Each cranial fossa is named from the front to the back as follows:
- Anterior cranial fossa (ACF)
- Middle cranial fossa (MCF)
- Posterior cranial fossa (PCF).
Which takes up more space the dorsal or ventral cavities?
Body Cavities The cavities, or spaces, of the body contain the internal organs, or viscera. The two main cavities are called the ventral and dorsal cavities. The ventral is the larger cavity and is subdivided into two parts (thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities) by the diaphragm, a dome-shaped respiratory muscle.
Which of these cavities contains the eye structures?
The orbit is the bony cavity that contains the eyeball, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels, as well as the structures that produce and drain tears.
Which of these body cavities is located on the front side of the body?
The ventral cavity is at the anterior, or front, of the trunk. Organs contained within this body cavity include the lungs, heart, stomach, intestines, and reproductive organs.
Which of these cavities contains the lungs and heart?
Thoracic. The thoracic cavity is the anterior ventral body cavity found within the rib cage in the torso. It houses the primary organs of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, such as the heart and lungs, but also includes organs from other systems, such as the esophagus and the thymus gland.
What is found in the dorsal cavity?
The dorsal cavity contains the spinal column, central nervous system (i.e., brain and spinal cord), and meninges (i.e., tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord). On the anterior side of the body, the ventral cavity is made up of the thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, and pelvic cavity.
What does the thoracic cavity contain?
[2] The thoracic cavity contains organs and tissues that function in the respiratory (lungs, bronchi, trachea, pleura), cardiovascular (heart, pericardium, great vessels, lymphatics), nervous (vagus nerve, sympathetic chain, phrenic nerve, recurrent laryngeal nerve), immune (thymus) and digestive (esophagus) systems.
What is the skull cavity called?
cranial cavityThe cranial cavity, also known as intracranial space, is the space within the skull that accommodates the brain. The skull minus the mandible is called the cranium.
What are the cavities spaces in the brain?
The ventricles of the brain are a communicating network of cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and located within the brain parenchyma. The ventricular system is composed of 2 lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, the cerebral aqueduct, and the fourth ventricle (see the images below).
How many types of cavities are there?
The three types of cavities are shown here. Smooth surface cavities occur on the smooth sides of your teeth, while root cavities develop on the surface over the roots. Pit and fissure cavities occur on the chewing surface of your teeth.
In which 3 cavities are the lungs located?
The pleural cavity is lined by the pleura that also surround the pair of lungs. Thus, the body cavities in which the lungs are located are pleural, ventral, and thoracic.
What body cavity provides the least protection?
the abdominal cavityThe least protective cavity is the abdominal cavity, in which the organs are held within a membranous structure called the peritoneum.
How many major body cavities are there?
two main body cavitiesHumans. The human body has two main body cavities. The first, the ventral cavity, is a large cavity which sits ventrally to the spine and includes all the organs from your pelvis to your throat. This cavity is the true coelom, as it forms during human embryogenesis from the mesoderm.
What is found in the anterior cavity of the eyeball quizlet?
The anterior chamber is filled with the aqueous humor. This jelly-like substance helps maintain pressure within the eye and holds the retina in place against the posterior wall of the eyeball.
What are the parts of cavity?
Human body cavities The dorsal (posterior) cavity and the ventral (anterior) cavity are the largest body compartments. The dorsal body cavity includes the cranial cavity, enclosed by the skull and contains the brain, and the spinal cavity, enclosed by the spine, and contains the spinal cord.
Which of the following is located in the posterior cavity of the eyeball?
The posterior segment or posterior cavity is the back two-thirds of the eye that includes the anterior hyaloid membrane and all of the optical structures behind it: the vitreous humor, retina, choroid, and optic nerve.
Which of the following fills the posterior cavity of the eye?
Fluid fills most of the inside of the eye. The chambers in front of the lens (both the anterior and posterior chambers) are filled with a clear, watery fluid called aqueous humour. The large space behind the lens (the vitreous chamber) contains a thick, gel-like fluid called vitreous humour or vitreous gel.
What are the parts of the skull?
Parts of the Skull. The skull consists of the rounded brain case that houses the brain and the facial bones that form the upper and lower jaws, nose, orbits, and other facial structures. Watch this video to view a rotating and exploded skull, with color-coded bones.
How many bones are there in the skull?
