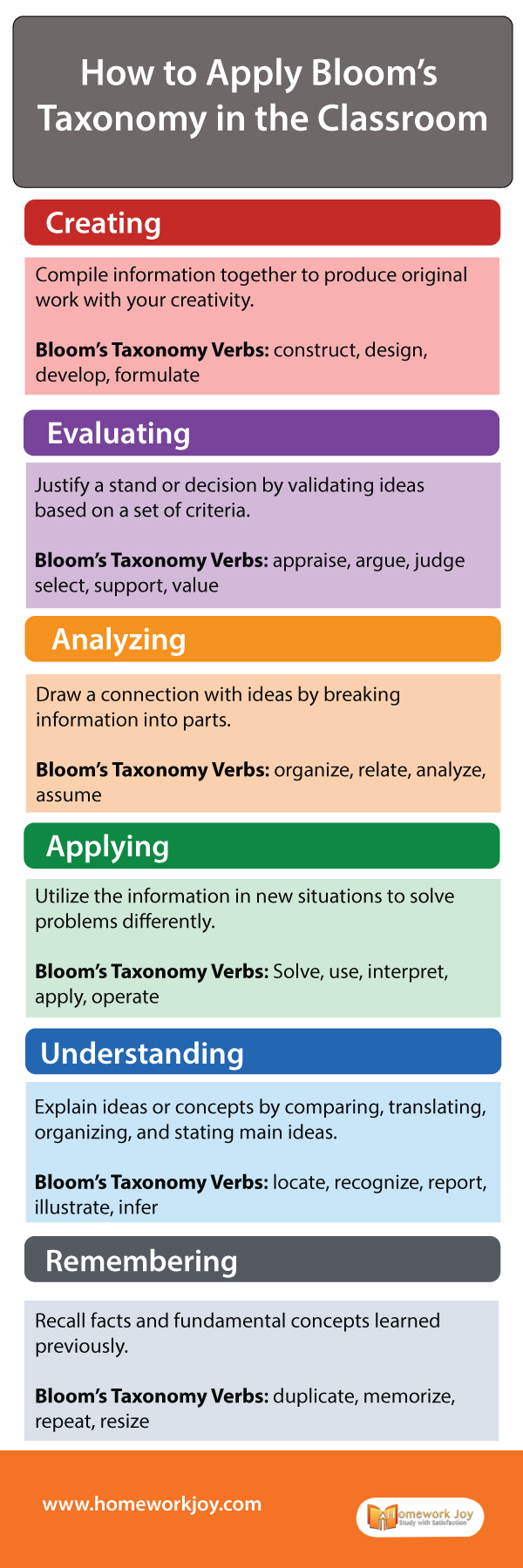
Learning can be divided into three domains:
- Cognitive: This is the most commonly used domain. It deals with the intellectual side of learning.
- Affective: This domain includes objectives relating to interest, attitude, and values relating to learning the information.
- Psychomotor: This domain focuses on motor skills and actions that require physical coordination.
What are the three domains of learning in education?
These three domains were cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. If you plan to pursue a career in the educational field, it’s important that you know these three taxonomies, which are detailed below. Take an online class in teaching with technology to further reach your students’ particular learning style.
What are the different areas of taxonomy for educational objectives?
Bloom’s classification system or Taxonomy for educational objectives is divided into 3 major areas called domains Cognitive Domain Psychomotor Domain Affective Domain 9/ 19 Taxonomy of Educational Objectives
What are the different types of learning objectives?
The models organize learning objectives into three different domains: Cognitive, Affective and Sensory/Psychomotor. The taxonomy was proposed by Benjamin Bloom in 1956, He was an educational psychologist at the University of Chicago. The first volume of taxonomy, Handbook I: Cognitive was published in 1956
How many domains are there in the cognitive domain?
2. The Affective domain ( Emotion-based) 3. The psychomotor domain ( Action based) 1. The cognitive domain: In the original version of the taxonomy, the cognitive domain is further divided into 6 levels.
