Soil Texture
| Soil textural group | Soil textural class | Feel by hand texturing |
| Coarse to very course | sand, loamy sand | gritty - does not ribbon or leave a stai ... |
| moderately course | sandy loam | gritty - leaves smear on hand, does not ... |
| medium | loam, silt loam, silt | smooth and flour-like, does not ribbon, ... |
| moderately fine | sandy clay, sandy clay loam, clay loam, ... | forms ribbon; clays from longer ribbons ... |
How can we determine soil texture?
- The sand, being the biggest and heaviest particles settles first. After a minute or two you will see the sand layer at the bottom of your jar. ...
- The silt layer settles next usually after one to two hours.
- The clay layer can take a long time to fully sink. ...
- You will also likely have a layer of organic matter that floats on the top of the water. ...
What are different soil types and soil texture?
Soil can be classified into three primary types based on its texture – sand, silt and clay. However, the percentage of these can vary, resulting in more compound types of soil such as loamy sand, sandy clay, silty clay, etc. 2. State the characteristics of sandy soil. Sandy soil essentially consists of small particles formed by weathering rocks.
What determines soil texture?
management. The textural class of a soil is determined by the percentage of sand, silt, and clay. Soils can be classified as one of four major textural classes: (1) sands; (2) silts; (3) loams; and (4) clays. In this fact sheet, we will discuss the importance of soil texture, different methods to determine soil texture, and the
How can differentiate between soil texture and soil structure?
Soil texture can be determined using qualitative methods such as texture by feel and quantitative methods such as hydrometer method. Soil structure is determined by how individual soil granules clump, bind together and aggregate resulting in the arrangement of soil pores between them.
What are the four soil textural classes?
Soil Texturesoil. The top layer of the Earth's surface, consisting of four major components: air, water, organic matter and mineral matter. ... Clay. As a soil separate, clay refers to mineral soil particles which are less than 0.02 millimeters in diameter. ... sand. ... soil separates.
How many textural classifications of soil are there?
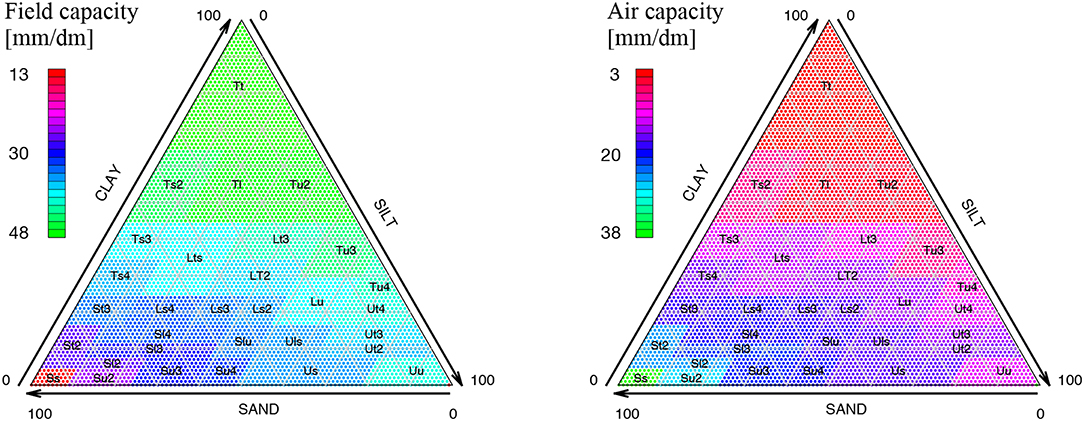
Correctly classify soils into one of the twelve major USDA textural classes using the textural triangle and laboratory data.
What are the 5 textures of soil?
In the United States, twelve major soil texture classifications are defined by the United States Department of Agriculture. The twelve classifications are sand, loamy sand, sandy loam, loam, silt loam, silt, sandy clay loam, clay loam, silty clay loam, sandy clay, silty clay, and clay.
