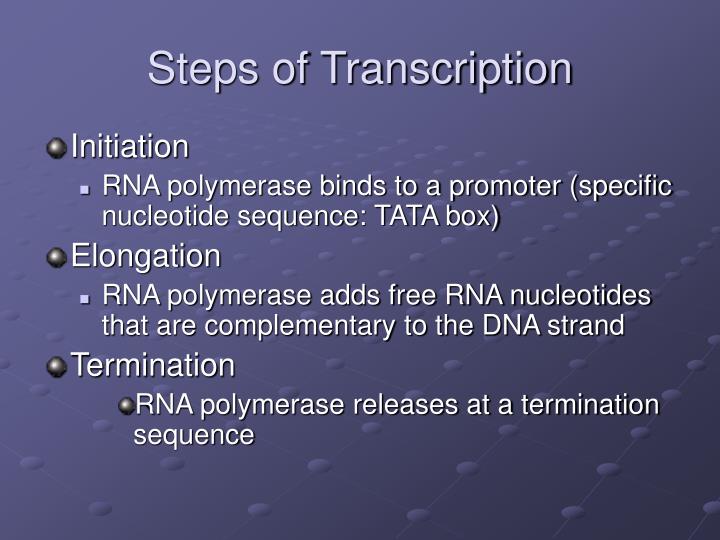
Key Takeaways: Steps of Transcription
- The two main steps in gene expression are transcription and translation.
- Transcription is the name given to the process in which DNA is copied to make a complementary strand of RNA. RNA then undergoes translation to make proteins.
- The major steps of transcription are initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination.
What are the three basic stages of transcription?
Transcription involves four steps:
- Initiation. The DNA molecule unwinds and separates to form a small open complex.
- Elongation. RNA polymerase moves along the template strand, synthesising an mRNA molecule.
- Termination. In prokaryotes there are two ways in which transcription is terminated.
- Processing.
What begins the process of transcription?
Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence near the beginning of a gene (directly or through helper proteins). RNA polymerase uses one of the DNA strands (the template strand) as a template to make a new, complementary RNA molecule. Transcription ends in a process called termination.
How would you describe the steps of transcription?
Transcription step; Transcription is the name given to the process in which DNA is copied to make a complementary strand of RNA. RNA then undergoes translation to make proteins The major steps of transcription are initiation promoter clearance elongation and termination Transcription Initiation.
How to get started as a transcriptionist?
What You Need to Get Started as a Transcriptionist
- Skills. To work as a transcriptionist, you’ll need to have stellar listening skills, including the ability to decipher audio with heavy accents, background noises and multiple speakers.
- Equipment. ...
- Transcription Training and Certifications. ...

What are the 3 transcription factors?
Many transcription factors are either tumor suppressors or oncogenes, and, thus, mutations or aberrant regulation of them is associated with cancer. Three groups of transcription factors are known to be important in human cancer: (1) the NF-kappaB and AP-1 families, (2) the STAT family and (3) the steroid receptors.
What are the 3 steps of translation?
Translation of an mRNA molecule by the ribosome occurs in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination.
What is the main process of transcription?
Transcription is the process in which a gene's DNA sequence is copied (transcribed) to make an RNA molecule. RNA polymerase is the main transcription enzyme. Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence near the beginning of a gene (directly or through helper proteins).
What are the 3 types of translation?
The 4 Most Common Different Types of TranslationLiterary translation.Professional translation.Technical Translation.Administrative translation.
What are the basic steps of transcription and translation?
Transcription is the name given to the process in which DNA is copied to make a complementary strand of RNA. RNA then undergoes translation to make proteins. The major steps of transcription are initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination.
What is the first process of transcription?
The first step in transcription is initiation, when the RNA pol binds to the DNA upstream (5′) of the gene at a specialized sequence called a promoter (Figure 2a). In bacteria, promoters are usually composed of three sequence elements, whereas in eukaryotes, there are as many as seven elements.
What are the steps in translating?
The multi-step translation process professional translators useStep 1: Scope out the text to be translated. The first step is to get a feel for the text you're going to translate. ... Step 2: Initial translation. ... Step 3: Review the accuracy of the translation. ... Step 4: Take a break. ... Step 5: Refine translation wording.
What are the 3 sites in translation?
There are three places on the ribosome where tRNAs bind: the A, P, and E site. The A site accepts an incoming tRNA bound to an amino acid. The P site holds a tRNA that carries a growing polypeptide (the first amino acid added is methionine (Met)).
How do you read codon chart?
1:427:50How to Read a Codon Chart - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo notice on the left side of the chart. It is for the first base. The top is for the second base.MoreSo notice on the left side of the chart. It is for the first base. The top is for the second base. And the right side is for the third base. We're looking at the codon. Aug.
What are the three stages of translation quizlet?
MatchInitiation. -the ribosomes attaches at a specific site of the mRNA (the short codon-AUG) -The small and large ribosomal subunites combine.Elongation. -peptide bonds join the amino acids together in sequence. ... Termination. -The process ends when a stop codon is reached by tRNA.
What are the steps of transcription?
Key Takeaways: Steps of Transcription 1 The two main steps in gene expression are transcription and translation. 2 Transcription is the name given to the process in which DNA is copied to make a complementary strand of RNA. RNA then undergoes translation to make proteins. 3 The major steps of transcription are initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination.
