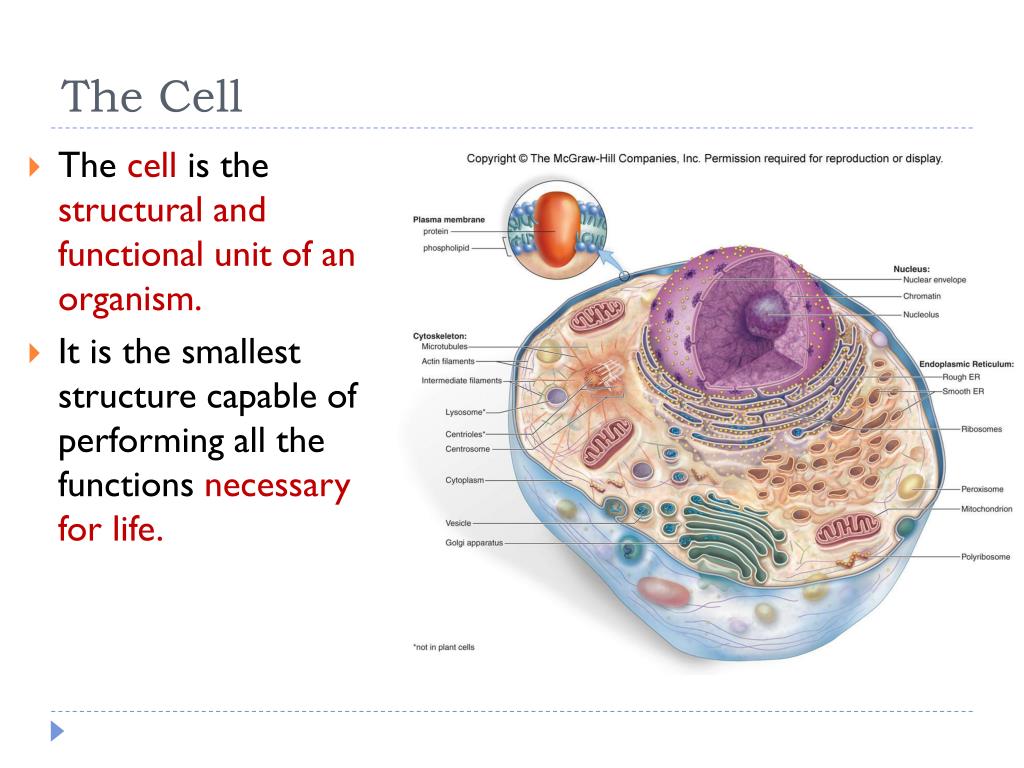
Within the cytoplasm, the major organelles and cellular structures include: (1) nucleolus (2) nucleus (3) ribosome (4) vesicle (5) rough endoplasmic reticulum (6) Golgi apparatus (7) cytoskeleton (8) smooth endoplasmic reticulum (9) mitochondria (10) vacuole (11) cytosol (12) lysosome (13) centriole.
How the structure and function of cells are linked?
The contents of the cell, or the structures of the cell, allow the cell to be "specialized." Together with the cell's proteins, they allow the cell to do specific things. They allow a cell to act like a neuron or a bone cell or a skin cell.
What is the structure of a cell?
A cell consists of three parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and, between the two, the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm lie intricate arrangements of fine fibers and hundreds or even thousands of miniscule but distinct structures called organelles.
Where are eukaryotic cells found?
The eukaryotic cells types are generally found in animals, plants, algae, and fungi. For the purpose of this article, the primary focus will be the structure and histology of the animal cell. The major differences between animal and plant cells will be explored as well. As previously stated, the fundamental components of a cell are its organelles.
What are the components of a cell?
As previously stated, the fundamental components of a cell are its organelles. These organelles are made up of varying combinations of atoms and molecules. The organelles drive different functions of the cell from metabolism, to energy production and subsequently to replication.
How do cells grow and replicate?
In order for cells to grow and replicate, they must produce the necessary building blocks to achieve this feat. Additionally, some cells – like the β-cells of the pancreas – produce protein based hormones to help maintain homeostasis . This process is achieved by ribosomes. Ribosomes are complex ribonucleic acid based molecules (i.e. ribosomal-ribonucleic acid; r-RNA) that are responsible for translating coded sequences of the messenger-RNA (m-RNA) to proteins. They are made up of a small and a large subunit which coordinate with each other to translate the m-RNA strand. Some ribosomes are membrane bound, while others float freely in the cytoplasm. While free ribosomes synthesize proteins that are used within the cell, the proteins synthesized by bound ribosomes are meant to be exported.
What is the smallest cell in an organism?