What are the 3 types of soil texture?
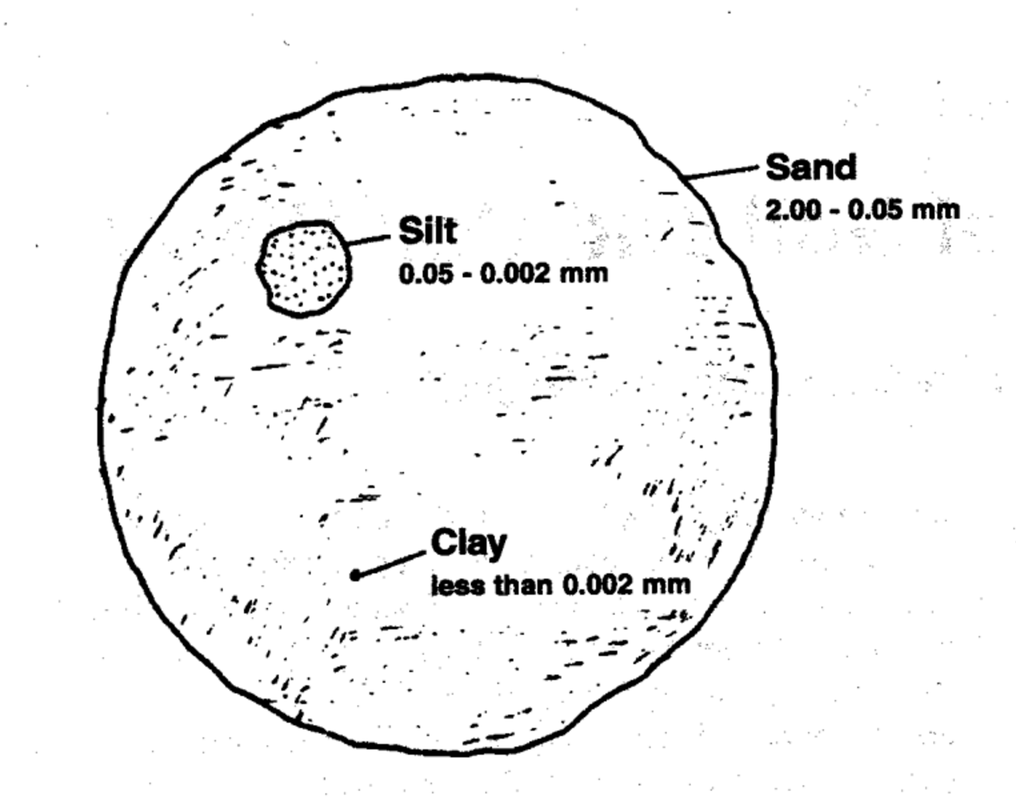
Soil Texture The particles that make up soil are categorized into three groups by size – sand, silt, and clay. Sand particles are the largest and clay particles the smallest. Most soils are a combination of the three.
What are the 12 soil textural classes?
Soil Texture Classes-The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has identified twelve (12) soil texture classes as follows: sand, loamy sand, sandy loam, sandy clay loam, loam, silt loam, silt, silty clay loam, clay, clay loam, sandy clay and silty clay.
What does textural classification tell you?
Based on the USDA system, soil particle sizes are separated into four groups: gravel, sand, silt, and clay. Soil textural class names are determined by the relative mass percentages of sand, silt, and clay-sized particles in the soil.
What are the 7 soil structures?
There are five major classes of structure seen in soils: platy, prismatic, columnar, granular, and blocky. There are also structureless conditions. Some soils have simple structure, each unit being an entity without component smaller units.
What is soil texture PDF?
The term soil texture refers to the size range of particles in the soil, i.e., whether the particles of which a particular soil is composed are mainly large, small, or of some intermediate size or range of sizes. As such, the term carries both qualitative and quantitative connotations.
How many types of soil are there?
The six types of soil There are six main soil groups: clay, sandy, silty, peaty, chalky and loamy.
