Examples of Polysaccharides:
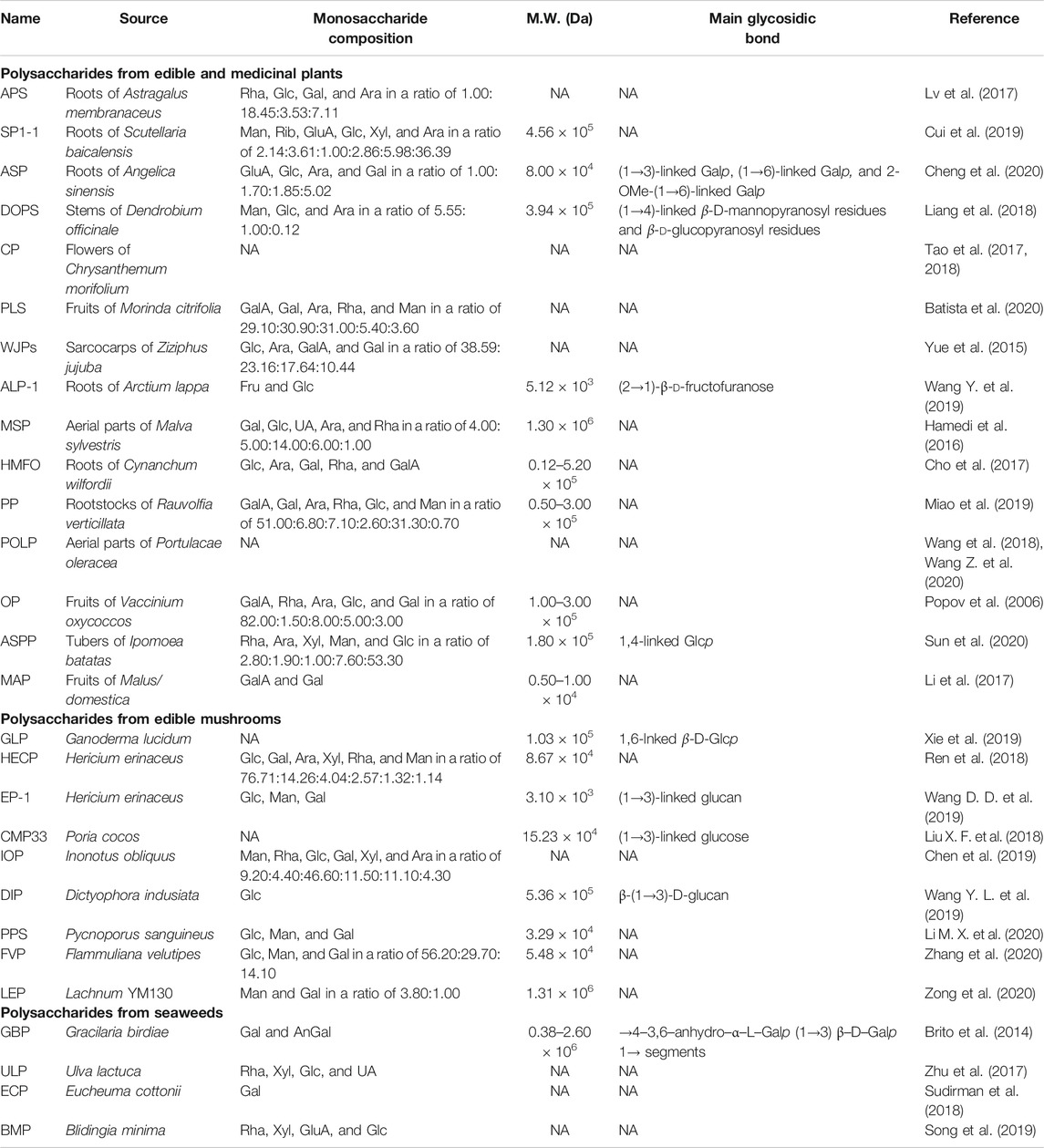
- 1. Starch An energy source from glucose units that are widely obtained from plants. Many starches are cereal grains, bread, pasta, pastries, cookies, potatoes, tapioca, wheat, oats, rye, barely, rice and yams to name a few. They are a polysaccharide energy source when digested in the body.
- 2. Cellulose A structural polysaccharide in plants that when consumed, it acts as a dietary fiber. ...
- 3. Glycogen
What are examples of three polysaccharides?
What are the 3 Types of Polysaccharides?
- Starch. Starch refers to a digestible energy source obtained from plants. ...
- Cellulose. Cellulose is a mostly-indigestible polysaccharide also composed of thousands of glucose molecules. ...
- Glycogen. Glycogen is a complex, multi-branched polysaccharide whose primary function is energy storage. ...
