The calvarium, also known as the roof or skull cap, consists of three bones:
- Frontal bones
- Parietal bones
- Occipital bones
What is the superior view of the base of the skull?
Superior view of the base of the skull 1 Anterior cranial fossa. This is formed by the orbital surface of the frontal bone and part of the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone. 2 Sphenoid bone. The sphenoid bone is a complex structure and it has many articulations. ... 3 Middle cranial fossa. ... 4 Posterior cranial fossa. ...
What bones make up the cranium?
The cranium (also known as the neurocranium), is formed by the superior aspect of the skull. It encloses and protects the brain, meninges and cerebral vasculature. Calvarium: Comprised of the frontal, occipital and two parietal bones. Cranial base: Comprised of six bones - the frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, occipital, parietal and temporal bones.
What are the different parts of the skull?
Looking at it from the inside it can be subdivided into the anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossae. The skull base comprises parts of the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, occipital and temporal bones. The face is referred to as all skull bones fronto-caudally connected to the cerebral cranium.
What is the uppermost part of the skull?
Also known as the neurocranium or braincase, the cranium is the uppermost part of the skull that encircles and protects the brain, as well as the cerebral vasculature and meninges. The hollow space taken up by the brain is called the cranial cavity. The 8 (2 paired and 4 unpaired) bones forming the cranium are called the cranial bones.

What is the superior part of the skull?
This cavity is bounded superiorly by the rounded top of the skull, which is called the calvaria (skullcap), and the lateral and posterior sides of the skull.
What is the most superior skull bone?
Parietal bone – Together, the two parietal bones form the top and upper sides of the skull.
What are the 4 Superior bones of the fetal skull?
At birth, the newborn's skull consists of five major bones (two frontal, two parietal, and one occipital) that are separated by connective tissue junctions known as cranial sutures.
What are the 5 major bones of the skull?
They include the frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, sphenoid and ethmoid bones.
What are the 4 major structures of the skull?
There are four major sutures that connect the bones of the cranium together: the frontal or coronal, the sagittal, the lambdoid, and the squamous.
Where is cranial and superior?
Superior or cranial - toward the head end of the body; upper (example, the hand is part of the superior extremity). Inferior or caudal - away from the head; lower (example, the foot is part of the inferior extremity). Anterior or ventral - front (example, the kneecap is located on the anterior side of the leg).
What are the names of the skull bones?
There are eight cranial bones, each with a unique shape:Frontal bone. This is the flat bone that makes up your forehead. ... Parietal bones. This a pair of flat bones located on either side of your head, behind the frontal bone.Temporal bones. ... Occipital bone. ... Sphenoid bone. ... Ethmoid bone.
What are the 22 bones of the skull?
The skull (22 bones) is divisible into two parts: (1) the cranium, which lodges and protects the brain, consists of eight bones (Occipital, Two Parietals, Frontal, Two Temporals, Sphenoidal, Ethmoidal) and the skeleton of the face, of fourteen (Two Nasals, Two Maxillae, Two Lacrimals, Two Zygomatics, Two Palatines, Two ...
How many bones are there in skull?
22 bonesIntroduction. The skull (also known as cranium) consists of 22 bones which can be subdivided into 8 cranial bones and 14 facial bones. The main function of the bones of the skull along with the surrounded meninges, is to provide protection and structure.
What is the top of the skull called?
calvariaThe calvaria is the top part of the skull. It is the upper part of the neurocranium and covers the cranial cavity containing the brain. It forms the main component of the skull roof. The calvaria is made up of the superior portions of the frontal bone, occipital bone, and parietal bones.
How do you remember the bones of the skull?
0:447:07Skull Bones Mnemonic (Cranial and Facial Bones) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe first pair of bones in the cranium are the parietal bones. The word parietal. Sounds similar toMoreThe first pair of bones in the cranium are the parietal bones. The word parietal. Sounds similar to pair.
What is the weakest part of the skull?