What are the 3 domains of educational objectives?
Learning can generally be categorized into three domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor.
How many domains of educational objectives are there?
The Three Domains of Learning The committee identified three domains of educational activities or learning (Bloom, et al. 1956): Cognitive: mental skills (knowledge) Affective: growth in feelings or emotional areas (attitude or self)
What is the importance of 3 domains of learning?
The domains of learning teach students to think critically by using methods that make the most sense to them. They benefit students by teaching them various ways to approach new ideas and concepts. They also give teachers tools to cater the learning experience to the specific needs of each student.
What is the important of the three domains?
Developing and delivering lessons by teachers are integral in the teaching process. It is hence important for teachers to ensure that the three (3) domains of learning which include cognitive (thinking), affective (emotions or feeling) and Psychomotor (Physical or kinesthetic) to be achieved.
The Original Cognitive Or Thinking Domain –
Based on the 1956 work, The Handbook I-Cognitive Domain, behavioral objectives that dealt with cognition could be divided into subsets. These subse...
The Affective Or Feeling Domain
Like cognitive objectives, affective objectives can also be divided into a hierarchy (according to Krathwohl). This area is concerned with feelings...
The Psychomotor Or Kinesthetic Domain
Psychomotor objectives are those specific to discreet physical functions, reflex actions and interpretive movements. Traditionally, these types of...
What are the domains of learning?
The domains of learning are a series of learning objectives created in 1956 by educational psychologist Dr. Benjamin Bloom. They involve three categories of education, and each one requires a different instruction style to achieve its intended outcomes.
Why are the domains of learning important?
The domains of learning are important because they teach students to think critically by using methods that make the most sense to them and help them understand new concepts in a different way. These domains benefit every student by teaching them various ways to approach new ideas and concepts.
Types of learning domains
Educational researchers have continued to expand upon the learning domains and what they encompass since Bloom's introduction of the concept. Here are the three domains of learning and the areas of student development they influence:
What are the three domains of learning?
It is hence important for teachers to ensure that the three (3) domains of learning which include cognitive (thinking), affective (emotions or feeling) and Psychomotor (Physical or kinesthetic) to be achieved. It is imperative to understand ...
When were domains of learning created?
DOMAINS OF LEARNING. Initially developed between 1956 and 1972, the domains of learning have received considerable contributions from researchers and experts in the field of education. Studies by Benjamin Bloom (on cognitive domain), David Krathwohl (affective domain) and Anita Harrow (Psychomotor domain) have been encompassed into ...
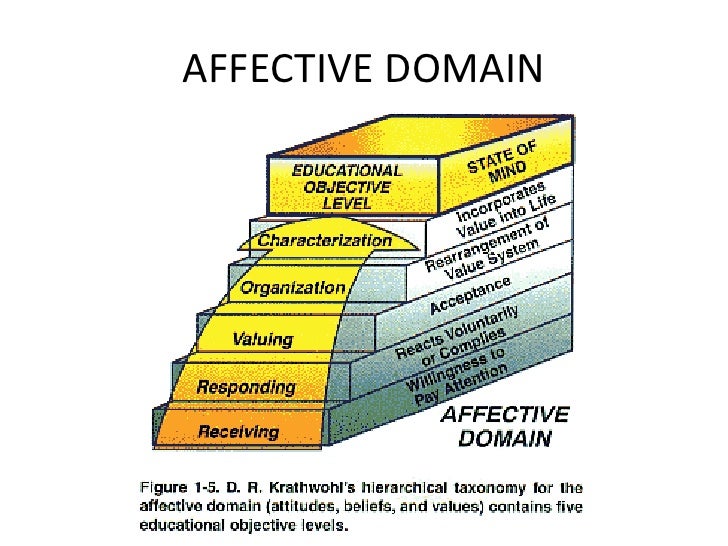
What are the categories of affective domain?
The categories of affective domain include receiving phenomena; responding to phenomena; valuing; organization; and characterization (Anderson et al, 2011). The sub domain of receiving phenomena creates the awareness of feelings and emotions as well as the ability to utilize selected attention.
