All sub-cellular organelles explained in details
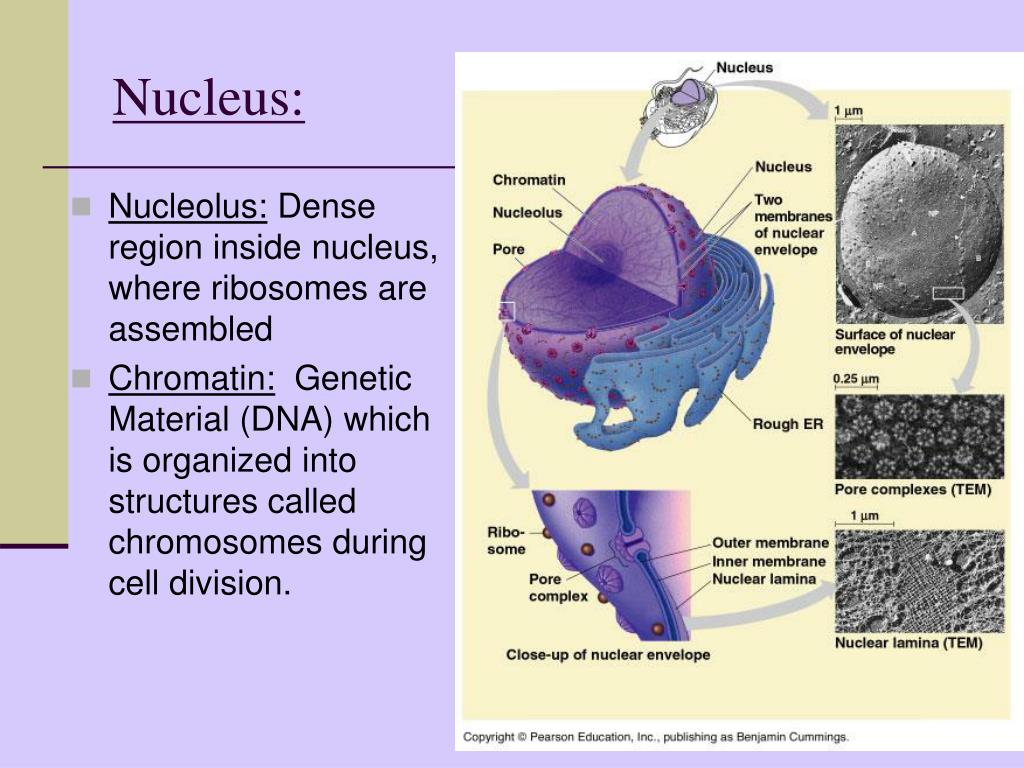
- Marker Enzymes Some enzymes are present in certain organelles only; such specific enzymes are called as marker enzymes. ...
- Endoplasmic reticulum It is a network of interconnecting membranes enclosing channels or cisternae that are continuous from outer nuclear envelope to outer plasma membrane. ...
- Golgi apparatus 1. ...
- Peroxisomes The peroxisomes have a granular matrix. ...
- Mitochondria ...
What are the subcellular organelle?
Subcellular organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function. Individual organelles are usually separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers [1].
What are subcellular organelles examples?
SUBCELLULAR STRUCTURESplasma membrane.glycocalyx.membrane microdomains.nucleus.mitochondria.chloroplasts.endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
What are the major and subcellular organelles of cell?
An organelle is a subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell, much like an organ does in the body. Among the more important cell organelles are the nuclei, which store genetic information; mitochondria, which produce chemical energy; and ribosomes, which assemble proteins.
What are the subcellular structures of a cell?
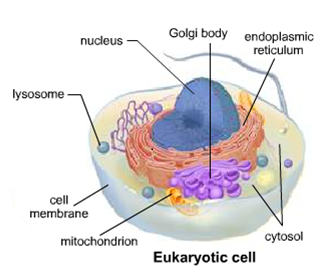
The subcellular components of cells include cell membrane, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, Nucleus, centrioles, lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, and mitochondria.
How many subcellular organelles are there?
Subcellular organelles that are connected by pathways of membrane traffic include (1) the ER, (2) the nucleus, (3) the Golgi apparatus, (4) various endosomes, and (5) lysosomes.
