Explore
When thrombosis is identified the condition is called heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis ( HITT ). HIT is caused by the formation of abnormal antibodies that activate platelets. If someone receiving heparin develops new or worsening thrombosis, or if the platelet count falls, HIT can be confirmed with specific blood tests.
Why does heparin induced thrombocytopenia cause thrombosis?
The use of heparin sodium is contraindicated in patients: With history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) (With or Without Thrombosis) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] With a known hypersensitivity to heparin or pork products (e.g., anaphylactoid reactions) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]
Is heparin contraindicated in thrombocytopenia?
The proactivating effects of heparin on platelets have been known for decades. Heparin can cause a moderate decrease in platelet count, which typically is seen at start of treatment with heparin in therapeutic doses. Concomitantly, markers of platelet activation are increased.
Does heparin lower platelet count?
The results suggest that heparin treatment prevents the development of severe fibrinoid vascular lesions and also attenuates the rate of the rise in systolic blood pressure; moreover, this reduction in blood pressure is not caused by a significant reduction in blood volume or an acute hypotensive effect of heparin.
Does heparin cause low blood pressure?

When should you suspect heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
HIT must be suspected when a patient who is receiving heparin has a decrease in the platelet count, particularly if the fall is over 50% of the baseline count, even if the platelet count nadir remains above 150 × 109/L.
What are the signs and symptoms of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
What Are the Symptoms of HIT?Skin tenderness.Swelling.Skin that's warm to the touch.Shortness of breath.Change in heart rate.Sharp pain in your chest.Dizziness.Anxiety.More items...•
What happens in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) occurs when a patient receives heparin, a blood-thinning medication, and subsequently forms antibodies against heparin and the platelet factor-4 (PF4) complex.
What is a common complication of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
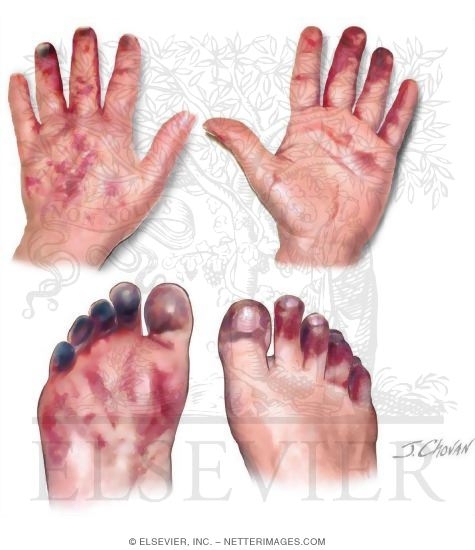
Because HIT causes a hypercoagulable state, venous and/or arterial thrombosis can occur. The most common complications are deep venous thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), or skin necrosis.
Which 2 patients are at the highest risk for developing heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
Multiple studies have reported that women have a higher risk of HIT than men. A higher risk of HIT in surgical patients, compared to medical patients, has been reported. HIT appears to be rare in patients aged <40 years.
How do you check for hits?
HIT Laboratory Testing Immunoassays detect the presence of PF4-heparin antibody in the patient's serum. The solid phase ELISA is the gold standard and is the most widely used test to evaluate HIT. This test is performed at UC Davis Medical Center as the screening test.
How fast does heparin induced thrombocytopenia occur?
onset of thrombocytopenia typically 5–10 days after initiation of heparin treatment, which can occur earlier with previous heparin exposure (within 100 days)
Does heparin induced thrombocytopenia go away?
In contrast to many allergies to other medications or foods, the allergy to heparin is not long-lasting. The PF4 antibody that causes HIT will usually disappear after approximately 3 months. Thereafter, heparin may be considered for use if a new clot did not develop from HIT and if the PF4 antibody test is negative.
How is heparin induced thrombocytopenia diagnosed?
Diagnosis of HIT is based on clinical assessment and laboratory results. Primary laboratory tests for HIT include immunologic assays, such as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and functional, platelet-activation assays, such as the serotonin release assay (SRA).
Who is at risk for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
Strong risk factors for HIT include: 1) the duration of heparin therapy (>5 days), 2) the type (UFH > LMWH > fondaparinux) and dosage of heparin, 3) the indication for treatment (surgical and trauma patients at highest risk), and 4) the patient's sex (female > male).