What is affective domain?
The affective domain includes the feelings, emotions and attitudes of the individual.
What are the three domains of learning?
These three domains were cognitive, affective, and psychomotor.
What is the cognitive domain?
The Cognitive Domain. The basic idea behind the cognitive domain involves the knowledge and intellectual skills that a student will develop. There are six categories involved within the cognitive domain, and they are usually considered to be stages of difficulty. Usually, the first category must be mastered before a student can move on to ...
What are the categories of cognitive bias?
These categories are knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. Learn more about cognitive biases with an online course.
What is an example of evaluation?
In a classroom, a good example of this would be book reports that involve summarizing what was read and giving an opinion of what they thought about the material.
What is the expert stage in learning a complex skill?
There is a higher proficiency in complex movement patterns with a minimum of energy used. If you have skills that fall under this category, you perform them without hesitation and automatically. Examples of this include people who can operate a computer with ease including downloading many programs without any help. Also, people who play instruments with ease and competence have achieved complex overt response regarding instrumental skill.
Is Bloom's taxonomy of learning the only theory out there?
Bloom’s taxonomy of learning is not the only theory out there. However, it is a good starting point for anyone interested in the education field. Other great theories to look at are the multiple intelligences and theories that build off of Bloom’s taxonomy. Discuss the learning theories you know in the comments below.
How many levels are there in the cognitive domain?
The cognitive domain: In the original version of the taxonomy, the cognitive domain is further divided into 6 levels. Revised edition of Bloom’s taxonomy In 2001, the levels are slightly different from original taxonomy: Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, Create (rather than Synthesize). the name is changed from noun to verb form.
Why is it important to organize objectives?
2. Organizing objectives helps to clarify objectives for themselves and for students. 3. Having an organized set of objectives helps teachers to: “plan and deliver appropriate instruction”; “design valid assessment tasks and strategies”; and. “ensure that instruction and assessment are aligned with the objectives.”.
What is affective domain?
Skills in the affective domain describe the way people react emotionally and their ability to feel other living things’ pain or joy. Affective objectives typically target the awareness and growth in attitudes, emotion, and feelings.
Is Bloom's approach to learning incomplete?
It is incomplete – Bloom concentrated his efforts only on learning, yet there is little about motivation or about classroom management. 3. It is too fixed – Classifying and separating learning into three domains and good hierarchies is a very modern, scientific view of learning.
What is the cognitive domain of Bloom's taxonomy of learning?
The cognitive domain of Bloom’s taxonomy of learning tries to cater to Bloom’s taxonomy objectives such as critical thinking, problem-solving and creating and enhancing a knowledge base. This was the first domain created by Bloom’s original team of researchers and includes hierarchies that are concerned with building new knowledge as well as refining previously gathered information. The different levels of the cognitive domain are as follows:
What is a projecting one's values in real time?
Concerned with projecting one’s values in real time to be able to work successfully in a team. For example, writing an essay as part of a team on how value systems need to adapt to the world of online learning

The Cognitive Domain
The Affective Domain
- The affective domain deals with a person’s emotions and how they are handled. Like the cognitive domain, there are major categories involved with this domain. They are receiving phenomena, responding to phenomena, valuing, organization, and internalizing values. Learn more about emotional intelligence in the classroom with an online class. When you receive phenomena, you …
The Psychomotor Domain
- The third and final domain of Bloom’s taxonomy involves physical movement, coordination, and motor-skill usage. Developing the skills involved with the psychomotor domain takes practice. There are seven major categories involved with this taxonomy: perception, set, guided response, mechanism, complex overt response,adaptation, and origination. Help...
Other Learning Theories
- Bloom’s taxonomy of learning is not the only theory out there. However, it is a good starting point for anyone interested in the education field. Other great theories to look at are the multiple intelligences and theories that build off of Bloom’s taxonomy. Discuss the learning theories you know in the comments below.