
The eye is made up of three layers: the outer layer called the fibrous tunic, which consists of the sclera and the cornea; the middle layer responsible for nourishment, called the vascular tunic, which consists of the iris, the choroid
Choroid
The choroid, also known as the choroidea or choroid coat, is the vascular layer of the eye, containing connective tissues, and lying between the retina and the sclera. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear of the eye, while in the outlying areas it narrows to 0.1 mm. The choroid provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer layers of the retina. Along with the ciliary body and iris, the choroid f…
Photoreceptor cell
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photons, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential.
What are the three layers of the eye?
know the three layers of the eye. fibrous tunic, vascular tunic, retina. function of fibrous tunic is located. external layer of the eye. the sclera and the cornea make up the following structure. limbus or corneal sclera junction.
What are the 3 tunics of the eye?
The Tunics of the Eye F IG. 869– Horizontal section of the eyeball. From without inward the three tunics are: (1) A fibrous tunic, (Fig. 869) consisting of the sclera behind and the cornea in front; (2) a vascular pigmented tunic, comprising, from behind forward, the choroid, ciliary body, and iris; and (3) a nervous tunic, the retina.
What is the vascular tunic of the eye composed of?
the vascular tunic is composed from the following. choroid, the ciliary body and the iris. choroid. houses capillaries that supply nutrients and O2 to the retina and inner layer of the eye wall.
What is the fibrous tunic of the eye?
—The sclera and cornea (Fig. 869) form the fibrous tunic of the bulb of the eye; the sclera is opaque, and constitutes the posterior five-sixths of the tunic; the cornea is transparent, and forms the anterior sixth. The Sclera.
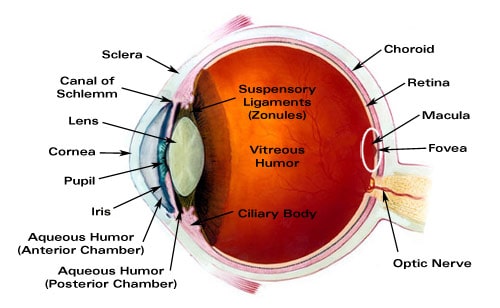
What are the 3 layers tunics of the eye?
The three tunics from the outside surface of the eye inward are, (1) the fibrous tunic (cornea and sclera), (2) the vascular tunic (iris, ciliary body, and choroid) and (3) the neuroectodermal (nervous) tunic (retina).
What are the three layers of the neural tunic of the eye wall quizlet?
The sclera, the choroid layer, and the retina.
What are the 3 layers the wall of the eye is made up of?
The wall of the eye is made up of three layers namely: The outer layer, which consists of the cornea and sclera. The middle layer, which consists of the iris, the ciliary body and the choroid. The inner layer, which consists of the retina.
What are the 3 layers of the wall of the eye and the function of each layer?
The eye is made up of three layers: the outer layer called the fibrous tunic, which consists of the sclera and the cornea; the middle layer responsible for nourishment, called the vascular tunic, which consists of the iris, the choroid, and the ciliary body; and the inner layer of photoreceptors and neurons called the ...
What are the three layers of eye tissue from superficial to deep?
The eyeball is composed of three principal layers: the fibrous tunic, the vascular tunic, and the neural tunic. The fibrous tunic is the outer layer, consisting of the sclera and cornea.
What are the internal layers of the eye quizlet?
Terms in this set (24)three layers of wall of eye. fibrous layer (outermost) ... fibrous layer. -outermost layer. ... sclera. white of the eye; bulk of fibrous layer;cornea. -anteriormost point of fibrous layer. ... Uvea. middle, vascular layer of wall of the eye.choroid. -posteriormost part of uvea. ... ciliary body. ... ciliary processes.More items...
What are the 3 major parts of the eye?
