What is it?
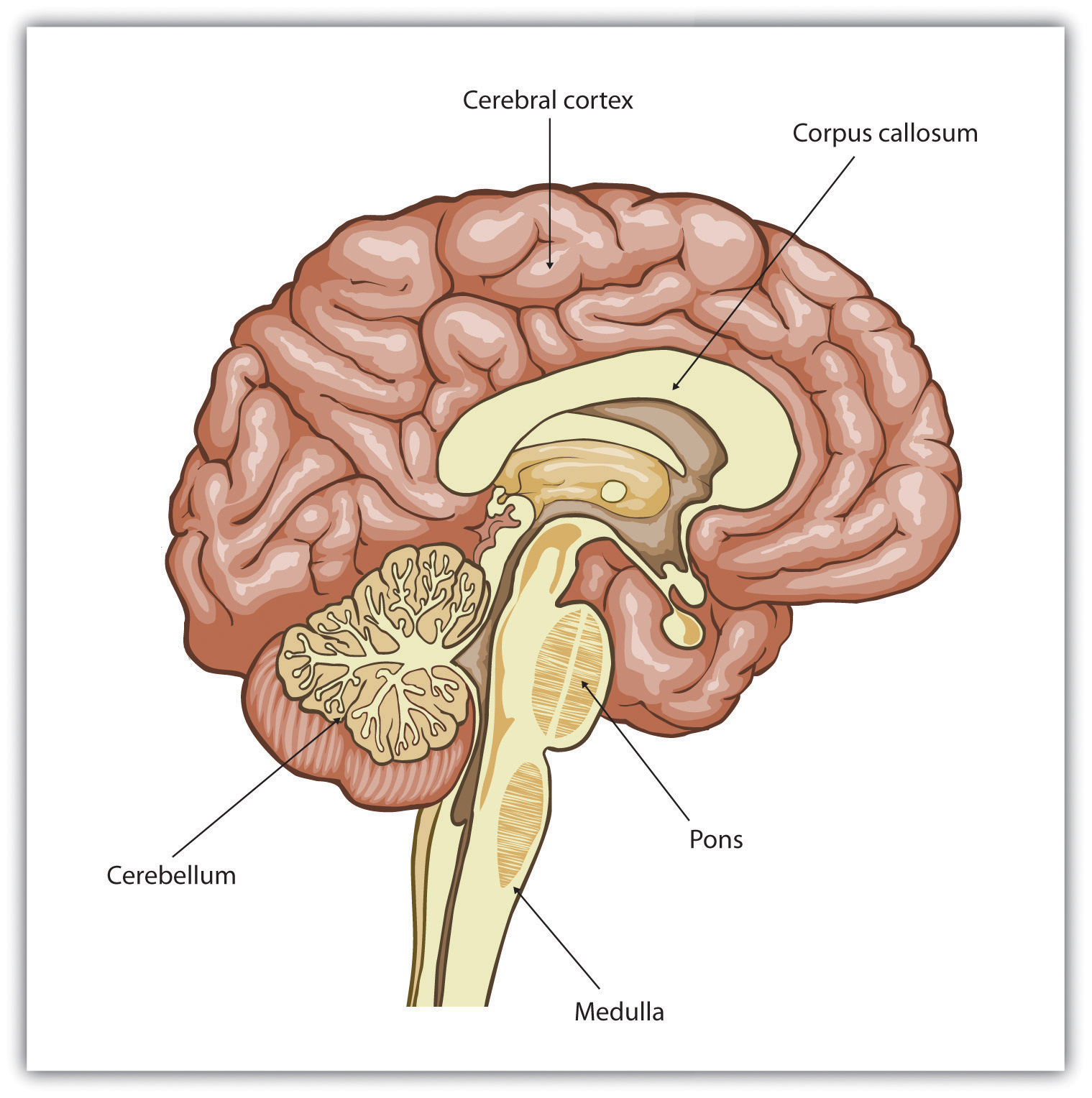
- Cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex is the outermost layer of the cerebrum, or its gray matter. ...