What is the process of transcription in bacteria?
The initiation of transcription in bacteria begins with the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter in DNA. Transcription initiation is more complex in eukaryotes, where a group of proteins called transcription factors mediates the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription.
What are the steps of gene expression?
The two main steps in gene expression are transcription and translation . Transcription is the name given to the process in which DNA is copied to make a complementary strand of RNA. RNA then undergoes translation to make proteins. The major steps of transcription are initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination.
Where does mRNA translation occur?
Translation of the mRNA into proteins also occurs in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the cell's nucleus. mRNA then moves to the cytoplasm for translation. DNA in prokaryotes is much more accessible to RNA polymerase than DNA in eukaryotes. Eukaryotic DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones to form structures called ...
What is the process of terminating transcription?
In eukaryotes, the termination of transcription involves cleavage of the transcript, followed by a process called polyadenylation.
Which direction is RNA synthesized?
RNA is synthesized in the 5' -> 3' direction (as seen from the growing RNA transcript). There are some proofreading mechanisms for transcription, but not as many as for DNA replication. Sometimes coding errors occur.
What is the role of DNA in RNA synthesis?
One strand of DNA serves as the template for RNA synthesis, but multiple rounds of transcription may occur so that many copies of a gene can be produced.
Why is transcription important?
Transcription is an essential step in using the information from genes in our DNA to make proteins. Proteins are the key molecules that give cells structure and keep them running. Blocking transcription with mushroom toxin causes liver failure and death, because no new RNAs—and thus, no new proteins—can be made.
What is the first step in gene expression?
Transcription is the first step of gene expression. During this process, the DNA sequence of a gene is copied into RNA. Before transcription can take place, the DNA double helix must unwind near the gene that is getting transcribed. The region of opened-up DNA is called a transcription bubble.
What is the process of RNA polymerase?
Transcription ends in a process called termination. Termination depends on sequences in the RNA, which signal that the transcript is finished.
What is the process of copying a gene's DNA sequence to make an RNA molecule?
Transcription is the process in which a gene's DNA sequence is copied (transcribed) to make an RNA molecule.
How does RNA polymerase open up DNA?
Once the RNA polymerase has bound, it can open up the DNA and get to work . DNA opening occurs at the element, where the strands are easy to separate due to the many As and Ts (which bind to each other using just two hydrogen bonds, rather than the three hydrogen bonds of Gs and Cs).
Which end of the RNA strand does RNA polymerase add a matching nucleotide?
For each nucleotide in the template, RNA polymerase adds a matching (complementary) RNA nucleotide to the 3' end of the RNA strand. [See the chemical reaction] RNA polymerase synthesizes an RNA transcript complementary to the DNA template strand in the 5' to 3' direction.
Which direction does RNA polymerase read DNA?
It synthesizes the RNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction, while reading the template DNA strand in the 3' to 5' direction. The template DNA strand and RNA strand are antiparallel.
What are the steps of transcription?
Transcription takes place in three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. The steps are illustrated in Figure 2.
What is the beginning of transcription?
Initiation is the beginning of transcription. It occurs when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a region of a gene called the promoter. This signals the DNA to unwind so the enzyme can ‘‘read’’ the bases in one of the DNA strands. The enzyme is now ready to make a strand of mRNA with a complementary sequence of bases.
What is the step of RNA polymerase?
Step 2: Elongation. Elongation is the addition of nucleotides to the mRNA strand. RNA polymerase reads the unwound DNA strand and builds the mRNA molecule, using complementary base pairs. There is a brief time during this process when the newly formed RNA is bound to the unwound DNA.
Where does transcription take place?
Transcription takes place in the nucleus. It uses DNA as a template to make an RNA (mRNA) molecule. During transcription, a strand of mRNA is made that is complementary to a strand of DNA. Figure 1 shows how this occurs. Figure 1.
What is the sequence of bases in a strand of DNA?
Transcription uses the sequence of bases in a strand of DNA to make a complementary strand of mRNA. Triplets are groups of three successive nucleotide bases in DNA. Codons are complementary groups of bases in mRNA. You can also walk through the steps of transcription in this link.
What is the process of transcribing genetic information from DNA to RNA?
A process that involves the transcribing of genetic information from DNA to RNA is DNA transcription. Colored image 4.9 explains DNA transcription. Protein is produced by the transcribed DNA message.
What enzyme is responsible for transcribed DNA?
DNA is transcribed by an enzyme known RNA polymerase. Specific nucleotide sequences inform RNA polymerase where to begin and where to end. At a specific area called the promoter region, RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA.
What are the bases of DNA?
DNA is comprised of four nucleotide bases namely adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T) which are paired together that is A-T and C- G. This is to give DNA its double helical shape.
How does DNA control cellular activity?
DNA controls cellular activity by coding for the production of enzymes and proteins. The information contained in DNA is not directly converted into proteins. First it be copied into RNA. This ensures that the information contained within the DNA does not become tainted.
How does RNA polymerase work?
RNA polymerase keeps on moving along the DNA until it reaches a terminator sequence. RNA polymerase releases the mRNA polymer at that point. This detachment from the DNA.