The anatomy of the eyeThe sclera, or white part of the eye, protects the eyeball.The pupil, or black dot at the centre of the eye, is an opening through which light can enter the eye.The iris, or coloured part of the eye, surrounds the pupil.More items...•
How many layers are there in eye?
three layersThe eye is composed of three layers, each of which has one or more very important components.
What is in the neural tunic?
Nervous tunic: The inner nervous tunic is the retina. The retina consists of an outer pigmented epithelium covered by nervous tissue (the neural layer) on the inside. The dark color of the pigmented epithelium absorbs light (as with the choroid) and stores vitamin A used by photoreceptor cells in the neural layer.
Which of the following is found on the neural tunic of the eye?
Macroscopic Anatomy of the EyeTunic of the EyeballLayer TypeStructurestunica fibrosa (fibrous tunic)fibrous layersclera, corneatunica vasculosa (vascular tunic)vascular layer (contains blood vessels)choroid, ciliary body, iristunica interna (neural tunic)internal layerretina, optic nerveJun 6, 2021
What structure is part of the inner tunic of the eye quizlet?
retina - Neural tunic of the eyeball; the innermost of the three tunics of the eye; contains photoreceptors (rods, cones) in the deepest layer, bipolar neurons, amacrine cells and horizontal cells in the middle layer, and ganglion cells in the superficial layer.
What are the three layers of the eye?
know the three layers of the eye. fibrous tunic, vascular tunic, retina. function of fibrous tunic is located. external layer of the eye. the sclera and the cornea make up the following structure. limbus or corneal sclera junction. corneas function. refract light coming into the cornea.
How many layers of the eye are there?
know the three layers of the eye.
Which layer of the retina provides vitamin A?
layers of the retina. pigmented layer and neural layer. pigmented layer does the following. provides vitamin A for the photoreceptor cell and light rays that pass are absorbed. neural layer. houses the photoreceptors converting them into nerve impulses. orginization of the neural layer.
How many layers are there in the cornea?
Structure (Fig. 871). —The cornea consists from before backward of four layers, viz.: (1) the corneal epithelium, continuous with that of the conjunctiva; (2) the substantia propria (3) the posterior elastic lamina; and (4) the endothelium of the anterior chamber.
What are the three tunics?
From without inward the three tunics are: (1) A fibrous tunic, (Fig. 869) consisting of the sclera behind and the cornea in front; (2) a vascular pigmented tunic, comprising, from behind forward, the choroid, ciliary body, and iris; and (3) a nervous tunic, the retina.
What is the arteria centralis retino?
The arteria centralis retinæ (Fig. 879) and its accompanying vein pierce the optic nerve, and enter the bulb of the eye through the porus opticus. The artery immediately bifurcates into an upper and a lower branch, and each of these again divides into a medial or nasal and a lateral or temporal branch, which at first run between the hyaloid membrane and the nervous layer; but they soon enter the latter, and pass forward, dividing dichotomously. From these branches a minute capillary plexus is given off, which does not extend beyond the inner nuclear layer. The macula receives two small branches (superior and inferior macular arteries) from the temporal branches and small twigs directly from the central artery; these do not, however, reach as far as the fovea centralis, which has no bloodvessels. The branches of the arteria centralis retinæ do not anastomose with each other—in other words they are terminal arteries. In the fetus, a small vessel, the arteria hyaloidea, passes forward as a continuation of the arteria centralis retinæ through the vitreous humor to the posterior surface of the capsule of the lens.
What is the vascular tunic?
872, 873, 874). —The vascular tunic of the eye is formed from behind forward by the choroid, the ciliary body, and the iris.
What is the cornea?