How many types of soil are there A to B 1 C 3 D 4?
OSHA classifies soils into four categories: Solid Rock, Type A, Type B, and Type C. Solid Rock is the most stable, and Type C soil is the least stable. Soils are typed not only by how cohesive they are, but also by the conditions in which they are found.
What are the 4 physical properties of soil?
Soil physical properties include texture, structure, density, porosity, consistence, temperature, and color.
What are the 8 soil structures?
Soil structure is the arrangement of the soil particles into aggregates. The eight primary types of soil structure are blocky, crumb, columnar, granular, massive, platy, prismatic, and single grain.
How many types of soil classification are there?
OSHA classifies soils into four categories: Solid Rock, Type A, Type B, and Type C. Solid Rock is the most stable, and Type C soil is the least stable. Soils are typed not only by how cohesive they are, but also by the conditions in which they are found.
What are the primary soil textural classes quizlet?
Terms in this set (13) Sand (2.0-0.05 mm) Silt (0.05- 0.002 mm) Clay (< 0.002 mm)
What are the properties of soil for Class 7?
The soil has the following special properties:Texture. The texture of the soil depends upon the relative amount of these particles. ... Absorption of water. Water holding capacity in different types of soils is different. ... Moisture. ... Colour. ... Soil pH. ... Percolation Rate. ... Soil contains air.
What are the different types of soil structure?
There are five major classes of structure seen in soils: platy, prismatic, columnar, granular, and blocky.
What is Soil Texture?
The texture of the soil is an indication of the relative content of particles of various sizes in the soil. It will indicate the percentage of sand, silt, and clay present in the soil. Soil texture will influence the ease with which the soil can be worked. The texture of the soil is dependent on:
What is the textural classification system?
The US Bureau of Public Roads recommends triangular classification system for soil which is commonly called as the textural classification system. The figure- 1 below shows the textural classification system, where the three sides of the equilateral triangle represent the percentage of sand, silt and clay. Where the size of,
What is the classification system for soil?
Soils containing different constituents can be easily classified by the textural classification system. This classification system ensures no particles greater than 2mm size is present. In cases where a certain amount of particles greater than 2mm is present a correction is required.
How many zones are there in an equilateral triangle?
As shown above, the equilateral triangle has 10 zones. Each zone of the triangle will represent each type of soil. Hence, by determining the zone the type of soil can be classified. In order to locate the point a key is given.
What is texture class?
Texture class is an expression, based on the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) system of particle sizes, for the relative portions of the various size separates (of individual mineral soil grains) of the fine earth fraction (less than 2 mm equivalent diameter) in a mass of soil.
What is the field method of texture?
Field method “texture-by-feel method” or apparent texture is guided by tactile perceptions where sand feels gritty, silt feels smooth or floury and clay feels sticky and or stiff. With practice individuals can become quite adept at determine the textural class accurately using texture-by-feel. No real gold standard specific methodology exists for texture-by-feel, but a suggested flow chart was authored by Thein (1979 [1]) and a modified version is presented below. The challenge is to be consistent and attempt to ignore organic matters influence on the way the soil feels.
What are the three classes of loam?
The loamy class in the three class system is divided into moderately course, medium, and moderately fine in the five class system. Moderately course is sandy loam in the twelve class system and medium in five class system is further separated into loam, silt loam, and silt in the twelve class system. The five class system moderately fine class is further separated into the clay loam, sandy clay loam, and silty clay loam in the twelve class system. Clayey in the three class system is fine in the five class system but is further separated into clay, sandy clay, and silty clay in the twelve class system.
How to determine relative fractions of sand, silt, and clay?
There are essentially three methods to determine the relative fractions of sand, silt, and clay to properly place the soil into a textural class. The are laser granulometer, gravity sedimentation, and texture–by–feel (or apparent texture).
How to measure soil density?