Can heparin-induced thrombocytopenia cause a stroke?
Conclusions: Stroke, particularly ischemic stroke, is common in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and significantly increases mortality risk.
Can you take blood thinners with low platelet count?
Indeed, anticoagulation is generally contraindicated if platelet count is <50×109/L,6 and patients with platelet count <100×109/L were excluded from recent clinical trials with non–vitamin K antagonist (VKA) oral anticoagulants (NOACs).
What causes HIT?
HIT happens when your body's immune system reacts to heparin. This causes changes in your blood. Some people have no symptoms of HIT. But it may cause a dangerous clot to form in blood vessels.
What is the treatment for heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
Treatment of HIT entails immediate withdrawal of all heparin, including heparin-containing flushes and catheters. Heparin cessation alone, however, is often insufficient to prevent thrombosis.
Can Thrombocytopenia be fatal?
Dangerous internal bleeding can occur when your platelet count falls below 10,000 platelets per microliter. Though rare, severe thrombocytopenia can cause bleeding into the brain, which can be fatal.
Can you use heparin after hit?
Full courses of heparin should be avoided in patients with a history of HIT. Patients with a history of HIT are more likely to develop platelet-activating antibodies (SRA seroconversion) within their anti-PF4/heparin response and thus to develop HIT if they receive postoperative heparin.
What Is Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia?
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a condition that causes a decrease of platelets in the blood. Platelets help the blood clot. HIT usually...
What Increases My Risk For Hit?
1. Recent surgery, especially heart or bone surgery 2. An IV or central line that is flushed with heparin or coated with heparin 3. A type of hepar...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of Hit?
1. Pain, redness, and swelling of an arm or leg 2. Bruise-like discoloration of your skin 3. A rash or sore where a heparin shot was given 4. Weakn...
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider?
1. You have a fever. 2. You have numbness in your arms or legs. 3. You have severe pain in your arms or legs that does not go away. 4. You have tro...
When Should I Seek Immediate Care Or Call 911?
1. You feel lightheaded, short of breath, and have chest pain. 2. You cough up blood. 3. Your arm or leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may lo...
How common is heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
Heparin remains one of the most commonly used anticoagulants more than a century after its discovery. Experts estimate that heparin use results in HIT between 0.1% and 5% of the time.
When to contact a doctor
Many people receiving heparin are already in the hospital. Tell your medical team about any symptoms you feel so they can monitor you for HIT.
What is heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a condition that causes a decrease of platelets in the blood. Platelets help the blood clot. HIT usually occurs after you are treated with heparin.
What is a heparin IV?
An IV or central line that is flushed with heparin or coated with heparin. A type of heparin used from cows or pigs. Taking heparin for more than 4 days. Female gender.
What is the best medicine for blood clots?
Antiplatelets , such as aspirin, help prevent blood clots. Take your antiplatelet medicine exactly as directed. These medicines make it more likely for you to bleed or bruise. If you are told to take aspirin, do not take acetaminophen or ibuprofen instead.
How to keep your gums from bleeding when taking blood thinners?
Watch for blood in your urine and bowel movements. Use a soft washcloth on your skin, and a soft toothbrush to brush your te eth. This can keep your skin and gums from bleeding.
Does heparin stop?
All heparin treatments will stop, including heparin flushes and catheters coated with heparin. You may need any of the following:
Can you skip taking blood thinners?
Take your blood thinner exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip does or take less than prescribed. Tell your provider right away if you forget to take your blood thinner, or if you take too much. Warfarin is a blood thinner that you may need to take.
Is warfarin a blood thinner?
Warfarin is a blood thinner that you may need to take. The following are things you should be aware of if you take warfarin: Foods and medicines can affect the amount of warfarin in your blood. Do not make major changes to your diet while you take warfarin.
What Is HIT?
Heparin -induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a life-threatening condition that can happen to some people after they take a medicine called heparin, a blood -thinning drug that helps prevent clots.
How Is HIT Diagnosed?