Which are examples of polysaccharides?
What are food examples of polysaccharides?
- Cereal foods, cornmeal, pretzels, flours, oats, instant noodles, pasta, rice.
- Potato, corn.
- Small amounts in other root vegetables and unripe fruit.
What are the examples of polysaccharide?
- Polysaccharides which are used for the purpose of energy storage will provide easy access to the monosaccharides which is constituted inside. ...
- Polysaccharides which are found in cell walls of plants are called structural polysaccharides. ...
- Storage polysaccharides are responsible for being converted to energy later for body functions. ...
What are examples of polysaccharide found in foods?
Examples of Polysaccharides: 1. Starch. An energy source from glucose units that are widely obtained from plants. Many starches are cereal grains, bread, pasta, pastries, cookies, potatoes, tapioca, wheat, oats, rye, barely, rice and yams to name a few. They are a polysaccharide energy source when digested in the body.
What are the 3 polysaccharide examples?
Polysaccharides– Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are examples of polysaccharides.
What's the most common polysaccharide?
The three most abundant polysaccharides are starch, glycogen, and cellulose. These three are referred to as homopolymers because each yields only one type of monosaccharide (glucose) after complete hydrolysis.
What are the 2 most common polysaccharides?
Cellulose and chitin are examples of structural polysaccharides. Cellulose is used in the cell walls of plants and other organisms and is said to be the most abundant organic molecule on Earth.
What are three polysaccharides important to humans?
Three major pectic polysaccharides are recognized; homogalacturonan (HG), rhamnogalacturonan-I (RG I), and rhamnogalacturonan-II (RG II) (Willats et al., 2006). HG comprises (1→4)-α-linked D-galacturonic acid units with occasional rhamnose residues, up to 200 units long.
What are 5 polysaccharides examples?
Examples of polysaccharides include cellulose, chitin, glycogen, starch, and hyaluronic acid.
How many types of polysaccharides are there?
Sometimes known as glycans, there are three common and principal types of polysaccharide, cellulose, starch and glycogen, all made by joining together molecules of glucose in different ways.
What are the 3 polysaccharides and how are they different?
Three important polysaccharides, starch, glycogen, and cellulose, are composed of glucose. Starch and glycogen serve as short-term energy stores in plants and animals, respectively. The glucose monomers are linked by α glycosidic bonds. Glycogen and starch are highly branched, as the diagram at right shows.
What are polysaccharides give two examples?
Starch, cellulose, gum and glycogen are polysaccharides.
Is starch is a polysaccharide?
Starch is a polysaccharide comprising glucose monomers joined in α 1,4 linkages. The simplest form of starch is the linear polymer amylose; amylopectin is the branched form.
Which are the polysaccharides are present in human body?
Polysaccharides that are well established in modern medical science include the mucilages and gums, glycosamine glycans and chitin, nutraceuticals and polysaccharide vaccines.
Is glucose a polysaccharide?
Glucose is not a polysaccharide. Glucose is a monosaccharide because it is just one sugar unit. Many polysaccharides such as starch are made of glucose units.
What is the most common polysaccharide in animals?
GlycogenGlycogen: It is the polysaccharide food reserve of animals, bacteria and fungi. Glycogen is popularly called animal starch. Glycogen is mainly stored inside liver (up to 0.1 kg) and muscles.
What is the most common polysaccharide in animals?
GlycogenGlycogen: It is the polysaccharide food reserve of animals, bacteria and fungi. Glycogen is popularly called animal starch. Glycogen is mainly stored inside liver (up to 0.1 kg) and muscles.
What disaccharides are the most common?
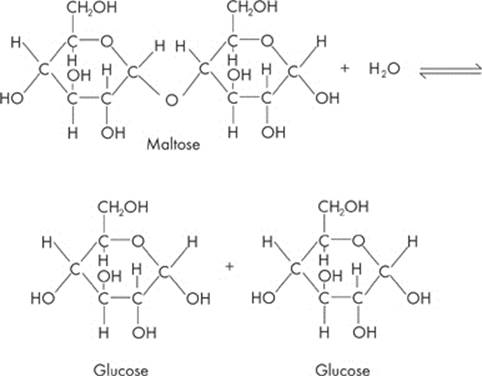
The most common disaccharide is sucrose which gives D -(+)- glucose and D-(-)- fructose on hydrolysis. Both the monosaccharides i.e. glucose and fructose are connected through the glycosidic linkage between alpha glucose and second carbon beta fructose.
What is a polysaccharide example?
Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are some examples of polysaccharides. In the food industry, the addition of polysaccharides acts as dietary fiber and stabilizers. Polysaccharides are also formed as products of bacteria, for example, in yogurt production).
Is the most common polysaccharide added to food products?