The first is a special hydrometer, calibrated in terms of the grams of soil suspended, is used to measure density. The hydrometer is gently placed into the cylinder containing the suspension after predetermined periods of time and a reading taken by determining where the meniscus of the suspension strikes the hydrometer. The second is removing an aliquot of suspension after a particular size of particle –the size larger than the ones you wish to measure– has past a threshold depth. The second is considerably more accurate than the first, but takes slightly longer. It is the second, pipette method, that is the gold standard of our current database.
What is sandy in the three class system?
Sandy in the three class system is the course class in the five class system which is sand and loamy sand in the twelve class system. The loamy class in the three class system is divided into moderately course, medium, and moderately fine in the five class system.
What are the three classes of particle size?
All the various particle-sized distributions can be grouped into three classes; sandy, loamy, and clayey. Sandy in the three class system is the course class in the five class system which is sand and loamy sand in ...
What is soil texture?
Soils are also classified on the basis of texture. Texture means the size of individual mineral particles. Thus, the term ‘soil texture’ refers to the size of soil particles and their arrangement.
What are the layers of soil called?
The layers are known as horizon . Most soil profiles include three master horizons, identified by the letters A, B and C. When a soil is used without proper care, the A and B horizons get eroded away. The soil profile is influenced by all the morphological characters, climate and land use practices.
How is water a determinant of soil fertility?
The presence of water in the soil is also a significant determinant of soil aeration and its fertility. The various forms of water are present in soil that exhibits a complex interrelationship. The proportion of exchangeable bases in a soil is obtained by the process of measuring concentration of hydrogen ions. It is assumed that the proportion of other ions which can be held by the clay humus complex depends on the ‘space’ left by hydrogen ions. The proportion of free hydrogen ion in the soil solution is measured and stated as pH value.
Why does sandy soil have low cation exchange capacity?
Sandy soils generally have low cation exchange capacities because of their smaller proportions of negatively charged material.
How does soil texture affect water?
Soil texture influences the rate at which water percolates through soil and the amount of water a soil can contain. Coarse soils are characterized by rapid infiltration, and hence low surface run-off, but they cannot retain much water.
What is the pH of soil?
Soils vary in pH from about 4, for strongly acid soils to about 10, for alkaline soils that contain free sodium carbonate. The pH range for most agricultural soils is 5 to 8.5. pH 7 is the natural value; values below pH 7 indicate an acidic soil and values above pH 7 indicate alkalinity.
Why is soil high in organic matter?
Soil high in organic matter has substantial cation exchange capacities because of the large negative charge developed by humus. The pH value of soil is influenced by the soil water ratio, the electrolyte content and the carbon dioxide level. The pH of soil varies considerably with its water content. Paragraphs on Soil Erosion.
What is the textural class of soil?
Sand is also the textural class name of any soil that contains 85 percent or more sand and no more than 10 percent clay. particles are the largest. The size ranges for the. soil separates. Categories of soil particles—sand, silt and clay—divided by particle size.
How many classes of soil are there?
The proportion of the different soil separates in a soil defines its soil texture. There are 12 classes of
What do the three sides of the textural triangle represent?
The three sides of the textural triangle represent increasing or decreasing percentages of sand, silt and clay particles. The textural triangle is easy to use once it is understood. Assume that you have a soil that is 60 percent clay, 20 percent silt and 20 percent sand.
What is the smallest particle in soil?
As a soil textural class, clay refers to soil material that is 40 percent or more clay, less than 45 percent sand, and less than 40 percent silt. particles are the smallest, while. sand. Individual rock or mineral fragments in a soil that range from 0.05 to 2.0 millimeters in diameter.
What are the three groups of soil particles?
Three categories for soil particles have been established — sand , silt and clay . These three groups are called soil separates. The three groups are divided by their particle size. Clay. As a soil separate, clay refers to mineral soil particles which are less than 0.02 millimeters in diameter.
What is soil texture?
Soil texture as defined by soil textural class and estimated by hand. Some small rock fragments may be present in soil as stones or gravel. While these rock fragments play a role in the physical properties and processes of soil, they are not considered in the determination of soil texture.
