What are the steps of hemostasis quizlet? Hemostasis
Hemostasis
Hemostasis or haemostasis is a process to prevent and stop bleeding, meaning to keep blood within a damaged blood vessel. It is the first stage of wound healing. This involves coagulation, blood changing from a liquid to a gel. Intact blood vessels are central to moderating blood's tendency to form clots. The endothelial cells of intact vessels prevent blood clotting with a heparin-like molecule an…
Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, in particular the large arteries and small arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels. The process is particularly important in staunching hemorrhage and acute blood loss. When blood vessels constrict, the flow of blood is restricted or decre…
What are the 3 steps of hemostasis?
Hemostasis has three major steps: 1) vasoconstriction, 2) temporary blockage of a break by a platelet plug, and 3) blood coagulation, or formation of a fibrin clot. These processes seal the hole until tissues are repaired. PROCESS. Hemostasis occurs when blood is present outside of the body or blood vessels.
What is hemostasis and how is it accomplished?
What is hemostasis, and List the three mechanisms by which hemostasis is accomplished. Hemostasis is the cessation of bleeding. 1. rapid constriction of the injured vessel to reduce flow. 2. Clumping of platlets to plug injured surface. 3.Clot formation. 2) Describe the first event in platelet aggregation.
What are the steps in the process of coagulation?
Terms in this set (5) Step 1: Vascular Spasms blood vessels constrict to slow blood loss Step 2: Platelet plug formation platelets stick together to plug break Step 3: Coagulation Enzymatic process requiring clotting factors and Ca2+ Step 4: Clot retraction and repair
What is the second stage of hemostasis?
The second stage of hemostasis involves platelets that move throughout the blood. When the platelets find an exposed area or an injury, they begin to form what is called a platelet plug. The platelet plug formation is activated by a glycoprotein called the Von Willebrand factor (vWF), which are found in the body’s blood plasma.

What are the 3 steps of hemostasis?
1) Constriction of the blood vessel. 2) Formation of a temporary “platelet plug." 3) Activation of the coagulation cascade.
What are the three types of hemostasis?
Hemostasis may be categorized into primary (platelet plug formation), secondary (formation of a stabilized fibrin clot through the coagulation cascade), and tertiary (formation of plasmin for breakdown of fibrin via fibrinolysis) concurrent processes.
What is hemostasis and what are the 3 main parts of hemostasis?
Hemostasis is the physiological process by which bleeding ceases. Hemostasis involves three basic steps: vascular spasm, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation, in which clotting factors promote the formation of a fibrin clot. Fibrinolysis is the process in which a clot is degraded in a healing vessel.
What are the stages of homeostasis quizlet?
Terms in this set (16) Vessel Spasm. ... Formation of Platelet Plug. ... Blood Coagulation. ... Clot Retraction. ... Clot Dissolution (Lysis)
What is the process of hemostasis?
What is hemostasis? Hemostasis is your body's normal reaction to an injury that causes bleeding. This reaction stops bleeding and allows your body to start repairs on the injury. This capability is essential to keep you alive, particularly with significant injuries.
What is the correct order of hemostasis quizlet?
Terms in this set (22) Hemostasis is the natural process that stops blood loss when an injury occurs.It involves three steps: (1) vascular spasm (vasoconstriction); (2) platelet plug formation; and (3) coagulation.
What is the first step in hemostasis quizlet?
The first step in hemostasis is: platelet plug formation.
What is hemostasis quizlet?
hemostasis. refers to the collection of events that STOPS the bleeding when a BLOOD VESSEL is damaged.
Which of the following lists the steps of hemostasis in the correct sequence?
Hemostasis includes three steps that occur in a rapid sequence: (1) vascular spasm, or vasoconstriction, a brief and intense contraction of blood vessels; (2) formation of a platelet plug; and (3) blood clotting or coagulation, which reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin mesh that acts as a glue to hold the clot ...
What are the steps of homeostasis?
Adjustment of physiological systems within the body is called homeostatic regulation, which involves three parts or mechanisms: (1) the receptor, (2) the control center, and (3) the effector. The receptor receives information that something in the environment is changing.
What are the 4 steps of homeostasis?
Homeostasis is normally maintained in the human body by an extremely complex balancing act. Regardless of the variable being kept within its normal range, maintaining homeostasis requires at least four interacting components: stimulus, sensor, control center, and effector.
What are the four steps of hemostasis quizlet?
MatchInitiation and formation of the platelet plug.Extension of the clotting process by the Coagulation Cascade.Termination of clotting by antithrombotic control mechanisms.Removal of the clot by fibrinolysis.
What is primary and secondary hemostasis?
Primary hemostasis is a procoagulation clot forming process associated with the initiation and formation of the platelet plug. Secondary hemostasis also a procoagulation clot forming process and it is associated with the propagation of the clotting process via the intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation cascades.
What is primary hemostasis?