The cell is the smallest functional unit within a living organism, which can function independently. It is made up of several types of organelles that allow the cell to function and reproduce. There are two general classes of cells that exist: the self-sustaining simple cells known as prokaryotic (bacteria and archaea) and the more complex dependent cells known as eukaryotic. The eukaryotic cells types are generally found in animals, plants, algae, and fungi. For the purpose of this article, the primary focus will be the structure and histology of the animal cell. The major differences between animal and plant cells will be explored as well.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
The plasma membrane is the outermost layer of the cell. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its environment. It is often referred to as a fluid mosaic phospholipid bilayer that is hydrophilic externally and internally, but hydrophobic at its core. The hydrophilic property arises from the charged phosphate molecule that forms the head of the phospholipid, and the hydrophobic nature is from the two lipid tails which forms the core. This feature allows the selective permeability of the membrane. For instance, particles that are hydrophilic (e.g. ions) are not able to pass through the hydrophobic core, and those that are hydrophobic (e.g. fats) are repelled from the outer surface. As a result, the cell is able to isolate its internal environment from the external environment.
How does the cell move substances?
The controlled movement of substance is done by protein channels and carrier proteins anchored in the plasma membrane that selectively or generally allow particular particles to enter and leave the cell.
Which type of cell has ribosomes bound to its surface, stores proteins, and is the extension of the?
Rough - has ribosomes bound to its surface, stores proteins, and is the extension of the nuclear membrane
Eukaryotic cells definition
Animals, plants, and fungi are all eukaryotic Cells, which are large complex organisms. It consists of membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotic cells classification
Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are the four types of eukaryotes. Protists are eukaryotic organisms that do not include animals, plants, or fungi; this group includes protozoa, slime moulds, and some algae. Animals and plants are multicellular, whereas protists and fungi are usually unicellular.
Eukaryotic cells organelles structure and function
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and is usually separately enclosed within its own lipid bilayer. Organelles are identified by microscopy, and can also be purified by cell fractionation.
The Three Main Components of Any Eukaryotic Cells
A bilipid membranous layer composed of proteins and carbohydrates makes up the structure. It has a fluid nature.
Division of Eukaryotic cells (Reproduction)
Some eukaryotic cells can divide only by asexual means while other eukaryotic cells divide both sexually as well as asexually.
What are eukaryotic cells?
By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ...
What is the membrane of an eukaryotic cell?
Like bacteria and archaea, eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environment. The plasma membrane controls the passage of organic molecules, ions, water, and oxygen into and out of the cell.
How many centrioles are in a centrosome?
Figure 8. The centrosome consists of two centrioles that lie at right angles to each other. Each centriole is a cylinder made up of nine triplets of microtubules. Nontubulin proteins (indicated by the green lines) hold the microtubule triplets together.
Why is the mitochondria called the energy factory?
Mitochondria (singular = mitochondrion) are often called the “powerhouses” or “energy factories” of a cell because they are the primary site of metabolic respiration in eukaryotes. Depending on the species and the type of mitochondria found in those cells, the respiratory pathways may be anaerobic or aerobic.
What is the cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm. The cytoplasm refers to the entire region of a cell between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope. It is composed of organelles suspended in the gel-like cytosol, the cytoskeleton, and various chemicals (see figure below).
Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis?
Chloroplasts are plant cell organelles that carry out photosynthesis. Like the mitochondria, chloro plasts have their own DNA and ribosomes, but chloroplasts have an entirely different function.
Which organelle pulls chromosomes to opposite ends of the cell?
The centrosome (the organelle where all microtubules originate in animal and yeast) replicates itself before a cell divides, and the centrioles appear to have some role in pulling the duplicated chromosomes to opposite ends of the dividing cell. However, the exact function of the centrioles in cell division remains unclear, as cells that have had their centrosome removed can still divide, and plant cells, which lack centrosomes, are capable of cell division.
What is an eukaryotic cell?
What is a Eukaryotic Cell? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota.
Where are eukaryotic cells found?
Eukaryotic cells are exclusively found in plants, animals, fungi, protozoa, and other complex organisms. The examples of eukaryotic cells are mentioned below:
Which structure is found only in plant cells?
These are double-membraned structures and are found only in plant cells. These are of three types: Chloroplast that contains chlorophyll and is involved in photosynthesis. Chromoplast that contains a pigment called carotene that provides the plants yellow, red, or orange colours.
What is the membrane that separates cells from the outside environment?
Plasma Membrane. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the outside environment. It comprises specific embedded proteins, which help in the exchange of substances in and out of the cell.
Why are cells called powerhouses?
These are also known as “powerhouse of cells” because they produce energy.
Which cell has a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells have the nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane.
Is a virus a prokaryote?
Viruses are neither eukaryotes nor prokaryotes. Since viruses are a link between living and non-living they are not considered in either category.
What are the organelles of eukaryotic cells?
Below is a list of organelles that are commonly found in eukaryotic cells. Organelle. Function. Nucleus. The “brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA. Mitochondria.
Which organelle is responsible for transporting all sorts of items around the cell?
Make, process and package proteins. Lysosome. Contains digestive enzymes to help break food down. Endoplasmic Reticulum. Called the "intracellular highway" because it is for transporting all sorts of items around the cell. Vacuole.