- White matter Beneath the cerebral cortex lie the deeper structures, often known as white matter. ...
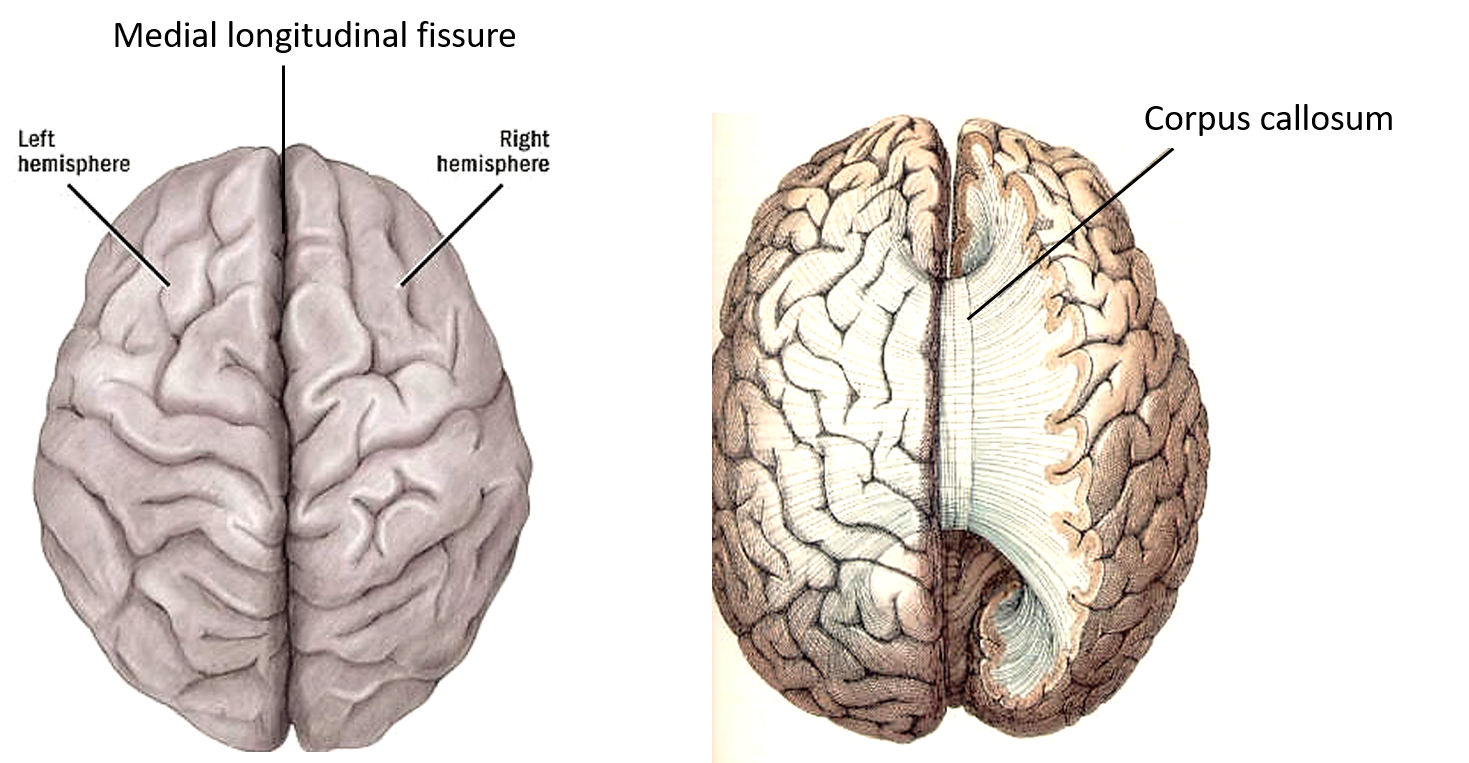
- Hemispheres A fissure divides the cerebrum into right and left hemispheres. ...
- Other structures The following are some other structures located within the cerebrum. ...
What forms the outer layer of the cerebral cortex?
