Types of Bifascicular Blocks
- Right bundle branch block + left anterior fascicular block.
- Right bundle branch block + left posterior ascicular block.
- Complete left bundle branch block: Equivalent to the block of both fascicles.
What type of heart block is bifascicular?
Bifascicular block – The term bifascicular block most commonly refers to conduction disturbances below the atrioventricular (AV) node in which the right bundle branch and one of the two fascicles (anterior or posterior) of the left bundle branch are involved.
How serious is a bifascicular block?
Bifascicular blocks of this type are potentially significant because they make ventricular conduction dependent on the single remaining fascicle. Additional damage to this third remaining fascicle may completely block AV conduction, producing third-degree heart block (the most severe form of trifascicular block).
What is a bifascicular block on ECG?
A bifascicular block on ECG is defined by the combination of a right bundle branch block and either a left anterior fascicular block or left posterior fascicular block.
Which heart block is the most serious?
3rd-degree heart block is the most serious and can sometimes be a medical emergency. All degrees of heart block can increase your risk of developing other heart rhythm problems, such as atrial fibrillation (an irregular and abnormally fast heart rate).
Can you have surgery if you have bifascicular block?
Bifasicular block is commonly RBBB (right bundle branch block) with left or right axis deviation. I need to explain to you that patients with this block are safe to undergo anesthesia.
How can you tell if you have a bifascicular block?
Clinically, bifascicular block presents with one of two ECG patterns: Right bundle branch block (RBBB) with left anterior fascicular block (LAFB), manifested as left axis deviation (LAD) RBBB and left posterior fascicular block (LPFB), manifested as right axis deviation (RAD) in the absence of other causes.
Which is worse right or left bundle branch block?
In older people with coronary artery disease, left bundle branch block is associated with greater risk of death. This is especially true for people with heart failure. Left bundle branch block is also linked to a greater risk of death after a heart attack.
How do you treat Fascicular blocks?
There's no specific treatment for left anterior fascicular block, but you'll most likely need treatment for what caused the block — heart disease.
Should I be concerned about a bundle branch block?
Because bundle branch block affects the electrical activity of the heart, it can sometimes complicate the accurate diagnosis of other heart conditions, especially heart attacks. It may lead to delays in proper management of those heart conditions.
What causes Bifascicular block?
What causes a bifascicular block? Congenital heart disease typically causes a bifascicular heart block. Congenital means a person is born with structural changes to their heart's anatomy. Symptoms of congenital heart disease may not develop until later in life.
Will a pacemaker help heart block?
The most serious types of heart block respond very well to treatment with a pacemaker, and deaths that are caused by these conditions are very rare.
What is the life expectancy with heart block?
Does this affect my life expectancy? With appropriate use of pacemaker therapy, most patients with advanced heart block can lead a normal life.
What happens if heart block is left untreated?
If left untreated, severe heart block can cause sudden cardiac arrest (your heart suddenly stops beating), but most commonly can cause either lightheadedness or fainting spells.
How long can you live with heart block?
Total mortality and estimated survival did not differ between the two groups. The estimated survival in the VDD group at 1, 3, and 5 years for patients without and with congestive heart failure was 94%, 86% and 78%, and 92%, 83% and 72%, respectively.
Can you live a long life with a right bundle branch block?
If you don't have heart disease, having right bundle branch block doesn't change your life expectancy or add to your risk level. But having right bundle branch block can put you at a higher risk of death if you also have heart failure or a heart attack.
What is the life expectancy of someone with left bundle branch block?
In young and healthy people, left bundle branch block is rare. This condition seems to have little effect on how long you live if you have no other underlying heart problems. You may not need any treatment at all, especially when you have no other disease affecting your heart.
What is the problem with bifascicular block?
The problem with bifascicular block is that the heart’s electrical conduction system is down to one fascicle. As such, the patient may be at risk for complete heart block (which is what would happen if all three fascicles were blocked).
What is the first rule when dealing with bifascicular blocks?
It’s worth remembering that the first rule when dealing with bifascicular blocks is to establish that you are dealing with a supraventricular rhythm. One of the reasons is that ventricular tachycardia often presents with a bifascicular pattern.