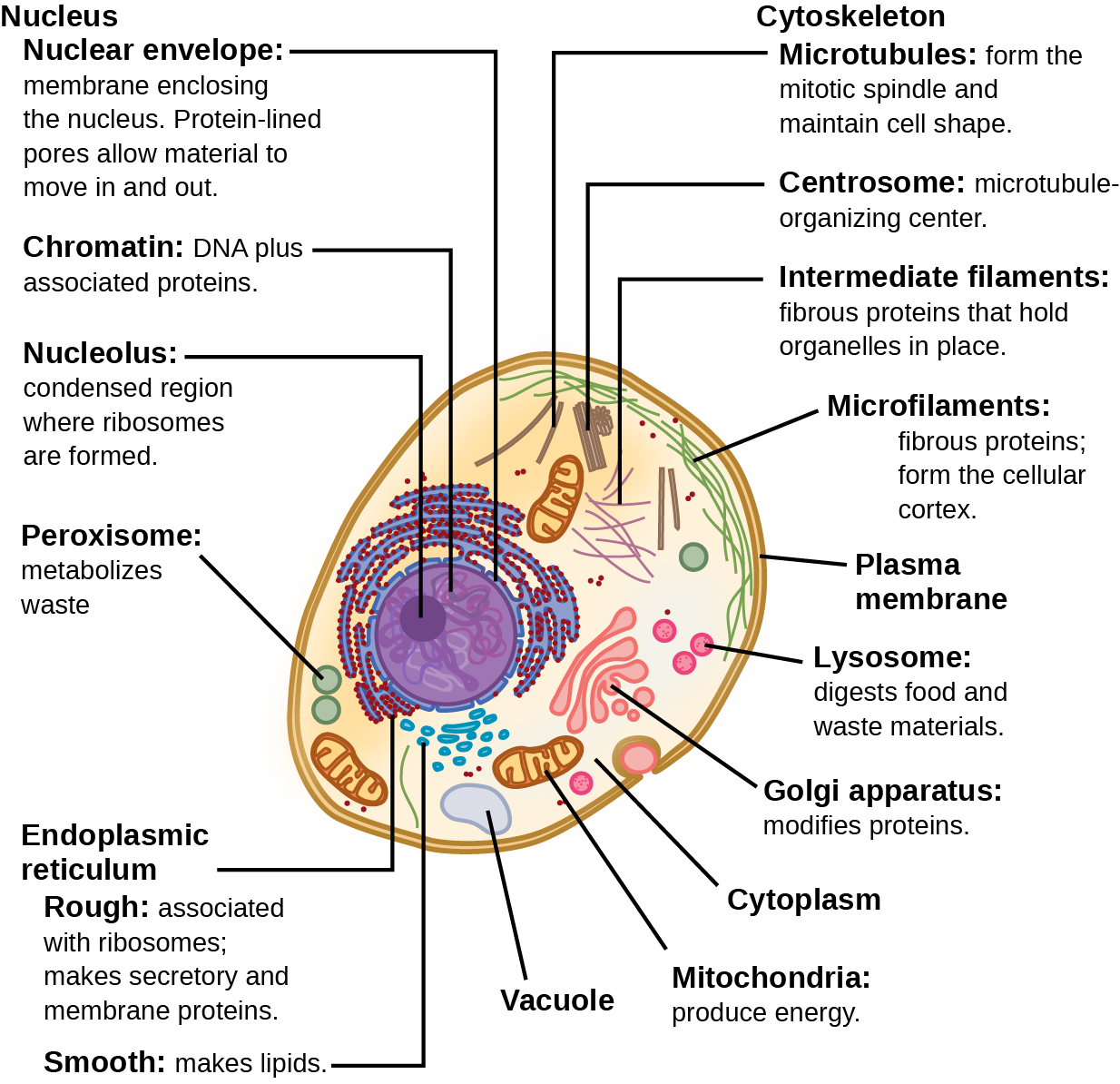
Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is also termed as a Cell Membrane or Cytoplasmic Membrane. It is a selectively permeable membrane of the cell, which is composed of a lipid bilayer and proteins.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is present both in plant and animal cells. They are jelly-like substances, found between the cell membrane and nucleus. They are mainly composed of water, organic and inorganic compounds. The cytoplasm is one of the essential components of the cell, where all the cell organelles are embedded.
Nucleus
The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle found in all eukaryotic cells. It is the largest organelle, which functions as the control centre of the cellular activities and is the storehouse of the cell’s DNA. By structure, the nucleus is dark, round, surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The Endoplasmic Reticulum is a network of membranous canals filled with fluid. They are the transport system of the cell, involved in transporting materials throughout the cell. There are two different types of Endoplasmic Reticulum:
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell as they produce energy-rich molecules for the cell. The mitochondrial genome is inherited maternally in several organisms. It is a double membrane-bound, sausage-shaped organelle, found in almost all eukaryotic cells.
Plastids
Plastids are large, membrane-bound organelles which contain pigments. Based on the type of pigments, plastids are of three types:
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are nonmembrane-bound and important cytoplasmic organelles found in close association with the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes are found in the form of tiny particles in a large number of cells and are mainly composed of 2/3rd of RNA and 1/3rd of protein.