They are:
- Dura mater, an outer, cloth-like layer of tissue that covers the brain and sits between the bones of the skull and the cerebrum.
- Arachnoid, a middle layer that's a delicate, fluid-filled structure that provides shock absorption in the event of brain movement.
- Pia mater, a thin, paper-like structure that lays directly atop the brain.
What are the three layers covering the brain?
The three membranes, or meninges (coverings) of the brain are as follows (from inside out):
- Pia Mater
- Arachnoid
- Dura Mater
What are the ridges in cerebrum called?
The convolutions have "ridges" which are called gyri (singular: gyrus), and "valleys" which are called sulci (singular: sulcus). Some of the sulci are quite pronounced and long, and serve as convenient boundaries between four areas of the cerebrum called lobes.
What are the parts and functions of the cerebrum?
- Frontal lobe. The largest lobe of the brain, located in the front of the head, the frontal lobe is involved in personality characteristics, decision-making and movement. ...
- Parietal lobe. ...
- Occipital lobe. ...
- Temporal lobe. ...
See more
What are the 3 parts of the cerebrum?
The brain can be divided into three basic units: the forebrain, the midbrain, and the hindbrain. The hindbrain includes the upper part of the spinal cord, the brain stem, and a wrinkled ball of tissue called the cerebellum (1).
What are the 3 major functions of the cerebrum?
The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature. Other areas of the cerebrum enable speech, judgment, thinking and reasoning, problem-solving, emotions and learning.
What are the parts of the cerebrum?
The cerebrum or brain can be divided into pairs of frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes. Each hemisphere has a frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobe. Each lobe may be divided, once again, into areas that serve very specific functions.
How many parts of the cerebrum are there?
The cerebrum is divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal.
What is cerebrum of the brain?
(seh-REE-brum) The largest part of the brain. It is divided into two hemispheres, or halves, called the cerebral hemispheres. Areas within the cerebrum control muscle functions and also control speech, thought, emotions, reading, writing, and learning.
What are the 3 parts of the cerebellum?
There are three functional areas of the cerebellum – the cerebrocerebellum, the spinocerebellum and the vestibulocerebellum.
How many parts of the cerebellum are there?
The cerebellum consists of two major parts (Figure 5.2A). The cerebellar deep nuclei (or cerebellar nuclei) are the sole output structures of the cerebellum. These nuclei are encased by a highly convoluted sheet of tissue called the cerebellar cortex, which contains almost all of the neurons in the cerebellum.
What are the 5 lobes of the cerebrum?
Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into five lobes, four of which have the same name as the bone over them: the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the occipital lobe, and the temporal lobe. A fifth lobe, the insula or Island of Reil, lies deep within the lateral sulcus.
What are the functions of cerebrum short answer?
Your cerebrum is the largest part of your brain and handles conscious thoughts and actions. Different areas within your cerebrum also have different responsibilities like language, behavior, sensory processing and more.
What is the major function of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum is important for making postural adjustments in order to maintain balance. Through its input from vestibular receptors and proprioceptors, it modulates commands to motor neurons to compensate for shifts in body position or changes in load upon muscles.
What are the functional areas of cerebrum?
(9) There are three functional areas in cerebral cortex. viz., sensory, association and motor area.
What are some functions of the cerebrum quizlet?
Cerebrum (includes the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobe.) Major processing center of the brain. associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving. controls voluntary muscle movements.
What is the largest part of the brain?
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and it's what most people envision when thinking of the brain. It is divided into two halves, or hemispheres, and its outer layer has large folds and creases of tissue that give the brain its characteristic wrinkly appearance.
How does the cerebrum affect the way you think?
Brain injuries and diseases can affect how the cerebrum functions and, by extension, can impact the way you think, move your body, or feel sensations. This article will give you an introduction to the structure of the cerebrum and its functions plus common conditions that can affect this brain region.
What are the two types of brain tissue?