How to identify fascicular block?
To identify fascicular blocks you need to be able to identify a right or left axis deviation in the frontal plane. One way to do that is to use a cheat sheet like this one.
How many fascicles are there in the heart?
Ventricular depolarizaiton is facilitated by the heart’s electrical conduction system, sometimes referred to as the His/Purkinje system, which by convention is said to have three main fascicles or branches. There is a single fascicle in the right ventricle referred to as the right bundle branch. There are two fascicles in the left ventricle: ...
Why do purists require qR complexes in the inferior leads and rS complexes in?
Purists also require qR complexes in the inferior leads and rS complexes in the high lateral leads because this pattern can also be caused by right bundle branch block and Q-waves from high lateral myocardial infarction. Sinus tachycardia with a rate of 113. The QRS is wide at 158 ms.
What is the duration of the sinus rhythm at a rate of 69?
Sinus rhythm at a rate of 69. The QRS duration is modestly prolonged at 108 ms. There is a left axis deivation with rS complexes in the inferior leads and qR complexes in the high lateral leads. There is a late transition (persistent S-wave) in the precordial leads.
What is the rate of sinus rhythm?
Sinus rhythm with a rate of 77. There is first degree AV block with a PR-interval of 252 ms. The QRS duration is wide at 172 ms. There is a terminal R-wave in lead V1. There is a left axis deviation with rS complexes in the inferior leads and qR complexes in the high lateral leads.
What is bifascicular block?
Bifascicular block is a conduction abnormality in the heart where two of the three main fascicles of the His/Purkinje system are blocked.
What is a left bundle branch block?
Some authors consider left bundle branch block (LBBB) to be a technical bifascicular block, since the block occurs above the bifurcation of the left anterior and left posterior fascicles of the left bundle branch.
Can a pacemaker be used for bifascicular block?
In those with bifascicular block and no symptoms, little with respect to treatment is needed. In those with syncope, a pacemaker is recommended.
What is RBBB plus LAFB?
The ECG will show typical features of RBBB plus either left or right axis deviation. RBBB + LAFB is the most common of the two patterns. This is due to a single coronary artery blood supply (LAD) to the anterior fascicle. RBBB + LPFB is less common due to a dual blood supply (right and left circumflex arteries), ...
Why is RAD indicating LPFB?
In the context of RBBB, RAD indicating LPFB may be due to other causes such as right ventricular hypertrophy, and these need to be excluded before the ECG is labelled bifascicular block
What wave is slurred in lead I?
RBBB with wide QRS, slurred S wave in lead I and slurred R in V1.
What is bifascicular block?
Bifascicular block is often associated with structural heart disease (50-80%) and extensive fibrosis of the conducting system. There is a risk of progression to complete heart block with additional damage to the third remaining fascicle, however clinical context is important:
What is the risk of progression for a patient with syncope?
Patients presenting with syncope have a 17% annual risk of progression. Syncope or presyncope in the context of a bifascicular block is an indication for admission and monitoring. If other causes of syncope are not identified on work-up, pacemaker insertion is recommended.
What pattern is RBBB?
RBBB is seen with RSR’ pattern in V1-3 and slurred S waves in lateral leads
Is RBBB a dual blood supply?
RBBB + LPFB is less common due to a dual blood supply (right and left circumflex arteries), and this combination may be associated with more extensive underlying cardiac pathology. Typical bifascicular block pattern: RBBB combined with LAFB (manifested as LAD)
How is Bifascicular Block Diagnosed?
If the treating physician suspects Bifascicular Block then the physician may order an echocardiogram to monitor the functioning of the heart. This condition can also be found incidentally when the physician is examining the patient for some other condition. An ECG may then be done to find out if the heart is beating in a normal fashion or whether there is some abnormality. By these studies the physician will be able to formulate a treatment plan best suited for the patient.
What is bifascicular block?
Bifascicular Block is a cardiac condition of a chronic nature in which the two bundles of vascular tissues control ling the heart start to malfunction and do not send appropriate signal as a result of which the heart does not get adequate electrical signals causing irregular heartbeats. There are three main fascicules present in ...