The pterionClinical significance The pterion is known as the weakest part of the skull. The anterior division of the middle meningeal artery runs underneath the pterion.
What is the weakest part of the skull?
The pterionClinical significance The pterion is known as the weakest part of the skull. The anterior division of the middle meningeal artery runs underneath the pterion.
What is the top of the head called?
crownThe crown of your head is located at the very top of your skull. You may also sometimes see it referred to as the vertex. Like other parts of your skull, the crown works to provide protection and support for the tissues of your head, including your brain.
What does superior view mean?
Superior. Toward the head/upper part of a structure (bird's-eye view, looking down) Inferior. Away from the head/lower part of a structure (bottom view, looking up)
What features of skull are seen in superior aspect of skull Norma Verticalis?
Superior View (norma verticalis – fig. 313) In some the outline is more or less oval : in others it is more nearly circular, but its greatest width is usually nearer to the occipital than to the frontal region. This aspect of the skull is traversed by three sutures.
3 Bones of the Skull
The human skull is comprised of a total of 22 separate bones (excluding the ear ossicles and hyoid bone).
Flat Bones of the Skull: Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, and Temporal
The flat bones of the skull making up the neurocranium or braincase have three basic structural layers. These comprise the outer and inner layers of compact bone and an intervening layer of spongy, cancellous bone called diploe.
Cranial Sutures
Sutures are the fine, irregular lines of junction between articulating cranial bones. The bones of the skull originate through intramembranous or endochondral bone formation. Ossification gradually progresses until only the suture lines with their thin layer of interposing fibrous tissue remain.
How many bones are in the cranial base?
Cranial base – comprised of six bones: frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, occipital, parietal and temporal. These bones articulate with the 1st cervical vertebra (atlas), the facial bones, and the mandible (jaw). By TeachMeSeries Ltd (2021) Fig 1 – Bones of the calvarium and cranial base.
What bones are found in the face?
The vomer, palatine and inferior conchae bone s lie deep within the face. caption] [start-clinical] Clinical Relevance: Facial Fractures. Fractures of the facial skeleton are relatively common and most frequently result from road traffic collisions, fist fights, and falls.
What is the pterion of cranial fracture?
When considering cranial fractures, one area of clinical importance is the pterion – a H-shaped junction between the temporal, parietal, frontal, and sphenoid bones.
Which part of the mouth is the Palatine?
Palatine (2) – situated at the rear of oral cavity and forms part of the hard palate. Maxilla (2) – comprises part of the upper jaw and hard palate. Vomer – forms the posterior aspect of the nasal septum. Mandible (jaw) – articulates with the base of the cranium at the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
What is the cranium?
The cranium (also known as the neurocranium) is formed by the superior aspect of the skull. It encloses and protects the brain, meninges, and cerebral vasculature. Anatomically, the cranium can be subdivided into a roof and a base: Cranial roof – comprised of the frontal, occipital and two parietal bones.
How many bones are there in the face?
It consists of 14 bones, which fuse to house the orbits of the eyes, the nasal and oral cavities, and the sinuses. The frontal bone, typically a bone of the calvaria, is sometimes included as part of the facial skeleton. The facial bones are:
What is the clinical relevance of the skull?
2.1 Clinical Relevance: Facial Fractures. 3 Sutures of the Skull. The skull is a bony structure that supports the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. It is comprised of many bones, which are formed by intramembranous ossification, and joined by sutures (fibrous joints).