Which is not a subcellular organelle?
So, the correct answer is 'Ribosome'.
What are the subcellular organelles of a eukaryotic cell?
Nucleus.Mitochondria.Chloroplasts.Golgi apparatus.Endoplasmic reticulum.Plasma membrane.Cytoplasm.Ribosome.More items...
What is the meaning of subcellular?
Definition of subcellular : of less than cellular scope or level of organization subcellular organelles subcellular studies.
What is the structure of subcellular components and organelles?
1:2713:06Cell Structure: Subcellular Components | AP Biology 2.1YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLet's start with the most ubiquitous cellular component ribosomes ribosomes are tiny cellularMoreLet's start with the most ubiquitous cellular component ribosomes ribosomes are tiny cellular components made of ribosomal rna and proteins. They complete the process of translation.
What two subcellular components are necessary in all cells?
All cells share four common components: 1) a plasma membrane, an outer covering that separates the cell's interior from its surrounding environment; 2) cytoplasm, consisting of a jelly-like region within the cell in which other cellular components are found; 3) DNA, the genetic material of the cell; and 4) ribosomes, ...
Which of the following is not a subcellular structure?
chapter 3 cellsQuestionAnswerwhich of the following is not a subcellular structureintercellular materialwhich of these is not a function of the plasma membraneit prevents potassium ions from leaking out and sodium ions from crossing into the cellextracellular matrix isthe most abundant extracellular material42 more rows
What are two other subcellular structures that can be found in an animal cell?
The main subcellular structures in animal cells are:The nucleus.Cell membranes.Mitochondria.Ribosomes.Cytoplasm.
What are subcellular entities?
(1) Smaller than an ordinary cell, as in subcellular organisms. (2) Below cellular level or scope, as in subcellular studies. (3) Occurring within a cell, as in subcellular site of a metabolic activity. Supplement.
Is ribosome a subcellular organelle?
Organelles without membrane: The Cell wall, Ribosomes, and Cytoskeleton are non-membrane-bound cell organelles. They are present both in the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell.
What does subcellular mean?
1. contained within a cell. 2. at a level of organization lower than the cellular.
What subcellular structures are in an animal cell?
The main subcellular structures in animal cells are:The nucleus.Cell membranes.Mitochondria.Ribosomes.Cytoplasm.
Which cell divisions have no membrane bound organelles?from khanacademy.org
The other two major divisions, Bacteria and Archaea are known as prokaryotes, and have no membrane bound organelles within.
Which organelle is single membrane bound?from collegedunia.com
Single membrane bound organelles: include vacuole, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum and lysosome and are present only in eukaryotic cells.
Why is the rough endoplasmic reticulum so called?from khanacademy.org
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is so-called because its surface is studded with ribosomes, the molecules in charge of protein production. When a ribosome finds a specific RNA segment, that segment may tell the ribosome to travel to the rough endoplasmic reticulum and embed itself.
What are the organelles that are found in plants?from collegedunia.com
Plastids are large and membrane bound organelles that are found in all plants and in euglenoids. They contain some specific pigments that are responsible for imparting specific colours to the plants. On the basis of the type of pigment, plastids can be classified into three types.
What is the transport system of the cell?from collegedunia.com
Endoplasmic reticulum is the transport system of the cell. Rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the Golgi apparatus?from khanacademy.org
Golgi apparatus is a membrane bound organelle composed of flattened, stacked pouches called cisternae. It is also called the Golgi complex. Golgi apparatus is responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids to their targeted destinations. These are found in both plant and animal cells.
What is the mitochondria?from collegedunia.com
Mitochondrion is a double membrane bound cell organelle that are not normally visible under the microscope. This cylindrical or sausage shaped structure is also called the power house of the cell as they are the sites for aerobic respiration of the cell and produce cellular energy in the form of ATP. The outer membrane and the inner membrane divide its lumen into two compartments i.e., inner compartment called matrix possessing single circular DNA molecule and a few RNA molecules. forming a number of infoldings called cristae and the outer membrane forming the continuous limiting boundary of the organelle. Depending on the shape, size and physiological activity of the cell, the number of mitochondria per cell are variable. The structure has a diameter of 0.2 to 1µm (average 0.5 µm) and length 1.0 to 4.1 µm.