Lab tests can tell your doctor if you have HIT. Those tests include ones that let your doctor know about your:
How long does it take for heparin to show up?
It's also possible to have something called early-onset HIT. That's when HIT symptoms come within 24 hours after you take heparin. It might happen if you took heparin in the last few months, your body has HIT antibodies, and you're exposed to heparin again.
How long does it take for a non immune HIT to heal?
It happens to 10% of people with HIT. If you get it, your body will recover about 4 days after you stop taking heparin.
What is a PE in medical terms?
Pulmonary embolism (PE), a clot that travels to a lung from a different part of your body.
How many people die from a hit?
Until recently, HIT was fatal for about 20% of people with it. Advances in treatments have dropped that number, but only to between 6% and 10%. So it's very important to get medical help as early as possible if you think you may have it.
Does heparin cause blood clots?
For some people, heparin triggers their immune system and causes a reaction where antibodies form and activate platelets -- tiny blood cells that clump together to form clots and stop bleeds in your body. That can make blood clots more likely.
What Is HIT?from webmd.com
Heparin -induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a life-threatening condition that can happen to some people after they take a medicine called heparin, a blood -thinning drug that helps prevent clots.
How Is HIT Diagnosed?from webmd.com
Lab tests can tell your doctor if you have HIT. Those tests include ones that let your doctor know about your:
How long does it take for antibodies to clear?from ashpublications.org
The median time to antibody clearance is 50 days for platelet activation assays and 85 to 90 days by immunoassays. 16, 92 Immunoassays may remain positive in ∼35% of patients for up to 1 year, with levels decreasing over time. 92 Platelets rebound to the normal range within 1 week of discontinuation in ∼65% of patients. 93 Even with platelet count recovery, patients remain at risk for thrombosis for 4 to 6 weeks after diagnosis 74 because of circulating anti-PF4/heparin antibodies. 16 Presently, there is no compelling laboratory or clinical evidence for immunologic memory in patients with HIT. 16, 94-96 Patients who are reexposed to the drug months to years after antibody disappearance often do not manifest anamnestic responses, and seroconversion risk appears similar to de novo heparin exposure. 16, 95, 96 In a small study of 17 patients with HIT who are reexposed to heparin for cardiac surgery, a higher proportion of patients developed anti-PF4/heparin antibodies (65%) relative to the incidence described in the literature (∼27% to 51%). 4, 38, 41, 97
How long does it take for a heparin to detect PF4?from ashpublications.org
In heparin-naïve individuals, PF4/heparin antibodies become detectable at a median of 4 days from start of heparin therapy. 89 Clinical manifestations of thrombocytopenia and/or thrombosis develop 5 to 14 days after initial heparin therapy, 72, 89 and on average ∼2 days (range 1-5 days) after antibody detection. 89 In patients with recent heparin exposure (<100 days), thrombocytopenia occurs precipitously within 24 hours of drug reexposure because of circulating anti-PF4/heparin antibodies. Another rare clinical variant called “delayed-onset HIT” is recognized days to weeks after heparin discontinuation. Although thrombocytopenia likely occurs in the expected time frame after heparin exposure, there is a delay in manifestations of thrombosis days to weeks after discharge. If unrecognized, patients may be inadvertently reexposed to heparin leading to significant morbidity and mortality. 90, 91 Delayed-onset HIT is caused by antibodies that are cross-reactive with PF4/GAG complexes found on cell surfaces and can trigger heparin-independent platelet activation in functional assays. 90
What is the importance of PF4/heparin ultralarge complexes?from ashpublications.org
Importance of PF4/heparin ultralarge complexes (ULCs) in HIT pathogenesis . (A) PF4, a positively charged protein, binds to negatively charged heparin through electrostatic interactions to form ULCs that govern HIT biology. At concentrations of PF4 or heparin excess, repulsive forces from excess charge predominate and are not permissive for complex formation. At stoichiometric ratios associated with charge neutralization, ULCs form capable of biological effects associated with in vivo immunogenicity 33 (B), differential clinical effects of UFH and LMWH 31 (C), and heparin-dependent reactivity in laboratory assays 19 (D).