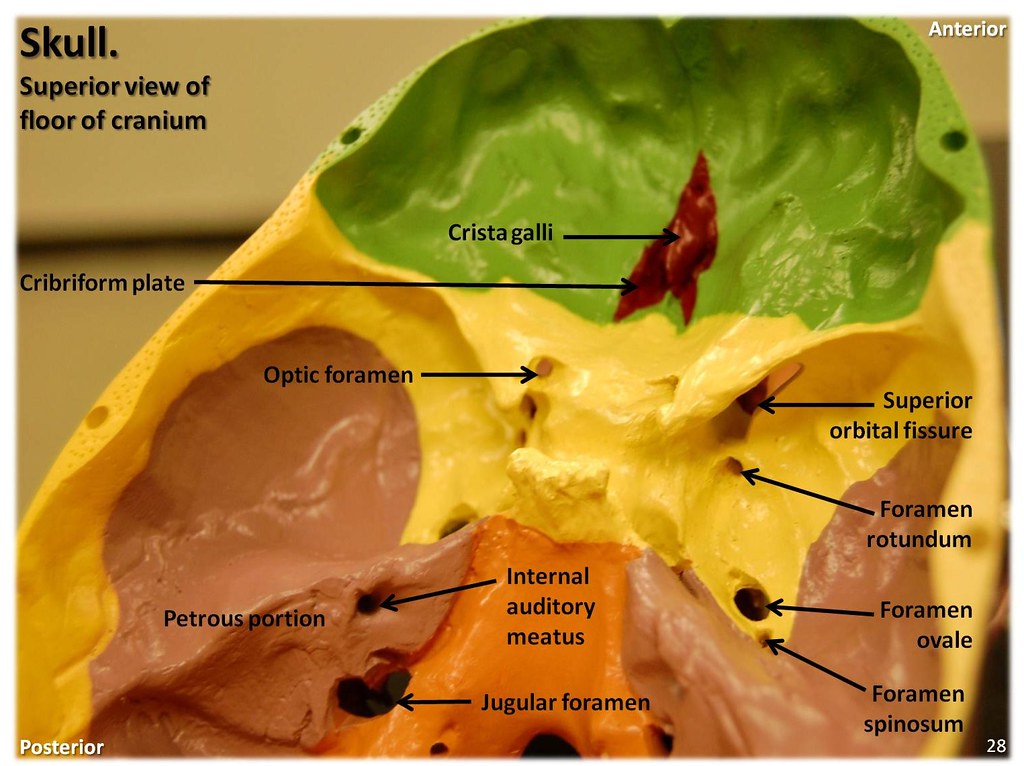
Important Foramina
The cranial base has multiple foramina and other openings to allow passage to the spinal cord, blood vessels, and cranial nerves. Here are the names of some of the most important foramina, along with the nerves they allow passage to:
Blood Supply
The skull primarily gets its blood supply from the common carotid artery, while the vertebral artery also contributes.
Muscles
The scalp and face muscles are innervated mainly by the facial, oculomotor, or trigeminal nerves. The hypoglossal nerve innervates the tongue. These muscles are responsible for everything from facial expressions, talking, and eating to lifting or lowering our eyebrows and moving our eyes to see.
Which bone is found superiorly?
The frontal bone is found superiorly while the mandible lies inferiorly, giving the skull an ovoid shape when looked at anteriorly. The frontal bone underlies the forehead; above the orbital cavities, the nasal bridge (which is formed jointly by the two nasal bones), and the frontal process of the zygomatic bone.
How many bones are there in the skull?
The human skull consists of 22 bones (or 29, including the inner ear bones and hyoid bone) which are mostly connected together by ossified joints, so called sutures. The skull is divided into the braincase ( neurocr anium) and the facial skeleton ( viscerocranium ).
How many bones are in the occipital bone?
It is formed by four bones; the frontal bone, the two parietal bones, and the occipital bone. These bones articulate through three sutures: The coronal suture: between the frontal and parietal bones. The lambdoid suture: between the occipital and parietal bones. The sagittal suture: between the two parietal bones.
What is the most important organ in the human body?
Its main task is the protection of the most important organ in the human body: the brain. The brain is almost entirely enclosed by the neurocranium with the exception of the foramen magnum and other foramina at the skull base which serve as entry and exit point for blood vessels and cranial nerves.
What is the skull base?
The skull base is the inferior portion of the neurocranium. Looking at it from the inside it can be subdivided into the anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossae. The skull base comprises parts of the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, occipital and temporal bones.
What are the components of the brain?