Which fascicules are present in the heart?
There are three main fascicules present in the heart which are the right bundle fascicule, the left anterior fascicule, and the left posterior fascicule. Bifascicular Block develops due to at least two of these pathways getting affected. Advertisement.
Can a bifascicular block be treated?
In majority of the cases Bifascicular Block is not treated but very closely observed. The associated conditions of Bifascicular Block may be treated with appropriate medications and other measures. In case the patient has a history of syncopal events along with Bifascicular Block then the patient may be implanted with a pacemaker to control the rate and rhythm so that any complications may be avoided due to Bifascicular Block.
Can bifascicular block cause shortness of breath?
As stated, Bifascicular Block may make it tough for the heart to transport sufficient amount of blood to the parts of the body. In most of the cases this condition is asymptomatic but in some cases the affected individual may have dizziness, syncopal events, chest pain with shortness of breath.
Is bifascicular block congenital?
Bifascicular Block normally is congenital in nature and is present at birth and this condition may not be diagnosed for quite a number of years in some individuals whereas in some cases this block is caused due to a cardiac condition like a heart attack or after a surgical procedure to the heart. There are certain classes ...
Can bradycardia cause cardiac arrest?
There may also be presence of bradycardia as well. Bifascicular Block is a potentially serious medical condition and may cause a variety of complications especially if the affected individual has other cardiac problems as well as it may result in cardiac arrest.
What is bifascicular block?
Good question: Bifascicular block refers to conduction disturbances in which the right bundle branch and the left anterior fascicle or left posterior fascicle are blocked (fail to conduct an electrical impulse). It may occur in heart disease or in an otherwise normal heart. Progression to complete block is rare. Risk for death is low. Treatment not usually required. If symptomatic may need pacemaker.
What are the 3 fascicles?
see below: There are 3 fascicles or pathways for cardiac conduction in the heart: the right bundle branch, and the left bundle branch which is subdivided into anterior and posterior fascicles. When 2 of the 3 don't function, it is easily detected on ekg. This causes no symptoms and requires no treatment. Nonetheless it is abnormal and should prompt an evaluation of your general heart health.
How long does it take to video chat with a doctor?
Video chat with a U.S. board-certified doctor 24/7 in less than one minute for common issues such as: colds and coughs, stomach symptoms, bladder infections, rashes, and more.
Can you use HealthTap for medical advice?
Content on HealthTap (including answers) should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment, and interactions on HealthTap do not create a doctor-patient relationship. Never disregard or delay professional medical advice in person because of anything on HealthTap. Call your doctor or 911 if you think you may have a medical emergency.
Can you call 911 for healthtap?
For these, please consult a doctor (virtually or in person). For potential or actual medical emergencies, immediately call 911 or your local emergency service.
What percentage of patients have bifascicular block?
1.5% of patients may have a bifascicular block on the electrocardiogram. This alteration is a combination of intraventricular conduction disturbances, which can carry a risk of progression to complete atrioventricular block, especially in patients with syncopal symptoms 1.
What is a bifascicular block?
A bifascicular block is the combination of a blockade of two of these branches.
What is the ventricular conduction system?
The ventricular conduction system can be classified as a three fascicles system. Consisting of the right bundle branch, and the anterior and posterior fascicles of the left bundle branch. A bifascicular block is the combination of a blockade of two of these branches.
Which fascicle is blocked in bifascicular block?
The most common of bifascicular blocks. The right bundle branch and the left anterior fascicle are blocked, so the depolarization of the ventricles is performed from the posterior fascicle of the left branch.
Which block has the characteristics of right bundle branch block combined with the corresponding left fascicular block?
So, the bifascicular block has on the electrocardiogram the characteristics of right bundle branch block combined with the corresponding left fascicular block.
Which fascicle is blocked in the right bundle?
The right bundle branch and the left posterior fascicle are blocked, so the depolarization of the ventricles is performed from the anterior fascicle of the left branch.
Can a bifascicular block be secondary to an atrioventricular block?
In patients with bifascicular block in the electrocardiogram and episodes of syncope, there is the possibility that symptoms are secondary to an unknown advance atrioventricular block.