What is PF4 released from?from ashpublications.org
PF4 is a positively charged platelet protein stored in platelet α-granules and released in high quantities at sites of platelet activation. 27 Released PF4 binds to negatively charged glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) on nearby endothelial cells, displaces bound antithrombin, 28 and renders the local milieu prothrombotic.
How long does it take for a heparin antibody to develop?from en.wikipedia.org
These antibodies are usually of the IgG class and their development usually takes about 5 days . However, those who have been exposed to heparin in the last few months may still have circulating IgG, as IgG-type antibodies generally continue to be produced even when their precipitant has been removed. This is similar to immunity against certain microorganisms, with the difference that the HIT antibody does not persist more than three months. HIT antibodies have been found in individuals with thrombocytopenia and thrombosis who had no prior exposure to heparin, but the majority are found in people who are receiving heparin.
What happens when PF4 is attached to heparin?
HIT can only occur if IgG, while attached to the heparin-PF4 complex, binds to the FC receptor on the platelet surface and leads to platelet activation. Activated platelets then release pro-thrombotic substances (such as thrombin) and PF4. As IgG activates more platelets, more PF4 is released forming more complexes with heparin, thus activating more platelets. This creates a severely hypercoagulable state and a continuous cycle that can only be broken when heparin is discontinued, and appropriate treatment is initiated.
What is a heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a severe complication that can occur in patients exposed to any form or amount of heparin products.[1] A fall in platelet counts and a hypercoagulable state characterize HIT. Patients who experience HIT may also develop thromboembolic complications that are associated with morbidity and mortality. This is a significant burden since heparin is widely used for treatment and prophylaxis of thromboembolism, line flushes, and heparin-coated catheters. This review will discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of patients with HIT.
How to treat a 4T score?
The first step in the treatment is the discontinuation of all forms of heparin, including heparin flushes, heparin-coated catheters, and heparin in the dialysate. [13] Next, an alternative anticoagulant must be initiated to prevent or treat any HIT-induced thrombosis. In patients recently started on warfarin, warfarin should be held, and phytonadione (vitamin K) should be administered to replete protein C and S stores. The PF4 ELISA an SRA should be sent to confirm the diagnosis. [14][15]
How long does it take for a type 2 heparin reaction to occur?
Type II HIT is an immune, antibody-mediated reaction. Because it takes time for the antibodies to form, this reaction usually occurs after 5 to 14 days of receiving heparin. However, if a patient has been exposed to heparin within the last 100 days, antibodies may remain in the system, causing this reaction to manifest as soon as day one of re-exposure to heparin. This is a very serious reaction that causes a hypercoagulable state and can lead to life-threatening complications. The rest of this review will focus on type II HIT and its management.
What does a 4T score mean?
A 4T score of 0 to 3 points means HIT is unlikely , and heparin therapy may continue while the clinician looks for other causes of thrombocytopenia. A score of 4 to 5 corresponds to intermediate probability, and a score of 6 to 8 means high probability. All forms of heparin, including line flushes, should be immediately discontinued, and treatment with an alternative anticoagulant should be pursued in any patient who scores 4 or more. Also, the clinical diagnosis with the 4T score should be confirmed with the PF4 ELISA and the Serotonin Release Assay (SRA).
What happens if you stop heparin after a HIT?
Because HIT causes a hypercoagulable state, venous and/or arterial thrombosis can occur. The most common complications are deep venous thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), or skin necrosis. The latter is particularly a risk if warfarin is administered in the acute phase. The risk of these complications is highest within the first 10 days, but the pro-thrombotic state persists up to 30 days after stopping heparin. [7]
What are the conditions that are considered on the differential when diagnosing HIT?
Other conditions to be considered on the differential when diagnosing HIT include, but are not limited to: type I HIT (HAT), disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), liver disease, bleeding, hemodilution, Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP), myelosuppression, as well as other drug-induced causes. [7]
How long does it take for a heparin-dependent antibody to develop?
HIT typically develops 5 to 10 days after exposure to heparin (range of 4-15 days) and can occur with unfractionated heparin, low molecular weight heparin, or, more rarely, fondaparinux. The presence of heparin-dependent antibodies alone, without any clinical manifestations, is insufficient for a diagnosis of HIT.