1. Starch. The polysaccharide starch is the main carbohydrate source for plant seeds and tubers, or vegetables that grow in the ground. While most vegetables are relatively low in carbohydrates per serving, starchy vegetables typically have 15 grams of carbohydrates per 1/2 cup cooked, per Johns Hopkins University.
What are the four examples of polysaccharides?
The four main examples of polysaccharides are cellulose, starch, glycogen and chitin. Starch and glycogen are storage polysaccharides, while cellul...
What are polysaccharides made of?
The linear or branched chains formed by the joining of monosaccharide units with glycosidic linkages are called polysaccharides.
What are the functions of polysaccharides?
a. They serve as storage of reserve food material in plants and animals. b. They form the structural components of the bodies of living organisms.
What are the food sources of polysaccharides?
a. Tubers- Potato, sweet potato, tapioca contain starch b. Seeds grains- such as rice, wheat, corn etc. contain starch c. Fruits- Pectin d. Gums an...
Are polysaccharides good or bad?
Polysaccharides are natural polymers found in plants, animals and microbes. They have high nutritive values and are essential for the good immune s...
What are structural polysaccharides?
Structural Polysaccharides: ADVERTISEMENTS: They are polysaccharides that take part in forming the structural frame work of the cell walls in plants and skeleton of animals. Structural polysaccharides are of two main types: chitin and cellulose. 1.
Where do mucopolysaccharides occur?
Isabgol). Mucopolysaccharides occur inside the plant cell walls, outside the cells or bodies of bacteria, blue-green algae and many aquatic plants, cementing layer between cells, inside body fluids, connective tissues and cartilages.
What is the component of starch?
Starch consists of two components, amylose and amylopectin (Fig. 9.7). Amylose is more soluble in water than amylopectin. In general, 20-30% of starch consists of amylose and the rest as amylopectin. Waxy starch of some varieties of Maize and other cereals consists entirely of amylopectin.
How are successive glucose units linked?
The successive glucose units are linked together by 1-4 α-linkages, that is, the link is between carbon atom 1 of one and carbon atom 4 of the other (Fig. 9.8). A molecule of water is lost during the formation of the linkage. A straight chain of amylose consists of 200-1000 glucose units.
What is waxy starch?
Waxy starch of some varieties of Maize and other cereals consists entirely of amylopectin. On the other hand, the starch of some varieties of Pea having wrinkled surface may have as much as 98% of amylose. Both amylose and amylopectin are formed by the condensation of α -D-glucose (pyranose forms).
How many units of glucose are in Amylopectin?
Amylopectin contains a large number of glucose units (2000-200,000). Besides a straight chain it bears several side chains which may be branched further.
How many glucose residues are in a glucose chain?
It has about 30,000 glucose residues and a molecular weight of about 4.8 million. Glucose residues are arranged in a highly branched bush like chains. There are two types of linkages 1-4 α -linkages in the straight part and 1-6 linkages in the area of branching. The straight part is helically twisted with each turn having six glucose units. The distance between two branching points is 10-14 glucose residues.
What are Polysaccharides?
The linear or branched chains formed by the joining of monosaccharide units with glycosidic linkages are called polysaccharides. So, polysaccharides are the polymers of monosaccharides. The monosaccharide units are linked with each other by glycosidic bonds.
What are the two main functions of polysaccharides?
Chitin is an example of a structural polysaccharide in animals. Thus, storage of energy and structure formation are the two main functions of polysaccharides.
What are the two main parts of a plant's storage polysaccharide?
Storage polysaccharides act as reserve food material while structural polysaccharides form the major part of structures such as cell walls, fibrous tissue and exoskeleton. Starch and glycogen are the storage polysaccharides in plants and animals, respectively.
What is the branched part of starch?
Amylopectin is the branched part of starch where α – D – glucose subunits are linked with each other by α – 1, 6 glycosidic linkage. vi. The branching appears approximately per 20 to 30 glucose residues in the chain. vii. Starch is hydrolyzed rapidly with amylase enzymes found in saliva and the small intestine. viii.
What are the components of a cell wall?
Bacterial cell walls and cell membranes contain a variety of polysaccharides and carbohydrate derivatives together called bacterial polysaccharides. Bacterial polysaccharides include peptidoglycans, lipopolysaccharides and exopolysaccharides. Peptidoglycan is the major constituent of the bacterial cell wall.
What are the bonds between polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are polymers of simple sugars linked with each other by covalent bonds called glycosidic bonds.
Where is starch hydrolyzed?
Starch is hydrolyzed rapidly with amylase enzymes found in saliva and the small intestine. viii. The amylose is naturally present in a coiled fashion. In such a state, it has spaces to accommodate the iodine molecules which form amylose-iodine complexes.
What are some examples of starch?
Starch food sources often are referred to as "starchy carbohydrates" and include foods like corn, potatoes and rice. Other examples include bread, cereal and pasta. These foods are the most common form of carbohydrates in your diet, comprising an estimated one-third of the foods you eat. The body breaks starches down into glucose, ...
What fruits and vegetables contain cellulose?
Many fruits and vegetables contain some aspect of cellulose, including in the skins of apples and pears, in the covering of whole grains like wheat bran and in plant leaves like spinach. Seeds and nuts also contain cellulose. Advertisement.
What is cellulose in food?
Cellulose is another polysaccharide commonly found in foods. Cellulose provides a protective covering and/or structure to fruits and vegetables and their seeds. It gives foods a crunchy texture and is undigestible in the body. However, cellulose does act as a source of dietary fiber, adding bulk to your stool and helping to maintain regular digestive processes. Many fruits and vegetables contain some aspect of cellulose, including in the skins of apples and pears, in the covering of whole grains like wheat bran and in plant leaves like spinach. Seeds and nuts also contain cellulose.
What is the prefix for carbohydrate?
Carbohydrates can be divided into several categories: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. Chemically speaking, the prefix before "saccharides" indicates how many saccharide chains are attached to the molecule. Polysaccharides have many chains and must be broken down into smaller portions before they can be fully digested.
Do polysaccharides taste sweet?
Although polysaccharides are a form of sugar, many of their food sources rarely taste sweet. Video of the Day.
What are the three main types of polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds. Three important polysaccharides, starch, glycogen, and cellulose, are composed of glucose. Starch and glycogen serve as short-term energy stores in plants and animals, respectively. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates composed of ten or up to several thousand monosaccharides arranged in chains. Think of these as simple sugars linked by glycosidic bonds. When it comes to nutrition, polysaccharides play a huge role in the body. Polysaccharides have two roles: some, like starch or glycogen, help store the energy we gain from consuming food. Others help with cell structure. The most common monosaccharides in polysaccharides are glucose, fructose, galactose and mannose.
What are some examples of polysaccharides?
Examples of Polysaccharides: 1. Starch. An energy source from glucose units that are widely obtained from plants. Many starches are cereal grains, bread, pasta, pastries, cookies, potatoes, tapioca, wheat, oats, rye, barely, rice and yams to name a few. They are a polysaccharide energy source when digested in the body.
How many polysaccharides are in a chain?
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates composed of ten or up to several thousand monosaccharides arranged in chains. Think of these as simple sugars linked by glycosidic bonds. When it comes to nutrition, polysaccharides play a huge role in the body.
Why are polysaccharides important?
Polysaccharides are critical when it comes to proper nutrition because they comprise the complex carbohydrates that, for many, serve as the body's primary energy source. Every bodily function relies on carbohydrates for energy. But, while the body can produce some energy, it's certainly not enough to sustain itself.
What is the most abundant organic molecule on earth?
2. Cellulose. A structural polysaccharide in plants that when consumed, it acts as a dietary fiber. Cellulose is the most abundant organic molecule on earth, since it is the main component of plant cell walls.
How many calories are in starch?
They are a source of energy; they provide about 4 Calories per gram.
Does polysaccharide help with fatigue?
But, while the body can produce some energy, it's certainly not enough to sustain itself. Polysaccharides can help a person overcome fatigue, support healthy blood pressure and blood sugar, encourage a positive mood, soothe irritation, support immune function, promote cardiovascular health, and even increase libido.
Which polysaccharide is the most abundant in nature?
Structure of cellulose, Polysaccharide most abundant in nature
Why are polysaccharides important?
In many cases polysaccharides are an important source of food for many organisms.
What is cellulose made of?
Cellulose is associated with hemicellulose, another polysaccharide made up of glucose and xylose bonds. Together with the polymer known as lignin, hemicellulose and cellulose form the compounds known as lignocellulosic compounds.
What is polysaccharide used for?
This polysaccharide is an important part of the human diet and is also consumed by many microorganisms associated with man's intestinal microbiota. It also finds many uses in the pharmaceutical and food industries.
What is reserve polysaccharide?
This polysaccharide is known as the reserve polysaccharide in animals, as it is a compound through which energy is stored in tissues and organs such as muscle and liver.
Is chitin a polymer?
Chitin is a polymer of N-acetylglucosamine with beta (1-4) bonds. Its structure is very similar to that of cellulose and is abundantly found in nature. The only polymer more abundant in the world than chitin is cellulose. Chitin is a highly insoluble polysaccharide, unlike its deacetylated form known as chitosan.
Where is starch found?
This polymer of glucose is highly consumed by mankind as it is easily found in different edible plants to which it serves as an energy reserve. Starch is easily found in foods such as corn, potatoes and rice among others .