- Muffled hearing.
- Inability to hear quiet sounds.
- Dizziness.
- Gradual loss of hearing.
- Ear pain.
- Fluid drainage from the ear.
- Feeling that your ears are full or stuffy.
Common Causes
Conductive hearing loss can be caused by problems in the external ear canal or in the middle ear. Possible causes include illnesses such as otosclerosis, cholesteatoma or inflammatory processes accompanied by middle ear effusion or scarring. Another frequent factor that causes conductive hearing loss is a buildup of earwax (cerumen), another ...
Related Conditions
The treatment options can include:
- Observation with repeat hearing testing at a subsequent follow up visit
- Evaluation and fitting of a hearing aid and other assistive listening devices
- Preferential seating in class for school children
- Surgery to address the cause of hearing loss
- Surgery to implant a hearing device
What are the top causes of conductive hearing loss?
Surgeries for hearing loss
- Cochlear implants. A cochlear implant is a surgery for adults, and, more commonly, children who have no, or very little, residual hearing.
- Bone-anchored hearing systems. Bone-anchored hearing systems, also called BAHAs, are surgically implanted devices. ...
- Stapedectomy. ...
- Insertion of middle ear tubes. ...
Which is best treatment for conductive hearing loss?
Signs and symptoms of hearing loss may include: Muffling of speech and other sounds Difficulty ...
How to fix conductive hearing loss?
What are the signs and symptoms of hearing loss?

What is the most common cause for conductive hearing loss?
According to Rothholtz, the most common cause of conductive hearing loss is a buildup of earwax that muffles sound. Rothholtz adds that some other types of conductive hearing loss include: Otosclerosis: This causes bone from the cochlea to grow onto the stapes bone in the middle ear, making it more difficult to hear.
What are two characteristics of a conductive hearing loss?
Signs of Conductive Hearing loss Sudden or unexpected hearing loss in one or both ears. All sounds seeming muffled or blocked in one ear. Feeling like your ear is full or stuffed. Struggling to hear soft sounds at both high and low pitches.
How do you treat conductive hearing loss?
Treatment for conductive hearing loss varies based on the circumstances. Antibiotics or antifungal medications are usually prescribed for ear infections, whereas surgery is usually an option for malformed or abnormal outer or middle ear structures and other physical problems.
What are 3 warning signs of hearing loss?
10 Signs of Hearing Loss You Shouldn't IgnoreYou get irritated at others for mumbling. ... You're having trouble following conversations. ... Talking on the phone is more challenging. ... Some sounds seem louder than normal. ... It's harder to carry on a conversation in a crowded room. ... Everyone is telling you to turn down the TV.More items...•
How do you test for conductive hearing loss?
Weber's test is performed by softly striking a 512-Hz tuning fork and placing it midline on the patient's scalp, or on the forehead, nasal bones, or teeth. If the hearing loss is conductive, the sound will be heard best in the affected ear.
Can conductive hearing loss go away on its own?
Conductive hearing loss is the result of damage to your outer or middle ear. It can make it very difficult to hear soft sounds. Some causes of conductive hearing loss are temporary and might even resolve on their own. Other causes are permanent and can be corrected with assistive hearing devices.
Who is most affected by conductive hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss is prevalent and affects a wide demographic, from the very young to the elderly. [3] The causes can also range from the trivial otitis media with effusion in young children to potentially severe conditions such as an effusion caused by a nasopharyngeal tumor in adults.
Does conductive hearing loss get worse?
Conductive hearing loss is generally not progressive, as it is a type of hearing loss that usually can be corrected with medical treatment or surgery. It occurs when sound waves cannot reach the inner ear because of earwax, fluid, anatomical problems, or a punctured eardrum.
Does conductive hearing loss get better?
Common reasons for conductive hearing loss include blockage of your ear canal, a hole in your ear drum, problems with three small bones in your ear, or fluid in the space between your ear drum and cochlea. Fortunately, most cases of conductive hearing loss can be improved.
How does hearing loss affect the brain?
“Brain scans show us that hearing loss may contribute to a faster rate of atrophy in the brain,” Lin says. “Hearing loss also contributes to social isolation. You may not want to be with people as much, and when you are you may not engage in conversation as much. These factors may contribute to dementia.”
Can stress and anxiety cause hearing loss?
To answer the question – yes, stress can cause hearing loss. According to Hearing Consultants, “When your body responds to stress, the overproduction of adrenaline reduces blood flow to the ears, affecting hearing.
What are the 5 levels of hearing loss?
There are 5 different levels of hearing loss: mild, moderate, moderately-severe, severe and profound. Mild Hearing Loss (26 dB- 40dB): this type of hearing loss is often associated with the inability to hear soft sounds. These sounds often include rustling leaves, bird chirping, or the refrigerator humming.
What is a conductive hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss happens when the natural movement of sound through the external ear or middle ear is blocked, and the full sound does not reach the inner ear. Conductive loss from the exterior ear structures may result from: Earwax—Your body normally produces earwax.
What is conductive hearing loss quizlet?
conductive hearing loss. result of deformation/malformation of outer or middle ear; can reduce or eliminate ear's natural conduction of sound as it travels to cochlea. microtia and atresia.
What is associated with conductive hearing loss?
Pathologies in the middle ear resulting in a conductive hearing loss include acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion (commonly referred to as glue ear). Otitis media with effusion is the most common cause of acquired hearing loss in children.
What does a conductive hearing loss look like on an audiogram?
On an audiogram, patients with otosclerosis commonly have conductive hearing loss with a drop in the bone-conduction threshold at 2,000 Hz, called a Carhart notch. This finding, in addition to an absent acoustic reflex, is generally thought to be diagnostic of otosclerosis.
Why do we have conductive hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss can occur if a structural component of the ear, liquid, or foreign object blocks the outer ear or middle ear from transmitting sound waves to the inner ear.
What test is used to determine if you have conductive hearing loss?
An audiogram test . Your doctor will use the graph generated by this test in order to look for specific indications of conductive hearing loss.
What causes a person to lose hearing?
According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, common causes of this type of hearing loss include: 1 Ear infections 2 Fluid buildup in the middle ear (usually due to allergies or a cold) 3 Hole in the eardrum 4 Blockage caused by earwax 5 Foreign object trapped in the ear 6 Benign tumors 7 Structural defects in the outer or middle ear
What is a Rinne hearing test?
A Rinne hearing test. This test distinguishes the sounds being transmitted through air conduction from those that are being transmitted through bone conduction in order to detect conductive hearing loss in one ear at a time, according to StatPearls publishing.
Can hearing loss be caused by a conductive hearing loss?
Working with your doctor will ensure you can identify the root cause of your hearing loss and decide on the proper treatment. Conductive hearing loss can happen any time something prevents sounds from getting across the outer and middle ear. A range of factors can cause this type of hearing loss in adults and children.
Is WebMD affiliated with any medical practice?
WebMD is not affiliated with and does not endorse any particular provider, service, or practice. WedMD also does not provide any medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. If you feel you may have a medical emergency, please call 9-1-1 immediately. By clicking “Submit,” you agree to WebMD providing your name and information (whether via phone, form, or chat box) to one of our providers, services, or practices. You consent to being contacted by a service, provider, or practice using autodialer technology, which may include text messages over which WebMD has no control. WebMD may also use your email to send you information regarding the Connect to Care program. Consent is not a condition of purchase. When you are connected with a service, provider, or practice in your area, WebMD may receive a fee.
Does WebMD have consent?
You consent to being contacted by a service, provider, or practice using autodialer technology, which may include text messages over which WebMD has no control. Consent is not a condition of purchase. When you are connected with a service, provider, or practice in your area, WebMD may receive a fee.
What is the treatment for conductive hearing loss?
When conductive hearing loss is caused by permanent structural conditions, such as a narrowed ear canal, treatment generally takes the form of an assistive hearing device.
What is it called when you lose your hearing?
When damage to your outer or middle ear causes hearing loss, it is called conductive hearing loss.
What does the results of hearing test tell you?
The results of your tests will confirm the type of hearing loss you have and its cause. Your ENT can discuss any treatment options and next steps with you.
What is the first step in hearing loss diagnosis?
A hearing test called an audiogram is one of the first steps in a hearing loss diagnosis. This test can determine if your hearing loss is conductive, sensorineural, or mixed. It can also determine how severe your hearing loss is.
What causes the middle ear bone to have an atypical structure?
an inherited condition called otosclerosis, which causes the middle ear bone to have an atypical structure
What is an acoustic reflex test?
Acoustic reflex. An acoustic reflex test measures the movement of your ear muscles in response to sounds.
What tests can be done to see if you have a swollen ear?
CT scans, MRI scans, or other imaging tests. These tests allow the ENT to see the structure of your ear.
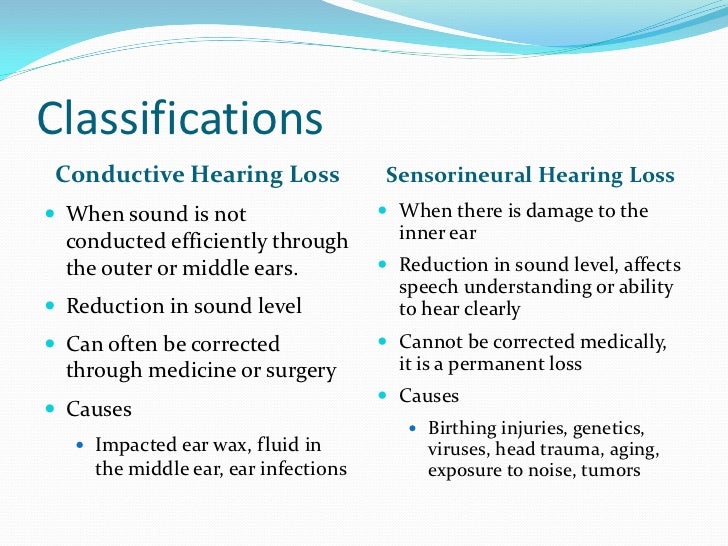
Conductive vs. Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Before we do a deep dive into conductive hearing loss, let’s briefly go over the two main types of hearing loss. Hearing impairment is broadly classified into two categories—conductive and sensorineural—based on where the hearing loss occurs.
Understanding the Conductive Component
Your ears are complicated mechanisms. Since conductive hearing loss occurs in the outer or middle ear, familiarizing yourself with the various parts will help you better understand this condition.
Conductive Hearing Loss Causes
Most of the most common causes of conductive hearing loss are not serious and can be reversed by simple medical treatments. However, some are caused by chronic conditions and may require surgery.
Symptoms Of Conductive Hearing Loss
The symptoms of conductive hearing loss may vary depending on the cause, but here are a few.
Diagnosing Conductive Hearing Loss
When you start to notice signs of hearing loss, your first step is to see a general practitioner or an ear, nose and throat doctor. The cause of conductive hearing loss is rarely a severe or chronic condition, so they’ll be able to treat you in most cases.
Treatment Options
Most causes of conductive hearing loss can be treated medically, but the treatment depends on the underlying condition.
Conclusion
Conductive hearing loss is one of the two main types of hearing loss. Now that you know how conductive hearing loss works and what causes it, you can distinguish it from sensorineural hearing loss. Knowing the type of hearing loss you have is the first step to treating and managing it.
What are the treatment options for conductive hearing loss?
Is conductive hearing loss curable? Can a conductive hearing loss be treated? Yes, in most cases a conductive hearing loss can be either cured or treated.
What should I do if I have a conductive hearing loss?
If you think that you might have a conductive hearing loss, you should see your family doctor or a hearing professional.
Why does my middle ear have conductive hearing?
In the middle ear conductive hearing loss occurs due to chronic middle ear infections or glue ear, where fluids fill up the middle ear, so that the eardrum cannot move.
What to do if you have a problem with your outer ear?
If you have a problem with your outer ear, do not try to do anything about it yourself. Rather, you should seek medical assistance.
Can ear wax cause hearing loss?
Can ear wax cause hearing loss? Yes, one of the most common causes of conductive hearing loss is a blockage in the external ear canal, usually caused by wax (excessive cerum). Other causes of conductive hearing loss can be infections of the ear canal, a perforated or ruptured eardrum (tympanic membrane), very small ears, cysts and tumours, or foreign objects in the ear canal. Otosclerosis, which is an abnormal growth of bone in the middle ear, can also cause a conductive hearing loss.#N#In the middle ear conductive hearing loss occurs due to chronic middle ear infections or glue ear, where fluids fill up the middle ear, so that the eardrum cannot move. Conductive hearing loss can also be caused by diseases, damage and physical changes in the middle ear such as otosclerosis, cholesteatoma, tumours and otic barotrauma.
Can you have hearing loss in one ear?
The hearing loss can be in one ear or both ears. If a conductive hearing loss occurs suddenly or the hearing is reduced more and more over a short time, you should see a doctor to get your ears examined.
Can you have conductive hearing loss in one ear?
You can have a conductive hearing loss in just one ear ( unilateral hearing loss) or in both ears ( bilateral hearing loss)
What causes ear wax to block?
Earwax blockage is also known as Cerumen Impaction. It occurs when there is an accumulation of earwax in the ear canal which makes hearing difficult.#N#Earwax produced at the normal level is good for your ears. The wax is produced by the body to prevent debris, fluids, and bacteria from getting into the inner ear. The built-up wax normally works its way out of the ear naturally. But when it is produced in excess, your ears may have a hard time getting rid of it.#N#When the ear is unable to get rid of the wax, it begins to accumulate, and in most cases, it solidifies. This blockage affects the flow of sound that is being transmitted into the ear.#N#Two major reasons cause earwax blockage. The first is when earwax is pushed further into the ear canal by the use of objects like cotton buds. The second cause of earwax blockage is the presence of solid excess wax.#N#Usually, conductive hearing loss caused by earwax blockage only lasts for as long as the blockage exists. The earwax blockage can be removed at home or in the hospital.
Why does the middle ear have serous?
Serous accumulates in the middle ear when the auditory tube and the eustachian tube responsible for draining the fluid out of the ear do not function properly. Fluid in the ear can be caused by ear infections, colds, and allergies that cause the auditory tube’s inflammation.
What is the eustachian tube?
The eustachian tube is a small passageway that connects the middle ear to the throat. The eustachian tube is responsible for draining fluid from the middle ear and equalizing ear pressure.
What is conductive hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss is a type of hearing loss that occurs when sound is unable to pass through the outer and middle ear to the inner ear. Even though the major organs responsible for processing and sending sound signals to the brain are located in the inner ear, they won’t have any signal to transmit if ...
Why is there a blockage in my ear?
The first is when earwax is pushed further into the ear canal by the use of objects like cotton buds. The second cause of earwax blockage is the presence of solid excess wax.
Why does my inner ear not generate electrical signals?
If the inner ear is perfectly functional, but no sounds are coming in from the outer and middle ear, the inner ear cannot generate any electrical signals. Conductive hearing loss often occurs as a result of damage to either the outer ear or middle ear. Damage to both the outer and the middle ear at the same time is often rare.
Why is it so hard to drain fluid out of the middle ear?
This is because the eustachian tube in children is leveler and shorter. This makes it hard for fluid to drain out of the middle ear. The eustachian tube of adults is longer and has a more sloped angle; this allows gravity to drain the fluid. Otitis media often occurs in children between three to seven years of age.
How do you know if you have hearing loss?
Although each person may experience symptoms of hearing loss differently, some of the most common symptoms may include: Inability to hear people clearly and fully. People may seem to mumble and those experiencing hearing loss may not hear all parts of a conversation. For instance, someone with hearing loss may miss the essence ...
What happens when your inner ear is damaged?
Permanent hearing loss occurs when inner ear nerves become damaged and do not properly transmit their signals to the brain. Those who suffer from this condition may complain that people seem to mumble or that they hear, but do not understand, what is being said.
Why doesn't my hearing help answer the doorbell?
Or, that the person with hearing loss doesn't answer the telephone or doorbell because they didn't hear it ringing. Although each person may experience symptoms ...
What causes conductive hearing loss?
Some common causes of this condition include: Otosclerosis, a condition in which there is an abnormal growth of bone of the middle ear. This bone prevents structures within the ear from working properly and causes hearing loss.
What is wax build up?
Wax build-up. Unusual growths or tumors in the ear. Otosclerosis, a condition in which there is an abnormal growth of bone of the middle ear. This bone prevents structures within the ear from working properly and causes hearing loss. For some people with otosclerosis, the hearing loss may become severe.
Why do people stare at people when they talk?
Tendency to need to stare at people when they are talking in order to make it easier to understand what they are saying . Fatigue at the end of the day from straining to hear. Avoidance of social situations because of difficulty following conversations in noisy environments.
Is mixed hearing loss conductive or sensorineural?
Mixed Hearing Loss. Some people have a combination of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. Hearing loss is often gradual and not immediately noticed by the person affected. Sometimes friends or family will notice a person's hearing problems before the person with the hearing loss recognizes it.
What are the treatment options for conductive hearing loss?from hear-it.org
Is conductive hearing loss curable? Can a conductive hearing loss be treated? Yes, in most cases a conductive hearing loss can be either cured or treated.
What should I do if I have a conductive hearing loss?from hear-it.org
If you think that you might have a conductive hearing loss, you should see your family doctor or a hearing professional.