What is a severe reaction to heparin?
A severe drug reaction to heparin that can lead to life- and limb-threatening venous and/or arterial thromboembolism. Diagnosis requires the combination of a compatible clinical picture and laboratory confirmation of the presence of heparin-dependent platelet-activating HIT antibodies.
What is the Warkentin 4Ts?
The Warkentin (4Ts) Probability Scale score is commonly used to determine the clinical probability of HIT.
What is heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a clinicopathological syndrome that occurs when heparin-dependent, IgG antibodies bind to heparin/platelet factor 4 (PF4) complexes to activate platelets and produce a hypercoagulable state.
Does Fondaparinux cause HIT?
Fondaparinux, a pentasaccharide anticoagulant, does not usually promote antibody binding to PF4, despite its structural similarity to heparin, owing to absent/weak cross-reactivity. Therefore, it has a very low risk of inducing HIT.
Does JSW have competing interests?
JSW declares that he has no competing interests.
Who makes Argatroban?
SD is a consultant for Mitsubishi Pharma, the manufacturer of argatroban.
What happens when heparin binds to PF4?
When heparin binds with PF4, it undergoes a conformational change and becomes immunogenic (fig 11),), leading to the generation of heparin–PF4 antibodies (HIT antibodies), most frequently IgG.9The heparin–PF4–IgG multimolecular immune complex then activates platelets via their FcγIIa receptors, causing the release of prothrombotic platelet‐derived microparticles, platelet consumption, and thrombocytopenia.9These microparticles in turn promote excessive thrombin generation, frequently resulting in thrombosis. The antigen–antibody complexes also interact with monocytes, leading to tissue factor production, and antibody‐mediated endothelial injury may occur. Both of these latter processes may contribute further to the activation of the coagulation cascade and thrombin generation.
What is a HIT type?
HIT type I (also known as heparin‐associated thrombocytopenia) is a non‐immunologic response to heparin treatment , mediated by a direct interaction between heparin and circulating platelets causing platelet clumping or sequestration. HIT type I affects up to 10% of patients, usually occurs within the first 48–72 h after initiation of heparin treatment, and is characterised by a mild and transient thrombocytopenia (rarely <100 000/mm3), often returning to normal within 4 days once the heparin is withdrawn.4No laboratory tests are required to diagnose HIT type I, and it is not associated with an increased risk of thrombosis, whereas HIT type II is immune‐mediated and associated with a risk of thrombosis. It has recently been proposed that the term “HIT type I” be changed to “non‐immune heparin associated thrombocytopenia” and that the term “HIT type II” be changed to “HIT” to avoid confusion between the two syndromes.5
How long does it take for a platelet count to rise after heparin?
The platelet count starts to rise within 2–3 days and usually returns to normal within 4–10 days after cessation of heparin treatment, and it takes another 2–3 months for antibodies to disappear.13In patients with persistent or worsening thrombocytopenia despite absolute discontinuation of heparin, other possible causes of thrombocytopenia must be considered and investigated; a decision to recommence heparin should be made after careful risk–benefit analysis in individual patients.
How long does it take for thrombocytopenia to appear after heparin?
onset of thrombocytopenia typically 5–10 days after initiation of heparin treatment, which can occur earlier with previous heparin exposure (within 100 days)
What is the molecular weight of heparin?
Low molecular weight heparins (LMWH), molecular weight 2000–10 000 Daltons (Da), are produced by chemical or enzymatic processes from unfractionated heparins (UFH).6UFH are heterogenous mixture of negatively charged, sulfated glycosaminoglycan (3000–30 000 Da) derived from animal sources.6HIT is caused by the formation of antibodies that activate platelets following heparin administration.7The principal antigen is a complex of heparin and platelet factor 4 (PF4), a small positively charged molecule of uncertain biological function, normally found in α‐granules of platelets.8Heparin's high affinity for PF4 depends upon molecular weight, chain length and its degree of sulfation, which explains the differences in incidence of HIT observed with different heparins.8
How long does it take to show signs after a UFH bolus?
Patients with acute inflammatory, cardiorespiratory, neurological, or other unusual symptoms and signs within 30 min after an intravenous UFH bolus
What is thrombocytopenia in HIT?