Types of Tissue. There are two types of brain tissue that make up the cerebrum. Gray matter, which is named for its gray-brown color, forms the outer surface of the brain and consists of the neurons' cell bodies. This outer layer of gray matter is the cerebral cortex and it is associated with most information processing, including language, ...
How is the cerebrum divided?
The cerebrum is divided lengthwise into two halves, separated by a deep crease called the longitudinal fissure. From side-to-side, a crease called the central sulcus divides each hemisphere in half again.
What is the cerebrum responsible for?
The cerebrum is responsible for processing sensory functions like vision, hearing, and touch; and it is involved in movement of your body. It's also the source of intellect and enables you to think, plan, read, hold memories, and process emotions—among many other tasks.
Which layer of the brain is responsible for most of the information processing?
This outer layer of gray matter is the cerebral cortex and it is associated with most information processing, including language, perception, and thought. White matter is an inner core of brain tissue that's mostly composed of axons, or nerve fibers, that are covered by myelin (a type of fat).
How many halves are there in the cerebral cortex?
The gray matter of the cerebral cortex is divided lengthwise into two halves, separated by a deep crease called the longitudinal fissure.
What is the middle layer of the cerebellum?
Purkinje cell layer. The middle layer (Purkinje cell layer) consists of a single layer of large pear-shaped Purkinje cells. Their cell bodies are largest in the cerebellum with unique and distinct appearance.
How is the cerebellum divided?
The cerebellum is divided into three subdivisions by two fissures that travel mediolaterally. The flocculonodular lobe is separated from the corpus cerebelli by the posterolateral fissure, while the primary fissure divides the corpus cerebelli into the anterior and posterior lobe.
How to remember the three layers of the cerebellar cortex?
' MPG ' or ' M other P lease G o' stands for: M olecular. P urkinje. G ranular. To remember the types of neurons present in the cerebellar cortex you can use the mnemonic ' G irls B ring G olden S tars in P ockets'.
What is the cerebellum in 2021?
Reading time: 9 minutes. Cerebellum (histological slide) The cerebellum, located dorsal to the pons and the medulla, is one of the primary structures of the hindbrain. It lies under the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. The cerebellum is an integral structure in transmitting sensory signals to ...
Why is the cerebellum similar to cauliflower?
This is due to the stemmed appearance of the white matter coated by the outer grey matter of the cortex.
Which layer of the cell contains granules and dendrites?
The outer molecular layer is synaptic and therefore contains many axons of granule cells and dendrites of the Purkinje cells with least density of cells. Superficially located stellate cells and basket cells are found in this layer. The stellate cells usually bear short dendrites in which make contact with small number of Purkinje cell dendrites. In comparison, basket cells have extensive dendritic processes that can make contact with much larger number of Purkinje cells. Both cells receive excitatory input from the parallel fibers and in turn exhibit inhibitory influence on the Purkinje cells
Which type of cell has short dendrites?
The stellate cells usually bear short dendrites in which make contact with small number of Purkinje cell dendrites. In comparison, basket cells have extensive dendritic processes that can make contact with much larger number of Purkinje cells. Both cells receive excitatory input from the parallel fibers and in turn exhibit inhibitory influence on the Purkinje cells
How many parts does the cerebellum have?
The cerebellum can also be divided in three parts based on both phylogenetic criteria (the evolutionary age of each part) and on functional criteria (the incoming and outgoing connections each part has and the role played in normal cerebellar function).
How many fibers does the cerebellum receive?
The cerebellum receives nearly 200 million input fibers; in contrast, the optic nerve is composed of a mere one million fibers. The unusual surface appearance of the cerebellum conceals the fact that the bulk of the structure is made up of a very tightly folded layer of gray matter, the cerebellar cortex.
How does the cerebellum differ from other brain areas?
As explained in more detail in the Function section, the cerebellum differs from most other brain areas in that the flow of neural signals through it is almost entirely unidirectional: there are virtually no backward connections between its neuronal elements. Thus the most logical way to describe the cellular structure is to begin with the inputs and follow the sequence of connections through to the outputs.
What is TA2 5788?