Primary hemostasis serves to immediately limit bleeding through the formation of a loose platelet plug. Platelets play a key role in the rapid response to blood vessel injury by: Adhering to the endothelial wall at the site of injury. Releasing potent anticoagulant compounds. Aggregating to form a plug.
What is normal hemostasis?
Hemostasis is the physiologic mechanism that stems bleeding after injury to the vasculature. Normal hemostasis depends on both cellular components and soluble plasma proteins. Circulating platelets adhere and aggregate at sites of blood vessel injury.
What is the difference between homeostasis and haemostasis?
Hemostasis and homeostasis are two different things. Hemostasis is the stopping of bleeding from a wound, which is often the first stage of wound healing. Homeostasis is the body's state of balance, or it's tendency to maintain a constant, stable state in the body.
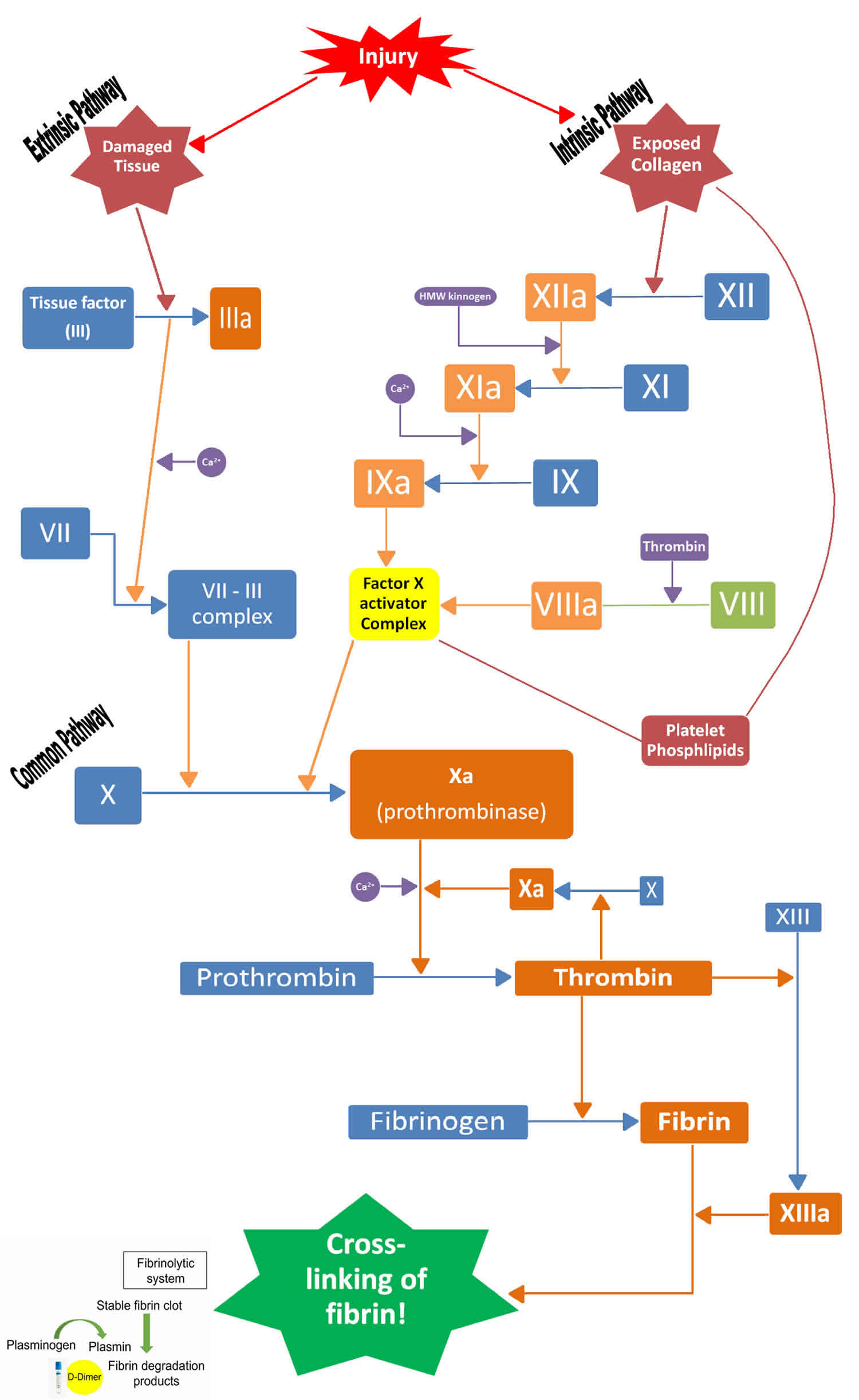
What is the process of coagulation?
Coagulation involves a complex cascade in which a fibrin mesh is cleaved from fibrinogen.
What is the reflex in which blood vessels narrow to increase blood pressure?
Vasoconstriction is a reflex in which blood vessels narrow to increase blood pressure.
What is a coagulation screening test?
a coagulation screening test used to monitor oral anticoagulant therapy; evaluates the function of the extrinsic and common pathways for coagulation abnormalities; also used to monitor the clotting times of patients using warfarin
What is the name of the drug that is administered orally to prevent blood clotting?
Coumadin. an anticougalant drug that is administered orally to prevent blood clotting. embolus. a mass of blood or foreign matter in circulation. hemmorhage. uncontrolled bleeding. hemostasis. the process of stopping bleeding. heparain.
What substances are released from platelets?
The substances released include: ADP, a stimulant for platelet aggregation; vasoactive amines; and thromboxane A2, a metabolite of the prostaglandins , which stimulates secretion of ADP from the dense granules. Thus platelet aggregation is enhanced.
What catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin?
Our good friend thrombin catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. Thrombin cleaves 4 of the six chains. This removes an A peptide from each alpha chain and a B peptide from each of the 2 Beta chains. The
What are platelets made of?
Platelets are disk shaped cells derived from megakarocytes in the bone mar row. Platlets do not have nuclei and contain distinctive granules called dense bodies.
Where are clotting proteins synthesized?
Clotting proteins are synthesiezed in the liver as preproproteins and are exported into general circulation. Most clotting proteins are glycoproteins.
Which factors are carboxylated in a vitamin K dependent reaction?
As factors 7,9 , 10 and 2 (prothrombin) traverse the ER they are carboxylated in a vitamin k dependent reaction by vitamin k dependent carboxylase. Vitamin k is a cofactor for this enzyme which carboxylates peptide bound glutamyl residues to gamma carboxyglutamyl (Gla) residues.
Which factor is activated by kininogen kallikrein?
Factor 9a and it's cofactor 8a form a complex on the membrane which increases factor 10a production 50-100 fold. Also factor 12 activation occurs by kininogen kallikrein it activates factors 9,11,8 and ultimately factor 10. Blood contact with glass causes activation of factor 12 so blood must be drawn with calcium chealators.
What are the steps of hemostasis?
Hemostasis has three major steps: 1) vasoconstriction, 2) temporary blockage of a break by a platelet plug, and 3) blood coagulation, or formation of a fibrin clot. These processes seal the hole until tissues are repaired.
How does hemostasis occur?
Hemostasis occurs when blood is present outside of the body or blood vessels. It is the instinctive response for the body to stop bleeding and loss of blood. During hemostasis three steps occur in a rapid sequence. Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug formation, platelets stick together to form a temporary seal to cover the break in the vessel wall. The third and last step is called coagulation or blood clotting. Coagulation reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin threads that act as a “molecular glue”. Platelets are a large factor in the hemostatic process. They allow for the creation of the “platelet plug” that forms almost directly after a blood vessel has been ruptured. Within seconds of a blood vessel’s epithelial wall being disrupted platelets begin to adhere to the sub-endotheliumsurface. It takes approximately sixty seconds until the first fibrin strands begin to intersperse among the wound. After several minutes the platelet plug is completely formed by fibrin. Hemostasis is maintained in the body via three mechanisms:
What is the role of coagulation in hemostatic hemostasis?
Coagulation reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin threads that act as a “molecular glue”. Platelets are a large factor in the hemostatic process. They allow for the creation of the “platelet plug” that forms almost directly after a blood vessel has been ruptured.
What is the first response to a vascular spasm?
Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug formation, platelets stick together to form a temporary seal to cover the break in the vessel wall. The third and last step is called coagulation or blood clotting.
How do clots form?
3. Blood coagulation – Clots form upon the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, and its addition to the platelet plug ( secondary hemostasis ). Coagulation: The third and final step in this rapid response reinforces the platelet plug. Coagulation or blood clotting uses fibrin threads that act as a glue for the sticky platelets. As the fibrin mesh begins to form the blood is also transformed from a liquid to a gel like substance through involvement of clotting factors and pro-coagulants. The coagulation process is useful in closing up and maintaining the platelet plug on larger wounds. The release of Prothrombin also plays an essential part in the coagulation process because it allows for the formation of a thrombus, or clot, to form. This final step forces blood cells and platelets to stay trapped in the wounded area. Though this is often a good step for wound healing, it has the ability to cause severe health problems if the thrombus becomes detached from the vessel wall and travels through the circulatory system; If it reaches the brain, heart or lungs it could lead to stroke, heart attack, or pulmonary embolism respectively. However, without this process the healing of a wound would not be possible.
How do platelets help with hemostatic process?
This process is regulated through thromboregulation. Platelets play one of the biggest factors in the hemostatic process. Being the second step in the sequence they stick together (aggregation) to form a plug that temporarily seals the break in the vessel wall.
Why do people develop hemostasis?
Hemostasis disorders can develop for many different reasons. They may be congenital, due to a deficiency or defect in an individual’s platelets or clotting factors. A number of disorders can be acquired as well.