Which organelle has a double membrane?
Mitochondria have a double membrane. The outer membrane is smooth, but the inner membrane is highly convoluted, forming folds. Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed sacs that contain hydrolytic enzymes. A vacuole is a membrane-bound sac that plays many and differing roles.
Which organelle is made of flattened sacs?
The next organelle, the Golgi Complex , is also made of a series of flattened sacs. However, these sacs are not physically connected to the endoplasmic reticulum. Rather, the Golgi complex sits closer to the cellular membrane, where it carries out several important functions.
How are ribosomes made?
Ribosomes are created out of multiple proteins and ribosomal RNA molecules, which weave together into a complex – but specific – structure. The ribosomal RNA and proteins weave together to form subunits of a ribosome. These subunits then come together around a messenger RNA molecule to function. The subunits come together perfectly, allowing the ribosome to grab onto a piece of messenger RNA. Once a piece of mRNA is found, the ribosome can begin its work.
What is the first section of Unit 2 in AP Biology?
The first section of Unit 2 in the AP Biology curriculum focuses on the subcellular components of cells, specifically the organelles within cells that allow them to function . This section covers ribosomes, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi complex, mitochondria, lysosomes, vacuoles, and chloroplasts. Check it out!
What are the only cellular components apart from DNA that are visible in prokaryotic cells and eukary?
Ribosomes are the only cellular components aside from DNA that are visible in prokaryotic cells AND eukaryotic cells. In fact, studies of the molecular structure of ribosomes in species as different as a human and a bacteria show that there is not much difference between their ribosomes.
What are the components of a cellular cell?
Let’s start with the most ubiquitous cellular component – ribosomes. Ribosomes are tiny cellular components made of ribosomal RNA and proteins. They complete the process of translation by connecting amino acids based on the information they receive from messenger RNA. Let’s consider their structure.
What is a vacuole in plants?
A vacuole is a membrane-bound sac that plays many and differing roles. In plants, a specialized large vacuole serves multiple functions.
What are non-membrane organelles?
Most non-membranous organelles are part of the cytoskeleton, the major support structure of the cell. These include: filaments, microtubules , and centrioles.
What are the functions of organelles?
Organelles are small structures within the cytoplasm that carry out functions necessary to maintain homeostasis in the cell. They are involved in many processes, for example energy production, building proteins and secretions, destroying toxins, and responding to external signals. Organelles are considered either membranous or non-membranous.
How do ribosomes synthesize proteins?
Ribosomes, either free in the cytosol or associated with rER, synthesize proteins as polypeptide chains. This occurs through the translation of RNA. Specifically, ribosomes bind to messenger RNA, abbreviated mRNA. The ribosome reads a series of nucleotide bases in groups of three called codons. The first codon read is the start codon. Each codon following the start codon represents a specific amino acid that is then brought to the ribosome by transfer RNA, abbreviated tRNA. The tRNA carrying the amino acid is bound into the A site of the ribosome. Here the amino acid is linked to the amino acid that precedes it, in the P site. The bond between two amino acids in a polypeptide chain is referred to as a peptide bond. After the peptide bond is created the ribosome translocates to the next three nucleotide bases on the mRNA strand and repeats the process until a stop codon is reached.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large network of membranes responsible for the production of proteins, metabolism and transportation of lipids, and detoxification of poisons. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum with separate functions: smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum. The presence or absence of ribosomes in the ER’s plasma membrane determines whether it is classified as smooth or rough ER.
What is the smallest unit of life?
Cells are the smallest units of life. They are a closed system, can self-replicate, and are the building blocks of our bodies. In order to understand how these tiny organisms work, we will look at a cell’s internal structures. We will focus on eukaryotic cells, cells that contain a nucleus.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Cell (mitochondria in green) Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell. Cellular respiration, the generation of energy from sugars and fats, occurs in these organelles. Some of the enzymes that catalyze respiration are found within the matrix. Other proteins involved in these reactions are built into the wall of the inner membrane.
Which type of cell lacks a nucleus?
We will focus on eukaryotic cells, cells that contain a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells, cells that lack a nucleus, are structured differently. A cell consists of two major regions, the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear envelope and contains DNA in the form of chromosomes.
