Three well characterized pathways in primate vision (midget-parvocellular, parasol-magnocellular, bistratified-koniocellular) have been traced from the first synapse
Synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron. Some authors generalize this concept to include the communication from a neuron to any other cell type, such as to a motor cell, although such non-…
Retina
The retina is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which translates that image into electrical neural impulses to the brain to create visual perception, the retina serving a function analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera.
Thalamus
The thalamus is a large mass of gray matter in the dorsal part of the diencephalon of the brain with several functions such as relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex, and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness.
Full Answer
What are the four parts of the visual pathway?
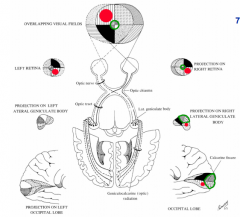
The retina, optic nerve, thalamic lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), and occipital lobe visual cortex comprise the main visual pathway. Each of these structures works in concert to modify the visual input, resulting in our visual impression of the outside world.
What is the pathway from retina to LGN to cortex?
Although the retina sends axons to many subcortical nuclei, only the pathway from the retina to LGN to cortex is critical to visual awareness. The LGN is a distinctively layered structure and is located at the posterior lateral margin of the dorsal thalamus ( Fig. 29.1 ).
What is the pathway of consciousness in the brain?
Conscious perception requires the visual information that passes through the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) in primates. Although the retina sends axons to many subcortical nuclei, only the pathway from the retina to LGN to cortex is critical to visual awareness.
How does the pathway of the eye work?
Ideally, the pathway is smooth and efficient, with predictable curves and directions leading from your optic nerve to your occipital lobe’s primary visual cortex. But sometimes that pathway is interrupted—and the driver has to adjust. Retina: This is your eye’s on-ramp.

What is the correct pathway from the retina to the visual cortex?
The optic nerve is the pathway that carries the nerve impulses from each eye to the various structures in the brain that analyze these visual signals.
What is the correct order of the vision pathway?
From the cornea, the light passes through the pupil. The iris, or the colored part of your eye, controls the amount of light passing through. From there, it then hits the lens. This is the clear structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina.
What are the 3 parts of the visual system?
The visual system comprises the sensory organ (the eye) and parts of the central nervous system (the retina containing photoreceptor cells, the optic nerve, the optic tract and the visual cortex) which gives organisms the sense of sight (the ability to detect and process visible light) as well as enabling the formation ...
What is the pathway from the lateral geniculate nucleus to the primary visual cortex of the occipital lobe?
Neurons of the LGN send their axons through the optic radiation, a direct pathway to the primary visual cortex.
What is the correct pathway from the retina to the visual cortex quizlet?
Solutions. The visual pathway consists of the retina, optic nerves, optic chiasm, optic tracts, lateral geniculate bodies, optic radiations, and visual cortex.
What are the steps of the visual pathway quizlet?
Terms in this set (10)Light enters the eye at the cornea where light waves are refracted.Eye fluids of the anterior chamber and lens refract light further.Light waves are focused through vitreous humor onto choroid layer of retina. ... As light waves are absorbed by choroid layer, rods and cones are stimulated by light.More items...
In what order does visual information pass through the retina quizlet?
Light passes through the retina in this order: ganglion cells > bipolar cells > cones.
What is the visual pathway?
The visual pathway refers to the anatomical structures responsible for the conversion of light energy into electrical action potentials that can be interpreted by the brain. It begins at the retina and terminates at the primary visual cortex (with several intercortical tracts).
Which type of sensory information travels from the retina through the thalamus to the visual cortex?
The correct answer is a. visual. This is somewhat obvious because the visual information goes to the visual cortex. They both are named for the sense of vision.
What is the correct pathway that light travels through the eye from the external world to the brain?
Light passes through the front of the eye (cornea) to the lens. The cornea and the lens help to focus the light rays onto the back of the eye (retina). The cells in the retina absorb and convert the light to electrochemical impulses which are transferred along the optic nerve and then to the brain.
Which of the following is the correct pathway for visual information Group of answer choices?
The correct answer is d. retina, feature detectors, optic chiasm, visual cortex.
What is the pathway and where pathway?
In the currently prevailing view, the different maps are organised hierarchically into two major pathways, one involved in recognition and memory (the ventral stream or 'what' pathway) and the other in the programming of action (the dorsal stream or 'where' pathway).
Which is the first order neuron in the vision pathway?
bipolar cellsIn summary, the visual pathway involves three consecutive neurons: The first neuron represents the bipolar cells of the retina and receives visual information from the neuroepithelial cell of the retina (e.g. rods and cones). The second neuron corresponds to the ganglion cell of the retina.
What are the first order neurons in the visual pathway quizlet?
Rods and cones synapse with the dendrites of bipolar cells, the first-order neurons of the visual pathway. They in turn synapse with the ganglion cells.