TA2. 5788. Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy. The anatomy of the cerebellum can be viewed at three levels. At the level of gross anatomy, the cerebellum consists of a tightly folded and crumpled layer of cortex, with white matter underneath, several deep nuclei embedded in the white matter, and a fluid-filled ventricle in the middle.
Which layer of the brain is responsible for motor learning?
This allows the circuitry of the cerebellar cortex to continuously adjust and fine-tune the output of the cerebellum, forming the basis of some types of motor learning and coordination. Each layer in the cerebellar cortex contains the various cell types that comprise this circuitry.
What is the upper part of the cerebellum?
Anatomists classify the cerebellum as part of the metencephalon, which also includes the pons; the metencephalon in turn is the upper part of the rhombencephalon or "hindbrain". Like the cerebral cortex, the cerebellum is divided into two hemispheres; it also contains a narrow midline zone called the vermis.
Where does the movement of the cerebellum occur?
The initiation of the movement is relayed to cerebellum via the corticoreticulocerebellar pathway. Those synapse ipsilaterally in the reticular formation, then via the inferior and middle peduncles into the cerebellar vermis.
What is the structure of a ray fin fish?
In ray-finned fishes the structure is somewhat different. The inner surfaces of the lateral and ventral regions of the cerebrum bulge up into the ventricles; these include both the basal nuclei and the various parts of the pallium and may be complex in structure, especially in teleosts. The dorsal surface of the cerebrum is membranous, and does not contain any nervous tissue.
What are the lobes of the cerebral cortex?
The lobes of the cerebral cortex include the frontal (blue), temporal (green), occipital (red), and parietal (yellow) lobes . The cerebellum (unlabeled) is not part of the telencephalon. Diagram depicting the main subdivisions of the embryonic vertebrate brain. Details.
What is the uppermost part of the cerebrum?
Above this, and forming the lateral part of the cerebrum, is the paleopallium, while the uppermost (or dorsal) part is referred to as the archipallium. The cerebrum remains largely devoted to olfactory sensation in these animals, in contrast to its much wider range of functions in amniotes.
What is the cerebrum?
In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the dorsal telencephalon, or pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia.
Where is the cerebrum located?
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Depending upon the position of the animal it lies either in front or on top of the brainstem. In humans, the cerebrum is the largest and best-developed of the five major divisions of the brain. The cerebrum is made up of the two cerebral hemispheres ...
What is the function of the cerebrum?
It functions as the center of sensory perception, memory, thoughts and judgement; the cerebrum also functions as the center of voluntary motor activities.
Which layer of the cerebrum is found only in mammals?
The cerebral cortex, the outer layer of grey matter of the cerebrum, is found only in mammals. In larger mammals, including humans, the surface of the cerebral cortex folds to create gyrus gyri (ridges) and sulci (furrows) which increase the surface area.

Anatomy of The Cerebrum
Function
- The role of the cerebrum is to coordinate and process sensory and motor functions required by the body, as well as to provide reasoning functions, process emotions, and contribute the unique personality traits that make each human being an individual. The cerebrum performs these functions using communication between nerve cells. Some of these processes, such as reasoni…
Associated Conditions
- Traumatic injury and an array of medical conditions can affect the cerebrum. Each can lead to many different types of problems with brain function depending on which regions of the cerebrum are affected or have the most damage. Conditions that affect the cerebrum may include: 1. Brain trauma occurs if a high-force accident shakes the brain inside the skull or if a projectile penetrat…
Tests
- Some brain conditionsare not diagnosed primarily through medical testing. For example, diagnosing Alzheimer's disease may rely on a person's individual and family medical histories and cognitive function testing. Other cerebral conditions may be diagnosed through different types of medical testing—alone, or in combination. Common types include: 1. Lumbar puncture (spinal ta…
Summary
- The cerebrum is a major part of the brain and its upper layer called the cerebral cortex is responsible for a range of complex functions. The cerebrum is the source of intellect and personality. It helps you move and understand what you see, hear, touch, and smell. Due to the cerebrum's many important roles, damage to any of its lobes from injuries...