In the adult, the skull consists of 22 individual bones, 21 of which are immobile and united into a single unit. The 22nd bone is the mandible (lower jaw), which is the only moveable bone of the skull. Figure 1. Parts of the Skull.
How many cranial fossae are there?
Inside the skull, the floor of the cranial cavity is subdivided into three cranial fossae (spaces), which increase in depth from anterior to posterior (see Figure 4, Figure 6b, and Figure 9). Since the brain occupies these areas, the shape of each conforms to the shape of the brain regions that it contains. Each cranial fossa has anterior and posterior boundaries and is divided at the midline into right and left areas by a significant bony structure or opening.
Which conchae are the largest?
The right and left inferior nasal conchae form a curved bony plate that projects into the nasal cavity space from the lower lateral wall (see Figure 11). The inferior concha is the largest of the nasal conchae and can easily be seen when looking into the anterior opening of the nasal cavity.
Where are the paranasal sinuses located?
The paranasal sinuses are named for the skull bone that each occupies. The frontal sinus is located just above the eyebrows, within the frontal bone (see Figure 15). This irregular space may be divided at the midline into bilateral spaces, or these may be fused into a single sinus space. The frontal sinus is the most anterior of the paranasal sinuses. The largest sinus is the maxillary sinus. These are paired and located within the right and left maxillary bones, where they occupy the area just below the orbits. The maxillary sinuses are most commonly involved during sinus infections. Because their connection to the nasal cavity is located high on their medial wall, they are difficult to drain. The sphenoid sinus is a single, midline sinus. It is located within the body of the sphenoid bone, just anterior and inferior to the sella turcica, thus making it the most posterior of the paranasal sinuses. The lateral aspects of the ethmoid bone contain multiple small spaces separated by very thin bony walls. Each of these spaces is called an ethmoid air cell. These are located on both sides of the ethmoid bone, between the upper nasal cavity and medial orbit, just behind the superior nasal conchae.
Where is the superior nasal concha?
The superior nasal concha is located just lateral to the perpendicular plate, in the upper nasal cavity.
What is the anterior skull?
The anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the bony support for the eyes and structures of the face. This view of the skull is dominated by the openings of the orbits and the nasal cavity. Also seen are the upper and lower jaws, with their respective teeth (Figure 2).
What is the name of the hair that helps the mucus to move through the nasal cavity?
Both air and mucus flow through your sinuses and drain into your nose, through tiny openings called ostia (or singular, ostium). Little hairs called cilia help the mucus move through the sinus cavities.
Where are the ethmoid sinuses?
There are three small pairs of the ethmoid sinuses. The sphenoid sinuses are behind the eyes, deeper into your skull. These sinuses collectively are called the paranasal sinuses. The name sinus comes from the Latin word sinus, which means a bay, a curve, or a hollow cavity.
What is the hair that moves mucus through the sinuses?
Little hairs called cilia help the mucus move through the sinus cavities. The mucus from the sinuses drains into your nasal passages and then down the back of your throat to be swallowed.
How many people have sinus infections?
Sinus infections are common and can be a major health problem. According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (ACAAI), 31 million people in the United States have sinus infections at a given time. You’re at higher risk for sinusitis if you: have allergies. smoke.
How to get rid of sinus headaches?
Other tips to manage symptoms: Take over-the-counter (OTC) pain medication to ease headaches. Try OTC drugs such as guaifenesin ( Mucinex) that thins your mucus, which can help to pass the mucus and lessen congestion. Try acupuncture; there’s some evidence that it’s useful for sinus-related symptoms.
What is the function of the sinuses?
The sinuses are part of your nose and respiratory system. They connect to your nasal passages in a complex network of air flow and drainage passages. As you breathe in air through your nose and mouth, it moves through the sinus passages.
How to identify the skull?
By the end of this section, you will be able to: 1 List and identify the bones of the brain case and face 2 Locate the major suture lines of the skull and name the bones associated with each 3 Locate and define the boundaries of the anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossae, the temporal fossa, and infratemporal fossa 4 Define the paranasal sinuses and identify the location of each 5 Name the bones that make up the walls of the orbit and identify the openings associated with the orbit 6 Identify the bones and structures that form the nasal septum and nasal conchae, and locate the hyoid bone 7 Identify the bony openings of the skull
Which bone forms the upper lateral side of the skull?
The parietal bone forms most of the upper lateral side of the skull (see Figure 7.5 ). These are paired bones, with the right and left parietal bones joining together at the top of the skull. Each parietal bone is also bounded anteriorly by the frontal bone, inferiorly by the temporal bone, and posteriorly by the occipital bone.