Thrombocytopenia in HIT is largely due to the clearance of activated platelets and antibody‐coated platelets by the reticulo‐endothelial system.1
What is the effect of platelets on thrombocytopenia?
Platelets activated by heparin-induced thrombocytopenia antibodies increase the release and surface expression of platelet factor-4. As a result, even more platelet activation takes place.
What is heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) occurs when a patient receives heparin, a blood-thinning medication, and subsequently forms antibodies against heparin and the platelet factor-4 (PF4) complex.
How long does it take for platelet count to increase after stopping heparin?
Once heparin is stopped, the platelet count should begin to increase in two to five days.
How long does it take for thrombocytopenia to develop after heparin?
DEVELOPMENT OF HEPARIN-INDUCED THROMBOCYTOPENIA. The fall in platelet count with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia most commonly develops five to seven days after the start of heparin for the first time.
Can you use heparin with warfarin?
Because of this clotting risk, the patient often needs alternative anticoagulation, depending on his or her clinical circumstances. Use of oral anticoagulation with warfarin alone should not be used in patients with this condition because of the high risk of developing warfarin-induced skin necrosis and gangrene in the veins of the limbs.
Can heparin cause blood clots?
Damage to the blood vessel wall and platelet clumping associated with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia can lead to blood clots despite the presence of heparin. It is unclear why some patients treated with heparin develop this problem. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia may occur in 1% to 3% of individuals receiving heparin for a week or more.
Can you take anticoagulant with warfarin?
Use of oral anticoagulation with warfarin alone should not be used in patients with this condition because of the high risk of developing warfarin-induced skin necrosis and gangrene in the veins of the limbs.
What is the condition resembling HIT but without heparin exposure?
In 2021 a condition resembling HIT but without heparin exposure was described to explain unusual post-vaccination embolic and thrombotic events after the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine. It is a rare adverse event (1:1 million to 1:100,000) resulting from COVID-19 vaccines (particularly adenoviral vector vaccines). This is also known as Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome or TTS.
What is a HIT?
Hematology. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia ( HIT) is the development of thrombocytopenia (a low platelet count), due to the administration of various forms of hep arin, an anticoagulant. HIT predisposes to thrombosis (the abnormal formation of blood clots inside a blood vessel) because platelets release microparticles ...
How long does it take for a heparin antibody to develop?
These antibodies are usually of the IgG class and their development usually takes about 5 days . However, those who have been exposed to heparin in the last few months may still have circulating IgG, as IgG-type antibodies generally continue to be produced even when their precipitant has been removed. This is similar to immunity against certain microorganisms, with the difference that the HIT antibody does not persist more than three months. HIT antibodies have been found in individuals with thrombocytopenia and thrombosis who had no prior exposure to heparin, but the majority are found in people who are receiving heparin.
What is heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia ( HIT) is the development of thrombocytopenia (a low platelet count), due to the administration of various forms of heparin, an anticoagulant. HIT predisposes to thrombosis (the abnormal formation of blood clots inside a blood vessel) because platelets release microparticles ...
What is the function of IgG antibodies?
This results in platelet activation and the formation of platelet microparticles, which initiate the formation of blood clots; the platelet count falls as a result, leading to thrombocytopenia. In addition, the reticuloendothelial system (mostly the spleen) removes the antibody-coated platelets, further contributing to the thrombocytopenia.
What is heparin used for?
Heparin may be used for both prevention and the treatment of thrombosis. It exists in two main forms: an "unfractionated" form that can be injected under the skin (subcutaneously) or through an intravenous infusion, and a "low molecular weight" form that is generally given subcutaneously. Commonly used low molecular weight heparins are enoxaparin, dalteparin, nadroparin and tinzaparin.
When was heparin first used?
While heparin was introduced for clinical use in the late 1930s , new thrombosis in people treated with heparin was not described until 1957, when vascular surgeons reported the association. The fact that this phenomenon occurred together with thrombocytopenia was reported in 1969; prior to this time, platelet counts were not routinely performed. A 1973 report established HIT as a diagnosis, as well as suggesting that its features were the result of an immune process.