What is the pathway and where pathway?
In the currently prevailing view, the different maps are organised hierarchically into two major pathways, one involved in recognition and memory (the ventral stream or 'what' pathway) and the other in the programming of action (the dorsal stream or 'where' pathway).
How does the visual pathway work?
The visual pathway starts with light as its stimulus. As light enters the eye, photoreceptors in the retina convert the stimulus into an electrical potential. There, the potential is transmitted from retinal photoreceptors to bipolar neurons, which form the large optic nerve (cranial nerve II).
What is the pathway to the primary visual cortex?
The vast majority of nerve fibers in the optic tract project to the dorsal thalamic lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). The principal relay along the...
How does the brain process visual information?
The journey begins with the sight and ends with the brain. The ganglion cell axons leave the retina to create the optic nerve, which goes to the th...
Which is the correct sequence for the visual pathway from the eye to the brain?
The retina, optic nerve, thalamic lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), and occipital lobe visual cortex comprise the main visual pathway. Each of thes...
Which level of the visual pathway allows preservation of relative spatial relationships?
retinotopically ; at each level organization parallels that of the retina, stimuli that excite adjacent neurons in the retina also excite the adjacent neurons at subsequent levels of the visual pathway; allows preservation of relative spatial relationships
Which layer of the visual cortex is V1?
V1, striate cortex; both magnocellular and parvocellular neurons of the LGN project to cortical layer IV of the primary visual cortex
Which part of the brain is grouped into functional vertical columns?
visual information flows from neurons with simple receptive fields to neurons with more complex fields, neurons in the striate cortex are grouped into functional vertical columns
Which neuron is monocular?
edge detectors; visual cortical neurons with rectangular receptive fields that respond maximally to orientation; rectangular, "on" and "off" regions, orientation and location sensitive, all are monocular
How many receptive fields does each neuron have?
each neuron has a receptive field in one eye only
Which neuron has a rectangular receptive field?
visual cortical neurons with large rectangular receptive fields that respond maximally to straight-edge stimuli in a certain orientation in any part of their receptive field; rectangular, larger receptive fields, do not have static "on" and "off" regions, not location sensitive, motion sensitive, many are binocular
How many parallel channels are there for visual information?
two parallel channels exist for communication of visual information through each lateral geniculate nucleus
What is the pathway that a primates use to gain visual awareness?
Conscious perception requires the visual information that passes through the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus ( LGN) in primates. Although the retina sends axons to many subcortical nuclei, only the pathway from the retina to LGN to cortex is critical to visual awareness. The LGN is a distinctively layered structure and is located at ...
Where does the efferent axonal output from the LGN end?
In primates the bulk of the efferent axonal output from the LGN terminates within the primary visual cortex and the visual sector of the thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN). Although not documented in primates, in cats the projection to the equivalent of the visual sector of the TRN comes from collateral branches of LGN relay cell axons not from a separate projection that goes solely to this thalamic nucleus. A smaller efferent projection from the LGN also has been reported to terminate in several extrastriate visual areas. The most well documented of these projections is to the middle temporal area (MT). This projection appears to originate from K LGN cells, based upon double labeling studies using retrograde tracers and immunocytochemistry for calbindin, and arises from K cells that do not send collateral projections to V1. Although this projection involves only about 1 percent of LGN cells, it has been implicated in the residual vision referred to as “blindsight” in patients that have lost their primary visual cortex ( Box 29.1 ).
How many layers of cells are there in a human?
In humans and some other primates, each P layer can split into two or more layers in the portion of the LGN that represents central vision (∼2–17 degrees). The normal human LGN can contain as few as two or as many as six P layers.
What are the layers of the nucleus of a monkey?
At this cross-sectional level of the nucleus there are four P layers, two M layers, and six K layers. Scale bar = 500 µm.
What is the purpose of the chapter on LGN?
The purpose of this chapter is to illuminate the structure and function of the LGN by first reviewing LGN anatomy and physiology and then current controversies over signal processing. The field has moved from static descriptions of LGN cell receptive field properties to dynamic descriptions that take into account eye movements, motor planning, arousal level, attention and possibly even more complex information concerning visual memories. In the following two sections, we describe the basic architecture, connections and neurochemistry of the LGN. The next four sections consider the LGN in a functional context beginning with the basics of signal processing in section four. Then we consider the potential functional impact of attention, motor planning, and binocular rivalry. The final section summarizes key points.
Why is the LGN important?
The most reasonable explanation is that the main role of the LGN is to regulate the flow and strength of visual signals sent to V1.
Which layer of the eye receives monocular input?
Each layer receives monocular input from the retina and only those layers receiving input from the contralateral eye (nasal retina) represent the entire contralateral visual hemifield since LGN layers receiving input from the ipsilateral eye (temporal retina) cannot represent the monocular portion of the hemifield.