Why does my middle ear have conductive hearing?from hear-it.org
In the middle ear conductive hearing loss occurs due to chronic middle ear infections or glue ear, where fluids fill up the middle ear, so that the eardrum cannot move.
What causes a person to lose hearing?from asha.org
This type of hearing loss can be caused by the following: 1 Fluid in your middle ear from colds or allergies. 2 Ear infection, or otitis media. Otitis is a term used to mean ear infection, and media means middle. 3 Poor Eustachian tube function. The Eustachian tube connects your middle ear and your nose. Fluid in the middle ear can drain out through this tube. Fluid can stay in the middle ear if the tube does not work correctly. 4 A hole in your eardrum. 5 Benign tumors. These tumors are not cancer but can block the outer or middle ear. 6 Earwax , or cerumen, stuck in your ear canal. 7 Infection in the ear canal, called external otitis. You may hear this called swimmer’s ear. 8 An object stuck in your outer ear. An example might be if your child put a pebble in his ear when playing outside. 9 A problem with how the outer or middle ear is formed. Some people are born without an outer ear. Some may have a deformed ear canal or have a problem with the bones in their middle ear.
What is it called when you lose your hearing?from healthline.com
When damage to your outer or middle ear causes hearing loss, it is called conductive hearing loss.
What is the media of otitis?from asha.org
Otitis is a term used to mean ear infection, and media means middle. Poor Eustachian tube function. The Eustachian tube connects your middle ear and your nose. Fluid in the middle ear can drain out through this tube. Fluid can stay in the middle ear if the tube does not work correctly. A hole in your eardrum.
What does the results of hearing test tell you?from healthline.com
The results of your tests will confirm the type of hearing loss you have and its cause. Your ENT can discuss any treatment options and next steps with you.
What is Conductive Hearing Loss?
Conductive hearing loss is an ear illness that happens when sound passing through the ear is blocked at the external or middle ear. Usually, people with conductive hearing loss have a hard time hearing because sound energy reduces on the way to the cochlea in the inner ear.
How Is Conductive Hearing Loss Diagnosed
Diagnosing conductive hearing loss usually involves a series of hearing tests, called audiograms. This will determine the severity of your hearing loss and the type. Based on the hearing test results and evaluations from your ENT specialist, you will receive various recommendations and treatment options.
Need to Schedule a Hearing Test?
If you are experiencing symptoms of conductive hearing loss, we recommend scheduling an appointment with a qualified audiologist. As stated above, they will run a hearing test.
Best Hearing Aids in 2021
Selecting the appropriate hearing aids for your condition can be a bit overwhelming. And this is partly because there are many hearing aids in the market right now, with each performing specific functions. This list will discuss the best hearing aids in the market based on reviews, functionality, and cost.
How does the vestibular nerve affect the sense of balance?
They convert the motion into electrical signals that are transmitted along the vestibular nerve to the brain. This sensory information enables you to maintain your sense of balance. Traveling to the brain. Electrical impulses travel along the auditory nerve and pass through several information-processing centers.
What are the three tubes in the inner ear called?
The other fluid-filled chambers of the inner ear include three tubes called the semicircular canals (vestibular labyrinth). Hair cells in the semicircular canals detect the motion of the fluid when you move in any direction. They convert the motion into electrical signals that are transmitted along the vestibular nerve to the brain. This sensory information enables you to maintain your sense of balance.
What is the middle ear?
The middle ear is an air-filled cavity that holds a chain of three bones: the hammer (malleus), the anvil (incus) and the stirrup (stapes). These bones are separated from the outer ear by the eardrum (tympanic membrane), which vibrates when struck by a sound wave.
What are the three types of hearing loss?
Hearing loss is defined as one of three types: Conductive (involves outer or middle ear) Sensorineural (involves inner ear) Mixed (combination of the two) Aging and chronic exposure to loud noises both contribute to hearing loss.
What part of the brain processes and interprets sound?
The auditory cortices sort, process, interpret and file information about the sound. The comparison and analysis of all the signals that reach the brain enable you to detect certain sounds and suppress other sounds as background noise.
How to protect your ears from noise?
Protect your ears. Limiting the duration and intensity of your exposure to noise is the best protection. In the workplace, plastic earplugs or glycerin-filled earmuffs can help protect your ears from damaging noise.
How many decibels are safe?
The chart below lists common sounds and their decibel levels. The Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) safe noise level is 70 decibels. The louder the noise, the less time it takes to cause permanent hearing damage.