What is the process used to determine soil separates?
The laboratory procedure used to identify soil separates is known as mechanical analysis . This process records the time it takes a specific weight of soil particles to fall to the bottom of a tall cylinder filled with water. A textural triangle can be used to determine soil textural class from the results of a
What are the different types of soil?
Classification of the soil, types of soil and texture, it is categorised clay, sandy, silt, gravel, alluvial, red, black, peat, chalk soil
What is the classification of soil?
Regarding this, “classification of the soil”, systems deals with the systematic classification of soils based on distinct characteristics as well as criteria which is used to group soils according to their order of performance under given set of physical condition and its intended purpose of the system.
What is fine grained soil?
Regarding this, fine grained soil, this is designed as fine grained if more than 50 percentage of the soil sample passes No. 200 US sieve that is divided in inorganic silt, inorganic clay, organic silt and organic clay.
What is alluvial soil?
Alluvial soil:- Regarding this, alluvial soil is widely spread and very important soil having various proportions of clay, silt and sand that is suitable for agriculture and rich in mineral contents , this type of soil can be also called as Bangar termed as (Old Alluvial) and Khadar termed as (New Alluvial). Black soil.
What is the percentage of fines in a soil?
This soil is containing less than 5 percentage fines are indicated by symbols for well graded GW and SW, if the percentage of fines having more than 12 percentage, then it is designated by symbols GM, GC, SM or SC, and lies between 5 to 12 percentage , course grained soils are designed by GW-GM or SP-SM.
Which type of soil is more suitable for farming?
This type of soil gain all properties of equilibrium of three types of soil Sandy, silt and clay due to fact that loam soil is more suitable for farming and also referred to as agricultural soil ,these soils are fertile and provide good drainage. Primary Sidebar. Categories.
What percentage of soil is retained on 75 micron is seive?
Regarding this, coarse grained, this soil is percentage of soil retained on 75 micron IS seive is greater than 50 percentage of the soil, it is designated as corse grained soil, if 50 percentage or more of the coarse fraction is retained in 475 micron US sieve, then it is degined for gravel, otherwise it is indicated as sand.
What is soil texture?
Soil texture refers to the proportions of sand (2.0 – 0.05 mm in diameter), silt (0.05 – 0.002 mm), and clay (less than 0.002 mm). The relative proportions determine the textural class. Soil texture influences nearly every aspect of soil use and management. Many of the physical and chemical properties of the soil depend on how fine (clayey) or coarse (sandy) a soil is. Soil texture is a permanent feature unless soils are subjected to rapid erosion, deposition, or removal.
What are the three soils that are separate?
Differentiate the three soil separates (sand, silt, and clay) based on their particle size diameters.
How do you determine soil texture?
Thus, by simply knowing the texture of the soil, inferences can be made in regard to many soil properties. Here, soil texture will be determined quantitatively using the hydrometer method, and estimated using the texture by feel method. Different soil structure types will also be observed. What you learn about texture and structure in these activities will be used later during the soil pit field trips to describe soil profiles in the field.
How to suspend soil particles in a sedimentation cylinder?
Suspend all soil particles in the sedimentation cylinder using one of the following methods: Plunger method: Carefully insert stirring plunger and move up and down the full length of the cylinder for 30 seconds, ensuring that all particles are thoroughly mixed. Hold base of cylinder firmly with other hand.
Is soil a permanent feature?
Many of the physical and chemical properties of the soil depend on how fine (clayey) or coarse (sandy) a soil is. Soil texture is a permanent feature unless soils are subjected to rapid erosion, deposition, or removal. Moreover, much of the reactivity of soils is related to the amount of surface area available.
Does sand settle faster than clay?
Note that the larger the diameter of the particle, the faster it settles (sand grains will settle faster than silt particles, which will settle faster than clay particles). Also, the density and viscosity of water vary with temperature, so the velocity of settling will be influenced by the temperature of the water (Figure 7.6).