The Cornea. —The cornea is the projecting transparent part of the external tunic, and forms the anterior sixth of the surface of the bulb. It is almost circular in outline, occasionally a little broader in the transverse than in the vertical direction. It is convex anteriorly and projects like a dome in front of the sclera. Its degree of curvature varies in different individuals, and in the same individual at different periods of life, being more pronounced in youth than in advanced life. The cornea is dense and of uniform thickness throughout; its posterior surface is perfectly circular in outline, and exceeds the anterior surface slightly in diameter. Immediately in front of the sclero-corneal junction the cornea bulges inward as a thickened rim, and behind this there is a distinct furrow between the attachment of the iris and the sclero-corneal junction. This furrow has been named by Arthur Thomson (* 145 the sulcus circularis corneæ it is bounded externally by the trabecular tissue already described as forming the inner wall of the sinus venosus scleræ. Between this tissue and the anterior surface of the attached margin of the iris is an angular recess, named the iridial angle or filtration angle of the eye (Fig. 870). Immediately outside the filtration angle is a projecting rim of scleral tissue which appears in a meridional section as a small triangular area, termed the scleral spur. Its base is continuous with the inner surface of the sclera immediately to the outer side of the filtration angle and its apex is directed forward and inward. To the anterior sloping margin of this spur are attached the bundles of trabecular tissue just referred to; from its posterior margin the meridional fibers of the Ciliaris muscle arise.
How are lamelli connected?
The lamellæ are connected with each other by an interstitial cement substance, in which are spaces, the corneal spaces. These are stellate in shape and communicate with one another by numerous offsets. Each contains a cell, the corneal corpuscle, resembling in form the space in which it is lodged, but not entirely filling it.
What is the fibrous tunic?
The Fibrous Tunic (tunica fibrosa oculi). —The sclera and cornea (Fig. 869) form the fibrous tunic of the bulb of the eye; the sclera is opaque, and constitutes the posterior five-sixths of the tunic; the cornea is transparent, and forms the anterior sixth.
What are the three main structures of the eye?
The eye is made up of three layers: the outer layer called the fibrous tunic, which consists of the sclera and the cornea; the middle layer responsible for nourishment, called the vascular tunic, which consists of the iris, the choroid, and the ciliary body; and the inner layer of photoreceptors and neurons called ...
Which layer of the cornea is responsible for keeping the cornea clear?
The endothelium removes water from cornea, helping to keep the cornea clear. The middle layer of the cornea, between the two membranes is called the stroma and makes up 90% of the thickness of the cornea. From the cornea, light passes through the pupil. The amount of light allowed through the pupil is controlled by the iris, ...
What is the fluid in the eye called?
The volume between the cornea and the iris is known as the anterior chamber, while the volume between the iris and the lens is know as the posterior chamber, both chambers contain a fluid called aqueous humor . Aqueous humor is watery fluid produced by the ciliary body. It maintains pressure (called intraocular pressure or IOC) and provides nutrients to the lens and cornea. Aqueous humor is continually drained from the eye through the Canal of Schlemm. The greatest volume, forming about four-fifths of the eye, is found between the retina and the lens called the vitreous chamber. The vitreous chamber is filled with a thicker gel-like substance called vitreous humor which maintains the shape of the eye.
How many cones are there in the retina?
There are only about 6 million cones contained with in the retina, largely concentrated in the center of the retina called the fovea. There are three types of cones. Each type receives only a narrow band of light corresponding largely to a single color: red, green, or blue.
Which muscle controls the amount of light that passes through the pupil?
From the cornea, light passes through the pupil. The amount of light allowed through the pupil is controlled by the iris, the colored part of the eye. The iris has two muscles: the dilator muscle and the sphincter muscle. The dilator muscle opens the pupil allowing more light into the eye and the sphincter muscle closes the pupil, restricting light into the eye. The iris has the ability to change the pupil size from 2 millimeters to 8 millimeters.
How does light enter the eye?
Light enters the eye through the transparent, dome shaped cornea. The cornea consists of five distinct layers. The outermost layer is called the epithelium which rests on Bowman's Membrane. The epithelium has the ability to quickly regenerate while Bowman's Membrane provides a tough, difficult to penetrate barrier.