Components and features. The braincase consists of the skullcap ( calvarium) and the skull base. The skull cap is made up of the pairs of parietal bones and parts of the frontal bone as well as the occipital bone. The most important sutures in the human skull are:
What is the facial skeleton?
The facial skeleton is referred to as all skull bones anteroinferior to the cranial cavity. Prominent representatives are the maxilla (upper jaw) and the mandible (lower jaw). The orbita and the nasal cavity are formed by the zygomatic, nasal, palatine, lacrimal bones, the vomer and the inferior nasal concha (lower turbinate).
People with similar attributes to Abigail Dickinson
Gathered from those who lived during the same time period, were born in the same place, or who have a family name in common.
Surname meaning for Dickinson
Historically, surnames evolved as a way to sort people into groups - by occupation, place of origin, clan affiliation, patronage, parentage, adoption, and even physical characteristics (like red hair). Many of the modern surnames in the dictionary can be traced back to Britain and Ireland.
Which bone articulates with all the other cranial bones to bind them together?from quizlet.com
Also called the "butterfly bone" articulates with all the other cranial bones to bind them together. The greater wings of the sphnoid bone form the sides of the skull and are located anterior to the temporal bones.
What is the bone between the eyes?from quizlet.com
A light spongy bone situated between the 2 orbits of the eyes. It forms the bony wall of the nasal septum and encases the ethmoid sinuses.
What is the bone on the outer wall of the nasal fossa called?from quizlet.com
Each side of the outer wall of the nasal fossa has a thin layer of curled bone called the inferior turbinate , ALSO KNOWN AS THE INFERIOR NASAL CONCHA. These bones provide support for the mucous membranes.
What bones are fused at the midline?from quizlet.com
Small oblong bones that are fused at the midline and form the bridge of the nose.They articulate (join) with the frontal, ethmoid, and maxillary bones.
How many parietal bones are there?from quizlet.com
There are 2 parietal bones one on each side of the head. They form the sides and roof of the skull & are joined at the midline by the saggtal suture. They join the occipital, the frontal, the temporal, & the sphenoid bones.
What is a zygomatic bone?from quizlet.com
THE ZYGOMATIC OR MALAR BONE, IS A PAIRED BONE, WITH ONE ON EACH SIDE OF THE HUMAN SKULL.
Which part of the mandible RESTS in a depression in the temporal bone?from quizlet.com
PART OF THE MANDIBLE THAT RESTS IN A DEPRESSION IN THE TEMPORAL BONE CALLED THE GLENOID OR MANDIBULAR FOSSA.

Anatomy and Structure of The Bones of The Skull
- Cranium
Also known as the neurocranium or braincase, the cranium is the uppermost part of the skull that encircles and protects the brain, as well as the cerebral vasculature and meninges. The hollow space taken up by the brain is called the cranial cavity. The 8 (2 paired and 4 unpaired) bones fo… - Facial Skeleton
The facial skeleton, also known as the viscerocranium, comprises 14 facial bones (2 unpaired and 6 paired). Together, these bones structure our face, cheeks, nose, mouth, and jaws. Here are the bones in the facial skeleton: 1. Maxillae/upper jaw bones (2) 2. Lacrimal bone(2) 3. Zygomatic b…
Important Foramina
- The cranial base has multiple foramina and other openings to allow passage to the spinal cord, blood vessels, and cranial nerves. Here are the names of some of the most important foramina, along with the nerves they allow passage to: 1. The spinal cord – foramen magnum in the occipital bone 2. Optic nerve and ophthalmic artery – Optic nerve canal in the sphenoid bone (the optic fo…
Blood Supply
- The skull primarily gets its blood supply from the common carotid artery, while the vertebral artery also contributes.
Muscles
- The scalp and face muscles are innervated mainly by the facial, oculomotor, or trigeminal nerves. The hypoglossal nerve innervates the tongue. These muscles are responsible for everything from facial expressions, talking, and eating to lifting or lowering our eyebrows and moving our eyes to see.