Which cell divisions have no membrane bound organelles?
The other two major divisions, Bacteria and Archaea are known as prokaryotes, and have no membrane bound organelles within.
Where are organelles found?
You can think of organelles as smaller rooms within the factory, with specialized conditions to help these rooms carry out their specific task (like a break room stocked with goodies or a research room with cool gadgets and a special air filter). These organelles are found in the cytoplasm, a viscous liquid found within the cell membrane that houses the organelles and is the location of most of the action happening in a cell. Below is a table of the organelles found in the basic human cell, which we’ll be using as our template for this discussion.
Why is the rough endoplasmic reticulum so called?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is so-called because its surface is studded with ribosomes, the molecules in charge of protein production. When a ribosome finds a specific RNA segment, that segment may tell the ribosome to travel to the rough endoplasmic reticulum and embed itself.
How are mitochondria unique?
Mitochondria are also somewhat unique in that they are self-replicating and have their own DNA, almost as if they were a completely separate cell. The prevailing theory, known as the endosymbiotic theory, is that eukaryotes were first formed by large prokaryotic cells engulfing smaller cells that looked a lot like mitochondria (and chloroplasts, more on them later). Instead of being digested, the engulfed cells remained intact and the arrangement turned out to be advantageous to both cells, which created a symbiotic relationship.
Which organelle is the final destination for proteins coming through the Golgi?
Lysosome: The final destination for proteins coming through the Golgi is the lysosome. Vesicles sent to this acidic organelle contain enzymes that will hydrolyze the lysosome ’s content.
What are the two types of cells?
There are two main types of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotes are cells that do not have membrane bound nuclei, whereas eukaryotes do. The rest of our discussion will strictly be on eukaryotes. Think about what a factory needs in order to function effectively.
What are plant cells made of?
Plant cells have protective walls made of cellulose (which also makes up the strings in celery that make it so hard to eat) while fungal cell walls are made from the same stuff as lobster shells. However, despite this vast range in size, shape, and function, all these little factories have the same basic machinery.
Which organelle is responsible for storing and storing energy?
While the endomembrane system is highly specialized for maintaining and repairing a growing cell, other organelles are responsible for capturing, storing, and utilizing the energy needed to power the many reactions the endomembrane system completes. These organelles are chloroplasts and mitochondria. Both of these organelles have a double-membrane system, likely because they evolved from symbiotic bacteria billions of years ago.
Which part of the cell is the Golgi complex?
The endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex are both a part of the endomembrane system – a series of membranes that form distinct chambers within a cell. These chambers can have completely different chemical properties than the cytosol surrounding them. The endoplasmic reticulum has two distinct portions: the rough ER and the smooth ER.
What is the second section of AP Biology?
The second section of Unit 2 in the AP Biology curriculum focuses on how the subcellular components of cells maintain the cell and gather energy. Specifically, this standard breaks down the two basic functional categories of cellular organelles: those that maintain and grow the cell, and those that capture and utilize energy. Thus, we will be looking at how the endomembrane system builds a cell, as well as seeing how chloroplasts and mitochondria work together to provide energy!
How do lysosomes digest?
Lysosomes are how the cell digests that material. Lysosomes attach to the food vesicle and merge with the lipid bilayer. As they do so, they dump their acid contents and hydrolytic enzymes into the food vacuole. This digests the bacteria inside the cell by breaking apart all of the polymers with hydration reactions.
Where are thylakoids organized?
The thylakoids are organized in stacks, called grana. Membranes contain chlorophyll pigments and electron transport proteins that comprise the photosystems. The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur in the grana. The stroma is the fluid within the inner chloroplast membrane and outside of the thylakoid.
How does the Golgi complex digest bacteria?
This digests the bacteria inside the cell by breaking apart all of the polymers with hydration reactions. The components the cell can recycle leach out of the food vacuole into the cytoplasm. Any waste products are dumped back into the bloodstream, where they will be removed by the kidneys and liver. The cell will then create more lysosomes with the Golgi complex, ready for the next bacterial cell it encounters.
What is the function of lysosomes in the mitochondria?
Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes, which are important in intracellular digestion, the recycling of a cell’s organic materials , and programmed cell death (apoptosis).