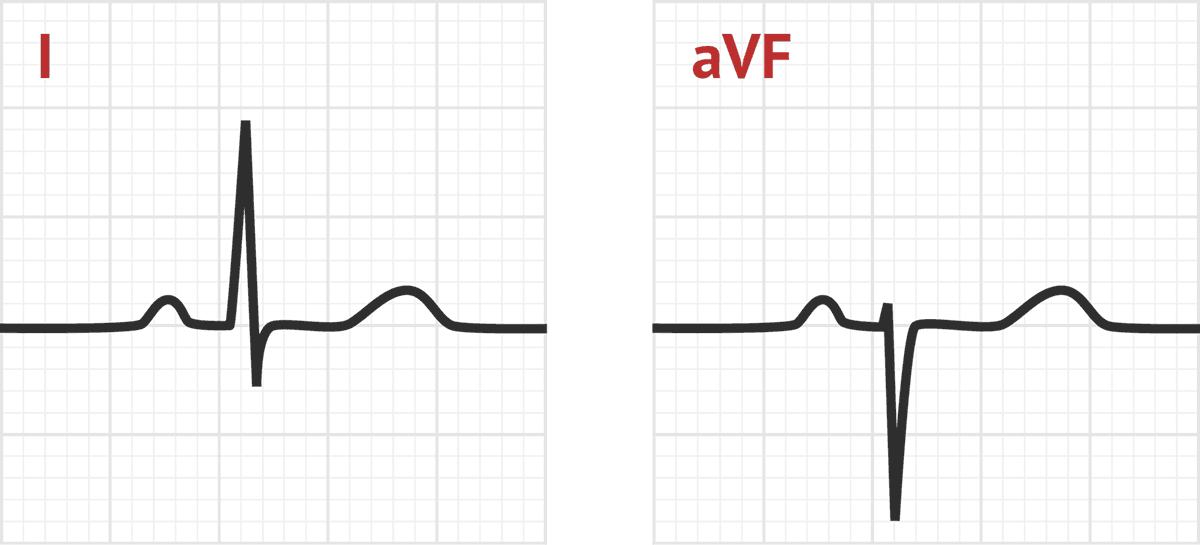
What is the ECG pattern of a left anterior superior fascicular block?
For example, a left anterior superior fascicular block will produce an ECG with an initially positive ( superior) deflection in the inferior leads: an rS pattern (Figure 9).
What is the most common disorder of the left anterior-superior fascicle?
Left Anterior Superior Fascicular Block. Disease of the left anterior-superior fascicle (LASF) is the most common disorder of the fascicles. The left superior anterior fascicle is anatomically narrow, like a single conducting wire.
Why is the anterior surface of the heart renamed?
This makes anatomical sense, as the anterior surface of the heart is superior to the posterior surface, but the reason for the renaming is mostly to set up a useful mnemonic: the direction of the initial deflection in the inferior ECG leads is the same as the name of the block.
What is the cardiac axis?
The term cardiac axis refers to the net cardiac vector, which is the summation of all of the tiny vectors that make up the cardiac depolarization wave. In reality, depolarization starts in many places simultaneously, and these individual depolarization waves sum together to form a net left-to-right septal vector [ 1 ].
Where does net depolarization occur in the heart?
In the normal heart, net depolarization begins at the septum and proceeds left-to-right across this structure. The depolarization then spreads down toward the apex of the heart. Finally, depolarization spreads back up to the walls of the ventricles (Figure 2) [ 1 ]. Since, in the normal heart, there is more myocardial mass to depolarize in the left ventricle than in the right, the cardiac axis on ECG ends up pointing left, between 0 and +90 degrees.
Where does depolarization occur in the anterolateral free wall?
Depolarization is initiated by the LASF at the endocardial surface of the anterolateral free wall, and spreads superiorly and leftwards, toward the epicardium (Figure 6) [ 5 ].
What causes right axis deviation?
There are other diseases that cause right-axis deviation, such as right ventricular hypertrophy, pulmonary embolism, COPD, and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. LPIFB cannot be diagnosed until other causes of right-axis deviation are ruled out [ 5, 6 ].