How many cranial fossae are there?
Inside the skull, the floor of the cranial cavity is subdivided into three cranial fossae (spaces), which increase in depth from anterior to posterior (see Figure 7.6, Figure 7.8 b, and Figure 7.11 ). Since the brain occupies these areas, the shape of each conforms to the shape of the brain regions that it contains. Each cranial fossa has anterior and posterior boundaries and is divided at the midline into right and left areas by a significant bony structure or opening.
Which bone is the largest of the conchae?
The largest of the conchae is the inferior nasal concha, which is an independent bone of the skull. The middle concha and the superior conchae, which is the smallest, are both formed by the ethmoid bone. When looking into the anterior nasal opening of the skull, only the inferior and middle conchae can be seen.
Where is the anterior nasal septum?
The anterior nasal septum is formed by the septal cartilage, a flexible plate that fills in the gap between the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid and vomer bones. This cartilage also extends outward into the nose where it separates the right and left nostrils. The septal cartilage is not found in the dry skull.
Which conchae are the largest?
The right and left inferior nasal conchae form a curved bony plate that projects into the nasal cavity space from the lower lateral wall (see Figure 7.13 ). The inferior concha is the largest of the nasal conchae and can easily be seen when looking into the anterior opening of the nasal cavity.
How many bones are in the brain?
The brain case consists of eight bones.
How many bones are in the cranial base?
Cranial base – comprised of six bones: frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, occipital, parietal and temporal. These bones articulate with the 1st cervical vertebra (atlas), the facial bones, and the mandible (jaw). By TeachMeSeries Ltd (2021) Fig 1 – Bones of the calvarium and cranial base.
Which bones are the smallest?
Zygomatic (2) – forms the cheek bones of the face and articulates with the frontal, sphenoid, temporal and maxilla bones. Lacrimal (2) – the smallest bones of the face. They form part of the medial wall of the orbit. Nasal (2) – two slender bones that are located at the bridge of the nose.
What is the pterion of cranial fracture?
When considering cranial fractures, one area of clinical importance is the pterion – a H-shaped junction between the temporal, parietal, frontal, and sphenoid bones.
Which part of the mouth is the Palatine?
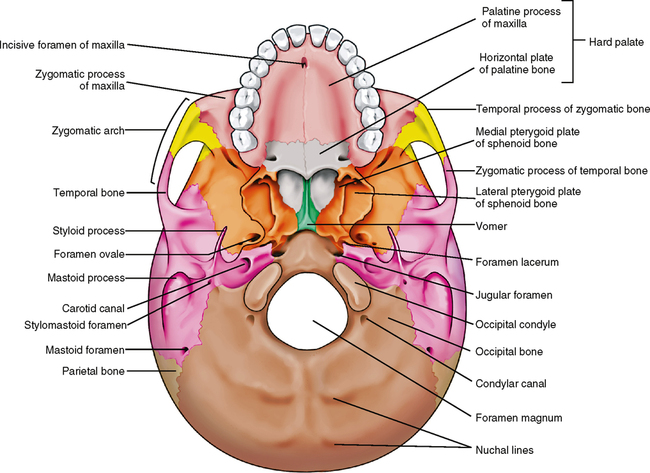
Palatine (2) – situated at the rear of oral cavity and forms part of the hard palate. Maxilla (2) – comprises part of the upper jaw and hard palate. Vomer – forms the posterior aspect of the nasal septum. Mandible (jaw) – articulates with the base of the cranium at the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
What is the cranium?
The cranium (also known as the neurocranium) is formed by the superior aspect of the skull. It encloses and protects the brain, meninges, and cerebral vasculature. Anatomically, the cranium can be subdivided into a roof and a base: Cranial roof – comprised of the frontal, occipital and two parietal bones.
What bones are found in the face?
The vomer, palatine and inferior conchae bone s lie deep within the face. caption] [start-clinical] Clinical Relevance: Facial Fractures. Fractures of the facial skeleton are relatively common and most frequently result from road traffic collisions, fist fights, and falls.
How many bones are there in the face?
It consists of 14 bones, which fuse to house the orbits of the eyes, the nasal and oral cavities, and the sinuses. The frontal bone, typically a bone of the calvaria, is sometimes included as part of the facial skeleton. The facial bones are:
